Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 09, 2024 1 year, 1 month, 4 weeks, 1 day, 18 hours, 11 minutes ago
Medical News: Annexin A2 (ANXA2), a multifunctional protein, plays a vital role in cellular processes ranging from cell structure to immune responses. Recent studies have linked abnormal levels of Annexin A2 to various digestive system cancers, including those in the stomach, liver, pancreas, and colon. Researchers are now exploring its potential as a diagnostic marker, a predictor of treatment response, and even a therapeutic target to slow cancer progression. This
Medical News report examines the findings of an international research team, which provide new insights into how Annexin A2 contributes to cancer and how it might help shape future treatment strategies.
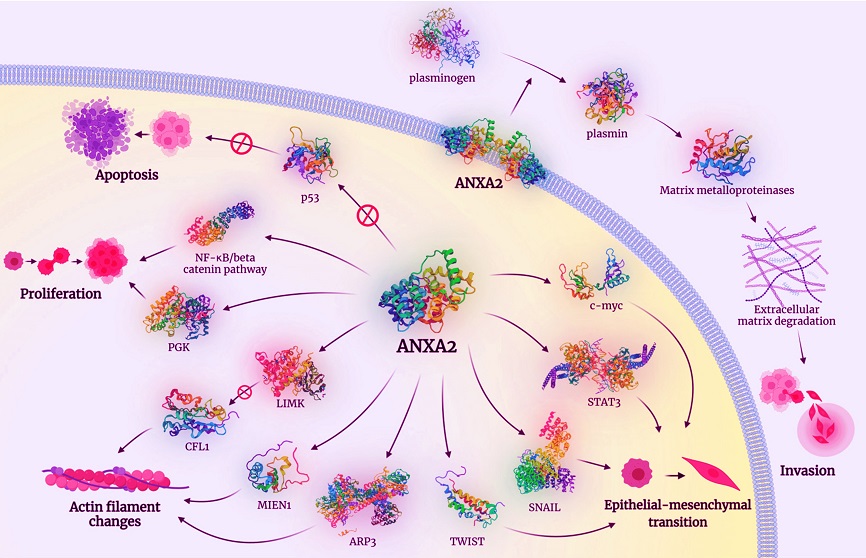 ANXA2 is implicated in a plethora of molecular pathways leading to tumorigenesis. Among others, ANXA2-induced c-myc, STAT3, SNAIL, and TWIST activation promotes the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of tumor cells. Activation of ARP3, MIEN1, and LIMK (that, in turn, inactivates CFL1) induces changes in actin filaments and the cytoskeleton, promoting cell motility. Activation of PGK and the NF-κB/beta catenin pathway results in increased cell proliferation and inhibition of p53 protein prevents apoptosis. In addition, ANXA2 catalyzes the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin which, in turn, activates matrix metalloproteinases that promote the degradation of extracellular matrix, allowing tumor cells to invade deeper in tissues.
Abbreviations: STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; SNAIL: zinc finger protein SNAI1; LIMK: LIM domain kinase; CFL1: Cofilin 1; ARP3: actin-related protein 3; MIEN1: Migration and Invasion Enhancer 1; PGK: 3-phosphoglycerate kinase, NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells.
The Potential of Annexin A2 in Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
ANXA2 is implicated in a plethora of molecular pathways leading to tumorigenesis. Among others, ANXA2-induced c-myc, STAT3, SNAIL, and TWIST activation promotes the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of tumor cells. Activation of ARP3, MIEN1, and LIMK (that, in turn, inactivates CFL1) induces changes in actin filaments and the cytoskeleton, promoting cell motility. Activation of PGK and the NF-κB/beta catenin pathway results in increased cell proliferation and inhibition of p53 protein prevents apoptosis. In addition, ANXA2 catalyzes the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin which, in turn, activates matrix metalloproteinases that promote the degradation of extracellular matrix, allowing tumor cells to invade deeper in tissues.
Abbreviations: STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; SNAIL: zinc finger protein SNAI1; LIMK: LIM domain kinase; CFL1: Cofilin 1; ARP3: actin-related protein 3; MIEN1: Migration and Invasion Enhancer 1; PGK: 3-phosphoglycerate kinase, NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells.
The Potential of Annexin A2 in Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Annexin A2 normally functions within the cellular environment, but it becomes overexpressed or underexpressed in certain cancers, signaling a shift in its activity. This study emphasizes that ANXA2 is linked to cancer in many ways. For instance, overexpression in cancer cells can contribute to invasion, migration, and metastasis, making the protein an essential target for researchers. In cancers of the digestive system, the protein’s abnormal levels may also impact the extracellular matrix, promoting cancer cell spread and reducing survival rates in affected patients.
