BREAKING COVID-19 News: Japanese Scientists Find That Supplementation With The Amino Acid D-Alanine Can Help Prevent And Treat COVID-19 Severity!
COVID-19 News - D-Alanine Supplements Prevents COVID-19 Severity Nov 29, 2022 3 years, 2 weeks, 4 days, 13 hours, 31 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: A new breakthrough study by researchers from the National Institutes of Biomedical Innovation, Health and Nutrition (NIBIOHN)-Japan and the Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine – Japan has found that supplementation with the amino acid D-Alanine can help prevent and also treat COVID-19 severity. The study besides finding the critical role that D-Amino acids play in viral infections also found that D-Alanine could also be used as a biomarker for COVID-19 disease severity.

D-Amino acids are amino acids where the stereogenic carbon alpha to the amino group has the D-configuration. For most naturally-occurring amino acids, this carbon has the L-configuration. D-Amino acids are occasionally found in nature as residues in proteins. They are formed from ribosomally-derived D-amino acid residues.
Diverse D-amino acids, such as D-serine, D-aspartate, D-alanine, and D-cysteine, are found in mammals. Physiological roles of these D-amino acids not only in the nervous system but also in the endocrine system are being gradually revealed along with their role in viral infections.
Previous
COVID-19 News coverage showed that supplementation with amino acids such as Lysine, Theanine and Cysteine could also have therapeutic and prophylactic benefits against SARS-CoV-2 infections.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/lysine-supplements-as-adjuvant-to-treat-covid-19-and-also-as-a-prophylactic
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-l-theanine-supplements-and-derivatives-could-be-used-to-treat-sars-cov-2-infections-especially-involving-delta-and-omicron-variants
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-treatments-amino-acids-cysteine-and-theanine-could-have-efficacy-against-sars-cov-2-according-to-japanese-study
To date, since the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in late 2019, biomarkers for evaluating disease severity, as well as supportive care to improve clinical course, remain insufficient.
The study team explored the potential of D-amino acids, rare enantiomers of amino acids, as biomarkers for assessing disease severity and as protective nutrients against severe viral infections.
It was found that in mice infected with influenza A virus (IAV) and in patients with severe COVID-19 requiring artificial ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, blood levels of D-amino acids, including D-alanine, were reduced significantly compared with those of uninfected mice or healthy controls.
Importantly, in mice models of IAV infection or COVID-19, supplementation with D-alanine alleviated severity of clinical course, and mice
with sustained blood levels of d-alanine showed favorable prognoses.
Furthermore, it was found that in severe viral infections, blood levels of d-amino acids, including D-alanine, decrease, and supplementation with d-alanine improves prognosis.
The study findings showed that D-Alanine has great potentials as a biomarker and a therapeutic option for severe viral infections.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease (Science Direct By Elsevier)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925443922002551
According to the study team, similar to bricks being key components in constructing a building, molecules known as amino acids are essential components in constructing proteins in the body.
The Japanese study team were the first to investigated the role of a particular group of amino acids, known as D-amino acids, in the progression of viruses like influenza A virus (IAV) and SARS CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19.
The study findings are the also the first to show a relationship between D-amino acids and severe viral infection in both animals and humans.
Although current understanding of COVID-19 has evolved in the last 3 years during the COVID-19 pandemic, methods to predict disease severity and treat severe COVID-19 infection have been somewhat limited.
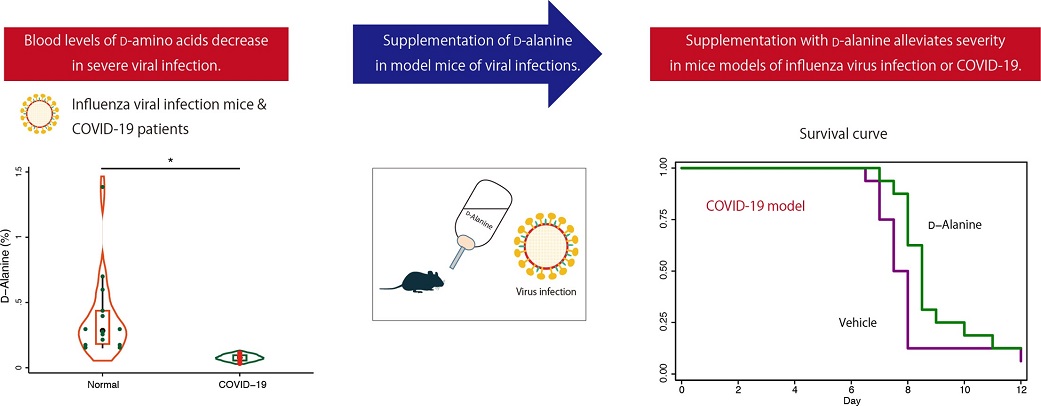 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Interestingly, D-amino acids have been previously shown to function as biomarkers for diseases such as kidney disease. However, the significance of D-amino acids in viral infection has not yet been explored, spurring the research team to investigate whether D-amino acids are affected during severe IAV infection or COVID-19.
Lead author, Dr Shihoko Kimura-Ohba a professor and head of the KAGAMI Project, National Institutes of Biomedical Innovation, Health and Nutrition (NIBIOHN)-Japan told Thailand Medical News, "We first assessed serum levels of D-amino acids in a mouse model of severe IAV infection and found that D-amino acids were greatly reduced in these mice compared with uninfected mice. When we evaluated serum from patients with severe COVID-19, we also found reduced levels of D-amino acids compared to those of healthy control subjects.”
The study team next explored the effects of supplementation with a specific D-amino acid known as D-alanine in mouse models of IAV infection and COVID-19. IAV mice exhibited a severe reduction in body weight that was mitigated by D-alanine treatment, while survival rates were improved in COVID-19 mice who received D-alanine treatment.
Senior author, Dr Tomonori Kimura from the Reverse Translational Research Project, Center for Rare Disease Research, National Institutes of Biomedical Innovation, Health and Nutrition (NIBIOHN) – Japan added, "Our study findings indicate that D-amino acids may serve as biomarkers to reflect the severity of viral infection. Additionally, although the observed effects of D-alanine supplementation were limited, treatment with D-alanine may help to improve clinical outcomes in patients with severe viral infection."
The study team added, “D-amino acids are natural nutrients present in daily foods or produced from the gut microbiota. In the presence of severe viral infection, the intake of d-amino acids from foods is likely insufficient or deregulated microbiota may not produce sufficient d-amino acids. D-alanine is suitable for the supportive care of viral infections, although its protective effect was limited. This may partially be attributable to the difficulty in maintaining its blood level. The dose of d-alanine should be adjusted to avoid its decline in blood level, whereas excessive amounts of d-amino acids could be biphasic. Monitoring the blood D-alanine level helps adjust the dosing of D-alanine and thus may maximize the supplemental effect of D-alanine. Besides D-alanine, the blood levels of other D-amino acids also reflected severity of viral infections even after supplementation with D-alanine. To monitor the safety, treatment efficacy and activity of infections, the blood D-amino acid levels should be measured upon supplementation of D-alanine.”
The detailed mechanism of D-alanine in the improvement of viral prognosis has yet to be elucidated. However, the study team's findings indicate that D-amino acids represent promising biomarkers and therapeutic options for the evaluation and treatment of severe viral infections, including those associated with COVID-19.
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Also Check Out: COVID-19 Supplements, COVID-19 Herbs, COVID-19 Drugs
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/covid-19-supplements
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/covid-19-herbs
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/covid19-drugs
(Please share these articles as they can help save lives)

