BREAKING COVID-19 News! Australian Scientists Discover A microRNA Called CoV2-miR-O8 That Is Encoded By SARS-CoV-2 And Is Possibly Pathogenetic!
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Dec 16, 2023 1 year, 4 months, 1 day, 7 hours, 39 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: In a watershed moment for COVID-19 research, scientists at the College of Medicine and Public Health, Flinders University, Australia, have made a groundbreaking discovery that promises to deepen our understanding of the disease's pathogenesis. The focus of their attention is a novel viral microRNA, CoV2-miR-O8, encoded by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). This revelation opens up new avenues for research and therapeutic interventions and may hold the key to addressing critical questions surrounding COVID-19.
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Since the very beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, Thailand
Medical News has also been warning that the SARS-CoV-2 is also able to produce viral proteins or peptides that are not part of its structure but do play a role in pathogenesis and are able to affect the human host even after the main viral RNAs are cleared from the host! We postulated then that some of these viral peptides could also paly a role in Long COVID even after SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance in a past
COVID-19 News coverages.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-long-covid-is-a-misnomer-the-conditions-are-being-caused-by-viral-persistence-and-viral-peptides-similar-to-retrotransposons-and-introns
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-discovery-of-sars-cov-2-short-rnas-by-scientist-from-john-hopkins-is-a-big-gamechanger-in-terms-of-pathogenesis-and-long-covid
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/there-is-no-such-thing-as-long-covid-sars-cov-2-exposure-causes-persistent-infections-along-with-continuous-presence-of-short-viral-rnas-svrnas
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-news-scientists-discover-sars-cov-2-mirnas-that-contributes-to-pathog
enesis-and-can-be-used-as-a-biomarker-for-covid-19-severity
The Complex Landscape of SARS-CoV-2 and Viral miRNAs
SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, has been under intense scrutiny since its emergence. Recent studies have shed light on the potential presence of viral microRNAs (v-miRNAs), small non-coding RNAs capable of modulating host gene expression, in various viruses, including its predecessor, SARS-CoV. This discovery paves the way for a comprehensive exploration of v-miRNAs in SARS-CoV-2 and their implications for disease progression and severity.
Identification and Significance of CoV2-miR-O8
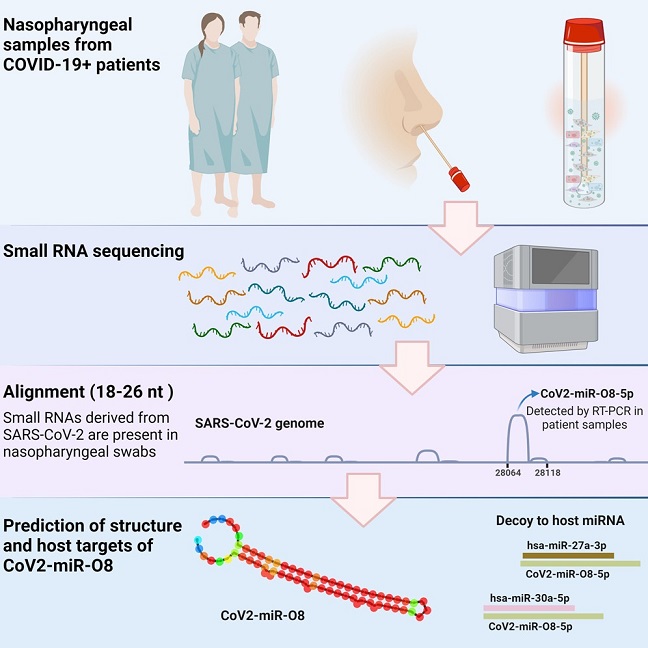
The Australian research team conducted a patient-based study utilizing small RNA sequencing (smRNAseq) on nasopharyngeal swabs obtained from individuals diagnosed with COVID-19. Through this innovative approach, they identified a specific and conserved sequence, CoV2-miR-O8, which is distinct to SARS-CoV-2 and preserved across its variants, including Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron. This newfound microRNA presents an opportunity to unravel the intricacies of SARS-CoV-2's interaction with the host and its potential impact on disease dynamics.