Key Findings Across Various Digestive Cancers
-Stomach Cancer (Gastric Cancer)
In gastric cancer, multiple studies have demonstrated that ANXA2 is generally upregulated in cancer tissues compared to normal ones. Research teams found high ANXA2 levels associated with increased cancer invasion depth, lymph node metastasis, and poor patient outcomes. The study further suggests that targeting ANXA2 could hinder cancer growth and possibly improve survival rates. One significant insight is ANXA2’s link with the expression of E-cadherin, a cell-adhesion protein. The
loss of E-cadherin, paired with high ANXA2, may help cancer cells invade other tissues, indicating a valuable pathway for potential treatments.
-Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma)
ANXA2 plays a particularly complex role in liver cancer. Overexpression of ANXA2 is common in liver cancer tissues, especially in aggressive, metastatic cases. In addition to its cellular overexpression, high levels of ANXA2 are found in the blood serum of liver cancer patients, presenting a potential non-invasive diagnostic tool. By examining liver cancer cell lines and patient samples, researchers discovered that ANXA2 contributes to the formation of new blood vessels in tumors, a process critical for tumor growth and spread. Experimental results suggest that blocking ANXA2’s effects could slow cancer growth and limit metastasis.
-Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is another area where ANXA2 shows significant impact. Studies identified ANXA2 as being notably elevated in pancreatic cancer cells, where it aids tumor invasion and metastasis. In cell experiments, pancreatic cancer cells with high ANXA2 levels also produced more blood vessel cells (angiogenesis), a process needed for tumor growth. Interestingly, targeting ANXA2 reduced the invasiveness of these cells, suggesting that treatments aimed at ANXA2 could be beneficial in managing pancreatic cancer.
-Colorectal Cancer
ANXA2 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer, where it may drive tumor progression by facilitating cellular invasion and movement. One study explored the relationship between ANXA2 and various molecules involved in cellular structure, finding that higher levels of ANXA2 were associated with poor outcomes. Specifically, the protein’s overexpression helped cancer cells invade deeper into surrounding tissues, suggesting that reducing ANXA2 levels could slow the cancer’s spread. This research indicates ANXA2 as a promising target for treatments designed to limit tumor invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer patients.
Exploring Mechanisms: How Annexin A2 Influences Cancer Progression
Research indicates that ANXA2 contributes to cancer growth and spread by interacting with molecules within the extracellular matrix. For instance, it assists in the breakdown of the matrix around cells, allowing cancer cells to move and invade new areas. The protein also participates in cellular signaling pathways, such as the NF-κB and STAT3 pathways, which are essential for cell survival, proliferation, and movement. Abnormal ANXA2 levels can activate these pathways, increasing tumor cell aggressiveness.
In addition, ANXA2 has been observed to interact with plasminogen, a molecule that helps break down blood clots. By converting plasminogen to plasmin, ANXA2 enhances the invasiveness of cancer cells, making it easier for them to penetrate blood vessels and spread. This plasminogen interaction also contributes to cancer metastasis by allowing cancer cells to enter new organs.
Potential Clinical Applications and Future Directions
The distinct role of ANXA2 in various types of digestive cancers makes it a promising biomarker for early diagnosis and prognosis. Blood tests measuring ANXA2 could offer a simple, non-invasive way to detect cancers in the digestive system. Elevated ANXA2 levels might alert doctors to early-stage cancers, enabling earlier intervention and improving patient outcomes.
Moreover, by targeting ANXA2 with therapeutic agents, future treatments could prevent cancer cells from spreading and reduce resistance to existing therapies. Some preclinical studies are already testing drugs that inhibit ANXA2 activity. These drugs could work in conjunction with traditional treatments like chemotherapy to enhance effectiveness and improve patient survival rates.
Conclusion: A Promising Path Forward in Cancer Treatment
Research on Annexin A2 has opened up promising avenues for cancer diagnosis and treatment, particularly for digestive system cancers. By identifying ANXA2 as a biomarker and therapeutic target, scientists are gaining tools that could significantly improve patient care. However, more clinical trials are essential to translate these findings into actual therapies. Future research may uncover more about how ANXA2 influences cancer, ultimately leading to effective, personalized treatment options for patients worldwide.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Cancers.
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/16/22/3764
For the latest Cancer News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/scientists-discover-novel-anxa2-migratory-hepatocytes-that-aid-with-liver-healing-and-regeneration
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/french-researchers-uncover-that-annexin-v-positive-extracellular-vesicles-could-be-promising-biomarkers-of-severe-covid-19-disease
