Anti-Aging News: Study Shows That 1,5-Anhydro-D-Fructose Has Preventive Effects On Aging-Associated Brain Diseases Via The AMPK/PGC-1α/BDNF Pathway
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 29, 2023 1 year, 4 months, 3 weeks, 3 hours, 59 minutes ago
Anti-Aging News: In the relentless pursuit of effective strategies to combat aging-associated brain diseases, a recent groundbreaking study has unraveled the potential of 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose (1,5-AF) in activating the 5'-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway. Spearheaded by a team of researchers from Kurume University School of Medicine in Japan and Kagoshima University, this study covered in this
Anti-Aging News report, represents a significant leap forward in our understanding of the intricate molecular mechanisms underlying aging-related cognitive decline.
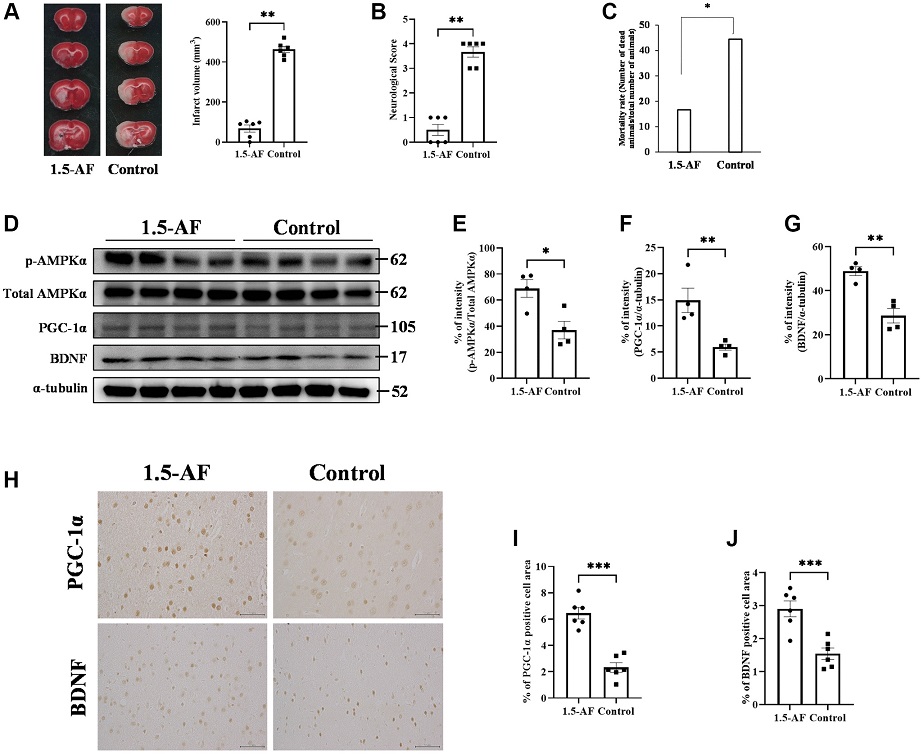 1,5-AF activates pAMPK, decreases infarct volume, and reduces neurological deficits. Representative TTC-stained cerebral sections from 1,5-AF and control rats (A); infarct volume (white region) was smaller in 1,5-AF rats than in control rats (1,5-AF: n = 6, control: n = 6). Neurological scores (1,5-AF: n = 6, control: n = 6) (B) and mortality rate (1,5-AF: n = 6, control: n = 6) (C) after AIS. Neurological scores were better and mortality rate was lower in 1,5-AF rats than in control rats. Immunoblotting results after AIS (1,5-AF: n = 4, control: n = 4) (D). Semiquantitative analysis of immunoblots revealed that protein levels of pAMPK (E), PGC-1α (F), and BDNF (G) were higher in 1,5-AF rats than in control rats. Photomicrographs of PGC-1α and BDNF immunoreactivities (1,5-AF: n = 6, control: n = 6) (H). PGC-1α (I) and BDNF (J) expression was higher in 1,5-AF rats than in control rats. Data are shown as the mean ± standard error. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Scale bar = 50 μm. Abbreviations: 1,5-AF: 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose; AIS: acute ischemic stroke; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; pAMPK: phosphorylated 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; PGC-1α: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ co-activator-1α; TTC: 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride.