Characterization of CoV2-miR-O8
CoV2-miR-O8 exhibits several characteristics typical of microRNAs, adding to its significance in the context of SARS-CoV-2 biology. The microRNA forms a distinctive hairpin structure and interacts with the Argonaute protein, a key player in RNA interference pathways. The study delves into the intricate details of CoV2-miR-O8's biogenesis, highlighting its generation through the Dicer and Drosha machinery. This microRNA duplex, with a peak at 22-23 nucleotides, aligns with the typical length of miRNAs, further emphasizing its potential role in the post-transcriptional regulation of host gene expression.
Detection and Validation Strategies
To validate the presence of CoV2-miR-O8, the researchers employed reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assays on additional nasopharyngeal swab samples from both COVID-19-positive and negative individuals. Notably, CoV2-miR-O8 was consistently detected in all COVID-19-positive patients but absent in negative cases. This not only establishes its association with active infection but also introduces the possibility of leveraging CoV2-miR-O8 as a potential diagnostic marker. The study further demonstrated a significant correlation between CoV2-miR-O8 expression levels and the severity of COVID-19 infection, as determined by the envelope (E) gene diagnostic RT-PCR assay.
Exploring Interactions and Targets
Intriguingly, the study utilized covalent ligation of endogenous Argonaute-bound RNAs (CLEAR)-cross-linking immunoprecipitation (CLIP) data to delve into the interactions of CoV2-miR-O8 with human RNA sequences. The results provided compelling evidence of sequences corresponding to CoV2-miR-O8 being purified, supporting its binding with Argonaute and generation as a microRNA. The data were also analyzed for the presence of chimeric transcripts, revealing sequences containing both CoV2-miR-O8 and human microRNA sequences. This observation hints at potential interactions and opens up avenues for exploring whether CoV2-miR-O8 acts as a decoy for these microRNAs or engages in more complex regulatory mechanisms.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
The study's findings extend beyond the laboratory, raising critical questions about the clinical implications of CoV2-miR-O8. Utilizing the miRanda algorithm, the researchers predicted potential interactions between CoV2-miR-O8 and the 3’ UTR, 5’ UTR, and coding sequences of human host mRNAs. Notably, a subset of predicted targets was associated with the type I interferon signaling pathway, suggesting a potential role of CoV2-miR-O8 in regulating antiviral immune responses during COVID-19 infection.
In a bid to bridge the gap between laboratory findings and clinical relevance, the study analyzed publicly available nasopharyngeal swab RNAseq data for upregulated and downregulated genes during COVID-19 infection. Intriguingly, a significant proportion of both upregulated and downregulated genes were predicted targets of CoV2-miR-O8. This observation hints at a complex regulatory role for CoV2-miR-O8 in shaping the host response during COVID-19 infection.
Conclusion
The discovery of CoV2-miR-O8 by Australian scientists represents a pivotal moment in COVID-19 research. This microRNA, encoded by SARS-CoV-2, not only confirms the existence of small viral RNAs in patient-based samples but also unravels a potential key player in the complex interplay between the virus and its host. As the scientific community delves deeper into the functional significance of CoV2-miR-O8 and its role in disease progression, the implications for diagnostics, therapeutics, and our broader understanding of COVID-19 pathogenesis are profound. This discovery propels us closer to addressing critical questions surrounding the virus, bringing us one step closer to effective strategies for managing and mitigating the global impact of the pandemic.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: iScience.
https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(23)02796-7
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News:
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/medical-alert-sars-cov-2-expresses-mirna:-vmir-5p-that-reduces-host-transcription-and-suppresses-host-genes,-increasing-its-pathogenicity
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/latest-sars-cov-2-research-study-discovers-that-sars-cov-2-encoded-small-rnas-represses-host-expression-of-serinc5-for-viral-replication-
