BREAKING! AI In Medicine: Researchers From The University Of Texas Develop AI Platform That Deciphers Human Thoughts From Brain Imagings!
AI In Medicine - Deciphering Human Thoughts From Brain Scans And Imagings May 12, 2023 1 year, 11 months, 5 days, 18 hours, 41 minutes ago
AI In Medicine: In a world where mind reading was once confined to the realms of science fiction, a groundbreaking development at the University of Texas, Austin, has made it a scientific reality. Harnessing the power of artificial intelligence, a team of researchers have pioneered a technology that deciphers human thoughts from brain images. This astonishing discovery could revolutionize communication and transform lives, especially for patients who have lost their ability to express themselves.
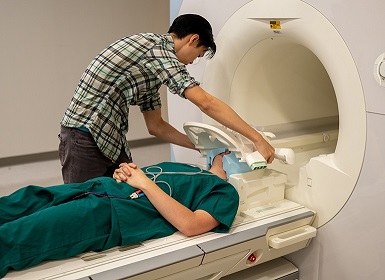
Drawing from advanced AI systems like ChatGPT or Bard, the study team have married fMRI technology with artificial intelligence to decode the human brain's complex language. This cutting-edge technique is non-invasive, thus eliminating the need for surgical implants that were a mainstay of previous attempts to crack the enigma of the human mind.
Describing the monumental leap forward, Alex Huth, one of the researchers, said, "This is a game-changer and shows how
AI In Medicine could be revolutionary. We're not just decoding single words or short sentences. We're decoding continuous language for extended periods with complex ideas."
But how does the system work? It's rather like an intense language immersion course for the AI. Participants spend several hours in an fMRI scanner, engrossed in podcasts, while the AI learns to identify the unique neural signatures of their thoughts. Once trained, the AI can then interpret the person's thoughts into text, provided the thinking happens within the scanner.
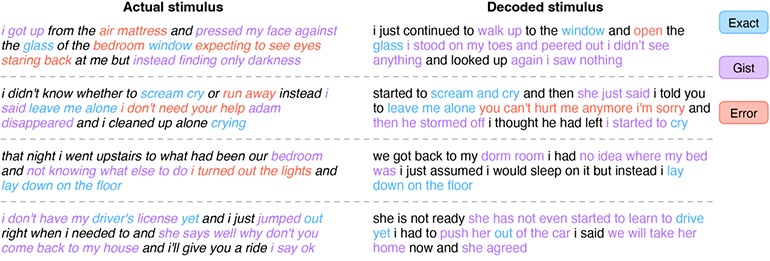
The interpretation, while not verbatim, provides a close approximation of the original thought. For instance, the thought "I don't have my driver's license yet" was translated as "She has not even started to learn to drive yet."
But what about privacy concerns? Could this technology be exploited for nefarious purposes, leading to a dystopian society where our thoughts are not our own? The researchers are fully aware of this potential risk. However, they emphasized that the system only works with cooperative participants who actively participate in training the system. Furthermore, the system can be easily thrown off-track if the participant chooses to think about different things.
"We take privacy concerns very seriously," said Jerry Tang, another researcher. "We've taken steps to prevent misuse. The technology should only be used when people want to, and it should help them."
Looking ahead, the team believes that the technology won't always require cumbersome fMRI systems. More portable imaging technologies, such as functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), could be used instead. Although the resolution with fNIRS would be lower, the approach remains the same, offering a tantalizing glimpse of a future where thoughts can be read in real-time.
This groundbreaking study, published in the peer reviewed journal: Nat
ure Neuroscience, has shown that a non-invasive decoder can reconstruct continuous language from cortical semantic representations.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-023-01304-9
The decoder can handle a range of tasks, from interpreting perceived speech to decoding imagined speech and silent videos. The technology's potential is vast, but the researchers stress that privacy is paramount and cooperation is required both to train and to apply the decoder.
As we stand on the cusp of a new era where AI and neuroscience intertwine, the question is: Are we ready to turn the page to a new chapter in human communication? This extraordinary invention from the University of Texas certainly gives us food for thought.
For the latest on
AI In Medicine, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.