The Role of AMPK in Aging-Associated Brain Diseases
1,5-AF activates pAMPK, decreases infarct volume, and reduces neurological deficits. Representative TTC-stained cerebral sections from 1,5-AF and control rats (A); infarct volume (white region) was smaller in 1,5-AF rats than in control rats (1,5-AF: n = 6, control: n = 6). Neurological scores (1,5-AF: n = 6, control: n = 6) (B) and mortality rate (1,5-AF: n = 6, control: n = 6) (C) after AIS. Neurological scores were better and mortality rate was lower in 1,5-AF rats than in control rats. Immunoblotting results after AIS (1,5-AF: n = 4, control: n = 4) (D). Semiquantitative analysis of immunoblots revealed that protein levels of pAMPK (E), PGC-1α (F), and BDNF (G) were higher in 1,5-AF rats than in control rats. Photomicrographs of PGC-1α and BDNF immunoreactivities (1,5-AF: n = 6, control: n = 6) (H). PGC-1α (I) and BDNF (J) expression was higher in 1,5-AF rats than in control rats. Data are shown as the mean ± standard error. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Scale bar = 50 μm. Abbreviations: 1,5-AF: 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose; AIS: acute ischemic stroke; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; pAMPK: phosphorylated 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; PGC-1α: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ co-activator-1α; TTC: 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride.
The Role of AMPK in Aging-Associated Brain Diseases
AMPK, a metabolic sensor crucial for maintaining cellular energy homeostasis, has emerged as a linchpin in the pathophysiology of aging-associated brain diseases. Dysregulation of AMPK has been implicated in various chronic conditions, including stroke and Alzheimer’s disease. This study ventures into uncharted territory by investigating how 1,5-AF, a bioactive monosaccharide, activates AMPK, offering potential neurovascular protection and cognitive benefits.
Animal Models: Probing the Effects of 1,5-AF
To comprehensively assess the impact of 1,5-AF, the research team employed a battery of animal models, each representing a distinct facet of aging-associated brain diseases. These models included an animal model of acute ischemic stroke (AIS), stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRSPs), and the spontaneous senescence-accelerated mouse-prone 8 (SAMP8) model.
In the AIS model, the administration of 1,5-AF via intraperitoneal injection yielded significant reductions in cerebral infarct volume, neurological deficits, and m
ortality. In SHRSPs, oral administration of 1,5-AF demonstrated a remarkable reduction in blood pressure and an extension of survival. Meanwhile, in the SAMP8 model, oral administration of 1,5-AF mitigated aging-related decline in motor cognitive function.
Activating AMPK: Unraveling the Molecular Tapestry
Despite the aging-related decline in the expression levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ co-activator-1α (PGC-1α) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), the study unearthed a pivotal discovery – 1,5-AF activates AMPK, leading to the upregulation of the PGC-1α/BDNF pathway. This activation suggests that 1,5-AF may induce endogenous neurovascular protection, presenting a groundbreaking approach to preventing aging-associated brain diseases.
The AMPK/PGC-1α/BDNF Pathway: A Nexus for Neuroprotection
The intricate interplay between AMPK, PGC-1α, and BDNF emerges as a focal point for understanding the preventive effects of 1,5-AF. In the AIS model, the study postulates that the reduction in cerebral infarct volume by 1,5-AF may be related to the enhancement of the fibrinolytic system by BDNF. Moreover, in SHRSPs, the BP-lowering effect of 1,5-AF was associated with a reduction in stroke incidence and preservation of muscle mass. The study also highlighted the potential cognitive benefits in SAMP8 mice, linking increased PGC-1α and BDNF expression to improved locomotor activity and reduced memory impairment.
Exploring the Molecular Landscape: Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Beyond
The research transcends the realms of AMPK activation, delving into the intricate molecular landscape influenced by 1,5-AF. The study revealed that 1,5-AF activates PGC-1α via AMPK, potentially inducing mitochondrial biogenesis and cytoprotective effects. Mitochondrial dysfunction, recognized as a pivotal contributor to aging-related diseases, may find amelioration through the regulatory role of PGC-1α in energy metabolism-related genes.
Comparisons with Established Interventions and Future Implications
Placing 1,5-AF alongside established anti-aging interventions such as exercise and metformin, the study underscores its potential to mimic the central effects of exercise by activating the AMPK/PGC-1α/BDNF pathway. Unlike some existing interventions, 1,5-AF stands out as a promising option with a wide spectrum of bioactive properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, and anticancer effects.
Considerations and Future Directions
While the study provides compelling evidence of the preventive effects of 1,5-AF, acknowledging certain limitations is imperative. Small sample sizes in the AIS model and the systemic alterations in animal models may influence the generalizability of the findings. Future research could further probe the effects of 1,5-AF by incorporating additional molecular analyses and investigating the role of other AMPK activators.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study on 1,5-Anhydro-D-Fructose marks a significant stride in the quest for effective interventions against aging-associated brain diseases. The activation of the AMPK/PGC-1α/BDNF pathway by 1,5-AF unveils a novel avenue for neuroprotection, potentially reshaping the landscape of anti-aging research.
As the scientific community eagerly awaits clinical studies to validate these findings, the study propels us into a new era of possibilities in the pursuit of healthy aging. The prospect of 1,5-AF as a preventative measure against aging-associated brain diseases holds promise, beckoning towards a future where the ravages of time on the mind may be tempered by the insights gained from this groundbreaking research.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Aging.
https://www.aging-us.com/article/205228/text
For the latest
Anti-Aging News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
