Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Oct 12, 2024 1 year, 3 months, 3 weeks, 4 days, 1 hour, 13 minutes ago
Medical News: The COVID-19 pandemic has left us with more questions than answers, especially when it comes to the long-term effects of the virus. One rare and concerning possibility is the development of angioedema - a condition characterized by sudden swelling in various parts of the body. This
Medical News report explores a case where a previously healthy individual developed angioedema after recovering from COVID-19. Researchers from Touro College of Osteopathic Medicine and Garnet Health Medical Center in Middletown, USA, investigated this unusual occurrence and raised concerns about the possible link between COVID-19 and angioedema.
 American doctors warn that COVID-19 can trigger Angioedema
A Rare Condition Linked to COVID-19?
American doctors warn that COVID-19 can trigger Angioedema
A Rare Condition Linked to COVID-19?
Angioedema is a condition known for causing non-itchy swelling, often affecting areas such as the skin, throat, and gastrointestinal tract. It is commonly associated with hereditary angioedema (HAE), a rare genetic disorder. However, this case study presents a 37-year-old man who experienced angioedema after a COVID-19 infection despite having no previous history of HAE or similar conditions. Could this be a new symptom of post-COVID complications?
The Patient's Case: Sudden Swelling After a Cold
The patient had a history of one prior episode of angioedema, which had occurred about a year earlier after contracting COVID-19. During his first episode, he experienced swelling in his lips, arms, and a widespread rash, along with mild abdominal pain. Doctors initially thought it was an allergic reaction, and he was treated with symptom-relieving medication before being discharged. However, about a year later, the man suffered from another episode of angioedema following a common cold.
This time, the patient had not been diagnosed with COVID-19, but the similarities between both episodes - unexplained swelling and their connection to respiratory infections - prompted further investigation. Although the doctors were unsure whether this second episode was triggered by COVID-19 or some other virus, they noted that the symptoms were strikingly similar to hereditary angioedema.
What Causes Angioedema?
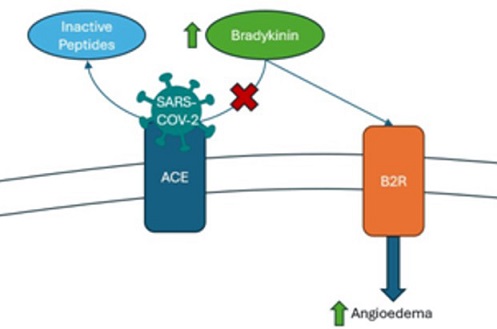
At its core, angioedema occurs due to increased levels of bradykinin, a chemical that causes blood vessels to leak, leading to swelling. Normally, bradykinin is broken down by an enzyme called ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme). When there is a disruption in the body’s ability to break down bradykinin, swelling can occur.
In this patient’s case, COVID-19 could have disrupted the ACE system. The virus enters the body through ACE2 receptors, which are found on the surface of many types of cells. Researchers theorize that the virus may bind to ACE2 receptors and interfere with the breakdown of bradykinin, leading to swelling in some individuals.
Study Insights: COVID-19’s Potential Role
The study conducted by Misleydi Rios Rodriguez and her colleagues explored how COVID-19 could contribute to angi
oedema in previously healthy individuals. The research revealed that the virus could impair the function of ACE, allowing bradykinin to build up and trigger angioedema symptoms. Although the condition is rare, this possibility is alarming because angioedema can lead to life-threatening complications, especially if the swelling affects the throat and blocks the airway.
The patient’s case raised many questions. Could SARS-CoV-2 directly cause angioedema in patients who don’t have hereditary angioedema? Is this a new symptom of post-COVID syndrome? More studies are needed to understand the relationship between COVID-19 and angioedema, but this case highlights the importance of further research.
Implications for Healthcare
Doctors need to be aware of the potential link between angioedema and COVID-19, especially when treating patients who experience unexplained swelling after a viral infection. Early recognition and treatment are crucial to prevent more severe complications. As more people recover from COVID-19, healthcare providers may encounter similar cases, and understanding the possible connection between the virus and angioedema will help guide treatment.
Additionally, this case raises awareness of the broader impact of COVID-19 on the body. While much attention has been focused on respiratory symptoms and complications, it’s clear that the virus can affect other systems as well, sometimes in unexpected ways.
The Study’s Conclusion
This case provides a glimpse into the complex relationship between COVID-19 and angioedema. The 37-year-old man’s experience of swelling after both COVID-19 and another viral infection suggests that some individuals may be more susceptible to angioedema following respiratory illnesses. The study highlights the need for increased awareness of angioedema as a possible post-COVID complication. While the exact mechanism remains unclear, the potential role of bradykinin and ACE2 receptors offers valuable insight.
The researchers call for further studies to explore how COVID-19 might trigger angioedema in patients without a prior history of the condition. The possibility that the virus can impair the body’s ability to regulate bradykinin could have implications for other post-COVID symptoms as well. As we continue to learn more about the long-term effects of the virus, it is essential to keep an open mind about the range of symptoms that may emerge.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, this case study underscores the importance of monitoring post-COVID symptoms carefully. Even seemingly unrelated conditions like angioedema may be linked to the virus, and understanding these connections is crucial for patient care. As researchers continue to explore the full impact of COVID-19, it is clear that the virus affects more than just the respiratory system. Whether through direct viral mechanisms or immune responses, COVID-19 could potentially trigger a variety of unexpected health issues, including angioedema.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Cureus.
https://www.cureus.com/articles/254576-acquired-angioedema-post-covid-19-infection-can-sars-cov-2-induce-angioedema#!/
For the latest COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-news-study-reveals-potential-new-form-of-brain-neurodegeneration-linked-to-covid-19
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/french-doctors-warn-that-even-mild-covid-19-can-cause-acute-cerebellitis-that-is-difficult-to-diagnose
