AI In Medicine: Taiwan Develops Revolutionary AI-Diabetic Retinopathy Software That Enables Rapid Diagnosis of Diabetic Eye Diseases
AI-In-Medicine - Taiwan - Point-of-Care AI-DR - diabetic retinopathy - diabetic macular edema Mar 29, 2023 2 years, 8 months, 2 weeks, 5 days, 7 hours, 43 minutes ago
AI In Medicine: Taiwan’s Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI), a leading non-profit research organization has introduced a groundbreaking AI-assisted system called Point-of-Care AI-DR.
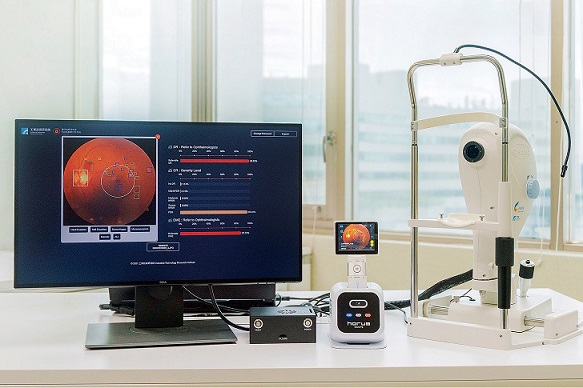
This innovative software is designed for rapid diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy (DR) and diabetic macular edema (DME) and can be integrated into handheld and desktop fundus cameras commonly used in hospitals and clinics worldwide. This revolutionary software has earned the prestigious 2022 R&D 100 Awards in the software/services category.
Point-of-Care AI-DR has the ability to diagnose diabetic retinopathy (DR) and diabetic macular edema (DME) within just 5 to 10 seconds, making it a game-changer in diabetes health monitoring and management.
Furthermore, it instantly assesses image quality before diagnosis to prevent misinterpretation by the AI system. This AI-driven software can locate four main lesions: microaneurysms, hemorrhages, soft exudates, and hard exudates and detect two anatomical landmarks: the optic disc and the macular area.
It can also identify 14 other common ocular fundus abnormalities, including retinal-related diseases, changes in blood vessels, and optic nerve-related diseases.
By classifying five severity levels of diabetic retinopathy and providing binary classifications for both diabetic retinopathy (DR) and diabetic macular edema (DME), Point-of-Care AI-DR enables general practitioners to make data-informed decisions regarding referrals to ophthalmologists.
This innovative software allows general physicians to perform early screenings for diabetic retinopathy (DR) and diabetic macular edema (DME) complications, increasing screening rates and reducing treatment costs, ultimately improving patient outcomes through early detection.
Diabetes is a global health concern, with the International Diabetes Foundation reporting that 537 million adults aged 20 to 79 were living with diabetes in 2021. This number is projected to rise to 643 million by 2030 and 783 million by 2045.
According to the U.S. National Eye Institute, over half of people with diabetes will develop diabetic retinopathy or DR, and approximately one in 15 will develop diabetic macular edema (DME).
Point-of-Care AI-DR offers a significant advancement in diabetes management, as it helps lower the risks of vision loss or blindness caused by diabetic eye complications. Tracking changes in fundus symptoms over time is crucial in diabetes management, as it provides a more reliable indicator than blood sugar levels, which patients can easily alter immediately before examinations.
Dr Pang-An Ting, ITRI General Director of Information and Communications Research Laboratories, told
AI-In-Medicine reporters from TMN, "Point-of-Care AI-DR is a collaboration of human and artificial intelligence through the expertise of ophthalmologists and AI analysis.To develop this innovative software, ITRI engaged 50 ophthalmologists who collected and labeled 150,000 fundus images, which served as the training data for robust AI models. As a result, Point-of-Care AI-DR boasts impressive sensitivity (>98%) and specificit
y (>96%) in DR diagnosis, enabling non-ophthalmologists to perform rapid point-of-care DR screenings like trained ophthalmologists.”
Compatible with all existing fundus cameras worldwide, Point-of-Care AI-DR can be utilized to create various solutions such as edge AI systems, standalone web applications, and private/public cloud-based services. ITRI has already licensed the software to Acer for its VeriSee DR diagnostic software, and other companies interested in licensing should contact ITRI for more information.
The AI-DR software joins a growing list of AI-powered diabetic eye screening tools in the Asia-Pacific region, including New Zealand-based Toku Eyes' ORAiCLE platform, Singapore Eye Research Institute's Singapore Eye Lesion Analyzer, and South Korean medical AI company VUNO's VUNO Med-Fundus AI. Additionally, a recent Google-backed study in Thailand has demonstrated the accurate detection of diabetic retinopathy using a new deep-learning system. Samsung is also contributing to the effort by repurposing old Galaxy smartphone devices into AI-powered fundus cameras to screen for diabetic eye diseases as part of its upcycling program. This initiative aims to improve access to eye health screening in underserved communities worldwide.
Point-of-Care AI-DR is poised to revolutionize the early detection and management of diabetic eye diseases by providing a fast and accurate diagnosis, as well as enabling better communication between general practitioners and ophthalmologists. Its impressive sensitivity and specificity, coupled with its compatibility with existing fundus cameras, make it a crucial tool for mitigating the risks associated with diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema. By making this technology more accessible, ITRI is helping to increase screening rates, reduce treatment costs, and ultimately improve patient outcomes for millions of people living with diabetes around the world.
For the latest
AI-In-Medicine News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
