Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Feb 01, 2025 2 months, 1 week, 4 days, 20 hours, 4 minutes ago
Medical News: A Breakthrough in Retinal Health, New Study Explores Ouabain’s Neuroprotective Properties
Vision loss, one of the most challenging health conditions, is often linked to the degeneration of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). These specialized neurons play a crucial role in transmitting visual information from the retina to the brain. In a groundbreaking study led by a team of researchers from the Federal Fluminense University, the Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, and the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro in Brazil, a steroid hormone called ouabain has been found to offer promising neuroprotective benefits by modulating key molecular pathways. This
Medical News report dives into the details of this pivotal discovery and its implications for future therapies.
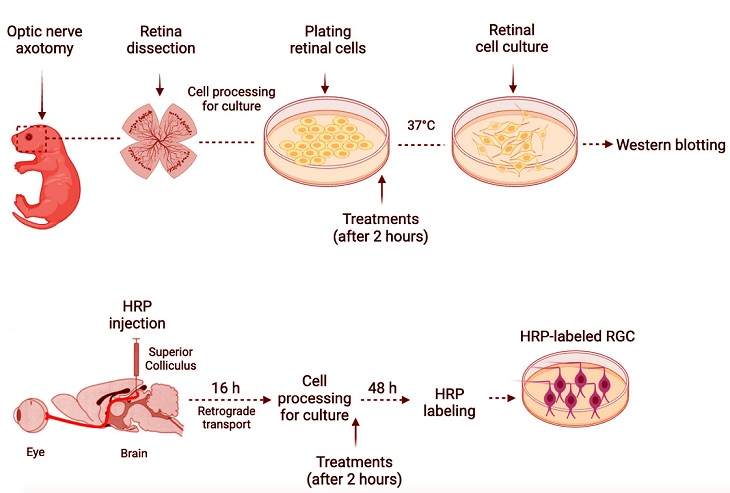 Experimental timeline. Briefly, retinal cells from newborn rats were isolated, plated, and maintained in culture at 37 °C. Two hours after cell plating, retinal cell cultures were treated with ouabain and/or MMP-9 inhibitor. After different time intervals (15 min, 45 min, 24 h, or 48 h), the cells were processed for Western blotting. For retrograde labeling of RGCs, horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was injected into each superior colliculus of newborn rats. After the time lapse necessary for retrograde transport of HRP to RGC soma (16 h), pups were euthanized and primary cultures from their retinas were prepared. Two hours after cell plating, retinal cell cultures were treated with IL-1β, IL-1Ra, or TNF-α. For mechanistic studies, retinal cultures were simultaneously exposed to selective inhibitors of signaling pathways. Forty-eight hours after the treatment, HRP-labeled RGCs were counted.
What is Ouabain
Experimental timeline. Briefly, retinal cells from newborn rats were isolated, plated, and maintained in culture at 37 °C. Two hours after cell plating, retinal cell cultures were treated with ouabain and/or MMP-9 inhibitor. After different time intervals (15 min, 45 min, 24 h, or 48 h), the cells were processed for Western blotting. For retrograde labeling of RGCs, horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was injected into each superior colliculus of newborn rats. After the time lapse necessary for retrograde transport of HRP to RGC soma (16 h), pups were euthanized and primary cultures from their retinas were prepared. Two hours after cell plating, retinal cell cultures were treated with IL-1β, IL-1Ra, or TNF-α. For mechanistic studies, retinal cultures were simultaneously exposed to selective inhibitors of signaling pathways. Forty-eight hours after the treatment, HRP-labeled RGCs were counted.
What is Ouabain
Ouabain is a plant-derived toxic substance historically used as an arrow poison in eastern Africa for hunting and warfare. Its name originates from the Somali word waabaayo ("arrow poison"). Also known as g-strophanthin, ouabain is classified as a cardiac glycoside. In lower doses, it has medical applications, particularly for treating hypotension and certain arrhythmias, due to its ability to inhibit the Na+/K+-ATPase, commonly referred to as the sodium–potassium ion pump.
Some species, particularly certain herbivorous insects, have developed resistance to ouabain through adaptations in the alpha-subunit of the Na+/K+-ATPase, achieved via amino acid substitutions.
In the United States, ouabain is classified as an extremely hazardous substance under Section 302 of the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002).
Ouabain is naturally found in various parts of Acokanthera schimperi and Strophanthus gratus, two plant species native to eastern Africa.
