BREAKING! Canadian Scientists Discover Novel Narnavirus Which Is Pathogenic To Humans Hiding Inside The Parasite Toxoplasma Gondii!
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team May 11, 2024 10 months, 3 weeks, 9 hours, 9 minutes ago
Medical News: The landscape of virology is rapidly evolving, ushering us into what can be termed a "Platinum Age of Virus Discovery." With the advent of metagenomics and advanced computational techniques, scientists are delving deep into the realm of virus biodiversity, uncovering previously unknown viral species and their interactions within diverse ecosystems. In this paradigm, viruses are not confined to direct infections of host cells but extend their influence across the microbiome, infecting bacteria, fungi, and unicellular parasites. The intricate web of interactions between viruses, hosts, and microbes presents a complex tapestry that demands sophisticated computational virology approaches for analysis and interpretation.
 Novel Narnavirus Which Is Pathogenic To Humans Found Hiding Inside The Parasite Toxoplasma Gondii
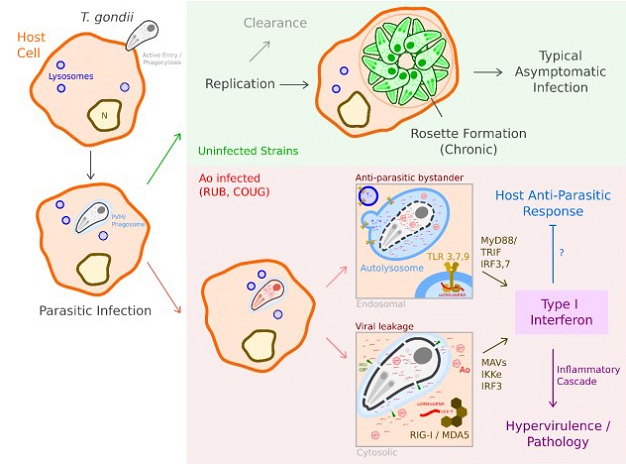
Hypervirulence model.
Novel Narnavirus Which Is Pathogenic To Humans Found Hiding Inside The Parasite Toxoplasma Gondii
Hypervirulence model.
T. gondii infects host cells. In uninfected strains, this either leads to successful clearance by the host or the establishment of chronic infection, typically asymptomatic. In virus+ strains, such as RUB and COUGAR, detection of viral RNA (vRNA) - either by endosomal TLRs after phagolysosome maturation following phagocytosis, or by RLRs surveying the cytosol after interferon-inducible GTPase (IRG/GBP)-mediated destruction of the parasitophorous vacuolar membrane - leads to the induction of type I IFN. The effect of this is twofold - the viral pathogen-associated molecular pattern drives additional inflammation which leads to pathology and overt symptoms, but potentially also impairs or diverts host anti-parasitic immunity.
The Rise of Computational Virology
The University of Toronto's groundbreaking research has epitomized this era of exploration. Through computational viral screening of human neuronal datasets, a team of scientists unearthed a novel narnavirus, Apocryptovirus odysseus (Ao), believed to reside within the neurotropic parasite Toxoplasma gondii. This discovery that is covered in this
Medical News report, opens a new chapter in understanding the intricate interplay between viruses and parasitic infections, particularly their potential impact on human health.
Exploring the Narnaviridae: A Simple Complexity
The Narnaviridae family represents a fascinating yet enigmatic group of viruses characterized by their simplicity - a naked, single-stranded RNA genome encoding an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. While initially associated with fungi, the discovery of narnaviruses in diverse organisms, including marine protists and arthropods, underscores their ubiquity and potential evolutionary significance.
Unveiling Parasitic Protozoan Viruses
A pivotal aspect of this narrative is the emergence of parasitic protozoan viruses (PPVs), which infect eukaryotic parasites like the Apicomplexa and Euglenozoa. These PPVs, while often poorly understood, play a crucial role in mod
ulating host-parasite interactions and immune responses. The presence of viral pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) within parasites can trigger innate immune responses in the host, with implications for disease severity and pathogenicity.
A Hidden Intruder: Apocryptovirus Odysseus
In this context, the discovery of Apocryptovirus odysseus within T. gondii marks a significant breakthrough. This highly divergent narnavirus is hypothesized to act as a pro-inflammatory factor, potentially contributing to the hypervirulence observed in certain strains of T. gondii. Computational analyses have illuminated the phylogenetic relationships and prevalence of Ao and related Apocryptovirus species, highlighting their association with parasitic Apicomplexa.
Deciphering the Mechanisms of Hypervirulence
The mechanistic underpinnings of Ao-mediated hypervirulence in T. gondii remain a focal point of investigation. Initial computational evidence suggests a link between Ao and the host's innate immune system, particularly the type I interferon (IFN) response. This intricate interplay between viral RNA sensing and immune activation underscores the complex dynamics driving parasitic pathogenicity.
Implications for Disease Pathogenesis
The implications of Ao's discovery extend beyond T. gondii infection to broader questions of disease pathogenesis and immune modulation. Insights gleaned from this research shed light on the potential role of PPVs in exacerbating host immune responses and driving pathological outcomes in parasitic infections. The intricate interplay between viruses, parasites, and hosts unveils a nuanced understanding of infectious disease dynamics.
Towards Therapeutic Interventions
The identification of Ao as a potential hypervirulence factor opens avenues for exploring therapeutic interventions targeting viral contributions to disease progression. Antiviral strategies, informed by structural and functional analyses of narnaviruses, could complement existing treatments for parasitic infections, offering new hope in managing complex infectious diseases.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite these groundbreaking discoveries, challenges remain in unraveling the full spectrum of virus-parasite-host interactions. Experimental validation of computational findings, coupled with comprehensive clinical studies, is essential to bridge the gap between observation and causality. The dynamic nature of viral evolution and its impact on disease outcomes necessitate ongoing vigilance and innovation in virology research.
Conclusion
The journey from computational screening to the discovery of Apocryptovirus odysseus within Toxoplasma gondii epitomizes the power of modern virology. It underscores the intricate connections between viruses and parasitic infections, offering new insights into disease pathogenesis and immune modulation. As we navigate this era of virus discovery, collaborative efforts across disciplines will pave the way for transformative advancements in infectious disease research and therapeutics.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Virus Evolution (Oxford Journals).
https://academic.oup.com/ve/advance-article/doi/10.1093/ve/veae040/7668577
For the latest about the novel Narnavirus, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