The Role of Retinal Ganglion Cells in Vision
Retinal ganglion cells are essential neurons that bridge the gap between light signals captured by the retina and the visual cortex in the brain. The loss of RGCs is a leading cause of irreversible blindness, with conditions such as glaucoma and optic nerve injuries being key contributors. Researchers have long sought effective strategies to pro
tect and regenerate these cells, and the findings of this study present an innovative avenue for exploration.
The study, recently conducted in a controlled laboratory setting, explored the ability of ouabain to counteract RGC death. Although previously known to interact with signaling pathways, the mechanisms underlying its neuroprotective effects were not fully understood until now.
Study Design and Methodology
The research was performed using primary cultures of neural retina derived from newborn rats. By treating these cultures with ouabain, the team investigated its effects on two critical pathways associated with cell survival: the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). Both of these molecules are integral to neuronal health, with BDNF promoting growth and survival, and IL-1β contributing to immune regulation and repair processes.
To explore ouabain’s effects, researchers assessed the levels of proBDNF (an immature precursor to BDNF) and its mature form (mBDNF), along with IL-1β signaling components such as active caspase-1 and its receptor IL-1R1. In addition, pharmacological inhibitors were employed to dissect the signaling pathways involved in ouabain’s neuroprotective action.
Key Findings: A New Era of Neuroprotection
-Stimulating BDNF Maturation
One of the most significant discoveries was ouabain’s ability to regulate the maturation of BDNF. The results demonstrated that ouabain promoted the conversion of proBDNF to mBDNF within 48 hours, enhancing the levels of phosphorylated tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB), a receptor critical for cell survival. The study highlighted that this process was mediated by matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), an enzyme responsible for cleaving proBDNF into its mature form. By increasing mBDNF and TrkB phosphorylation, ouabain effectively shifted the signaling balance toward pathways that promote RGC survival.
-Modulating IL-1β Signaling
Ouabain also played a pivotal role in enhancing IL-1β signaling. The hormone stimulated the activation of caspase-1, an enzyme essential for processing proIL-1β into its active form. Furthermore, it upregulated the receptor IL-1R1 while transiently decreasing the levels of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra). This modulation ensured a controlled and beneficial activation of IL-1β signaling, preventing excessive inflammatory responses that could harm the retina.
-The Synergistic Effect of Pathways
Both BDNF and IL-1β pathways converge to enhance RGC survival. The study found that these pathways rely on a shared set of signaling molecules, including Src kinase, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and protein kinase C (PKC). By activating these pathways, ouabain created a robust environment for neuronal protection and repair.
Broader Implications for Retinal Health
The implications of this research are profound. Retinal diseases such as glaucoma and optic neuropathy often involve the progressive loss of RGCs, leading to irreversible vision impairment. The ability of ouabain to enhance BDNF and IL-1β signaling offers a novel therapeutic strategy to halt or even reverse this degeneration. Unlike current treatments, which primarily aim to reduce intraocular pressure or manage symptoms, ouabain’s approach targets the root cause - cell survival and repair.
Additionally, the study’s findings underscore the importance of balanced signaling. While IL-1β has been associated with inflammatory damage in other contexts, its controlled activation by ouabain demonstrates its potential for neuroprotection. This dual role highlights the complexity of cytokine signaling and the need for precision in therapeutic interventions.
Conclusions and Future Directions
The findings of this study shed light on the intricate mechanisms by which ouabain promotes RGC survival. By enhancing the maturation and signaling of BDNF and IL-1β, ouabain not only protects RGCs but also creates a foundation for their regeneration. This discovery opens new doors for the development of targeted therapies for retinal diseases.
Moving forward, further research is needed to validate these results in vivo and explore the long-term effects of ouabain treatment. Additionally, clinical trials will be essential to determine its safety and efficacy in humans. The potential to combine ouabain with existing treatments, such as BDNF delivery or anti-inflammatory drugs, could lead to comprehensive strategies for preserving vision.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Brain Sciences.
https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3425/15/2/123
For the latest on Retinal Health, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/the-phytochemical-genipin-from-gardenia-plants-can-help-regenerate-damaged-or-diseased-human-nerves
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/complement-protein-c5a-boosts-nerve-regeneration-after-injury
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/new-hope-for-nerve-repair-breakthrough-in-axon-regeneration
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-a-new-approach-to-nerve-regeneration-utilizing-developmental-genes
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/medical-news-swiss-and-british-scientists-discover-that-axonal-regeneration-and-repair-is-regulated-by-the-circadian-clock
