BREAKING COVID-19 News! Largest Male Study To Date Reveals That SARS-CoV-2 Deteriorates Prostate And Urological Health!
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Oct 19, 2023 1 year, 5 months, 2 weeks, 2 days, 44 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: The COVID-19 pandemic has raised many questions and brought to light numerous aspects of human health that were previously unexplored. One such aspect is the impact of the SARS-CoV-2 virus on the male reproductive system, specifically the prostate. Recent research has suggested a link between SARS-CoV-2 infection and the deterioration of male benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a common condition that affects aging men. In this comprehensive study, researchers from Prince of Wales Hospital, Hong Kong-China and The Chinese University of Hong Kong-China delve into the correlation between SARS-CoV-2 infection and BPH complications, using large-scale real-world data.
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
A previous
COVID-19 News report by Thailand Medical News has shown that SARS-CoV-2 infections could affect the prostate tissue in men and give rise to various issues.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-warning-for-males-as-sars-cov-2-is-able-to-cause-both-inflammation-and-damage-to-prostate-tissues
Materials and Methods
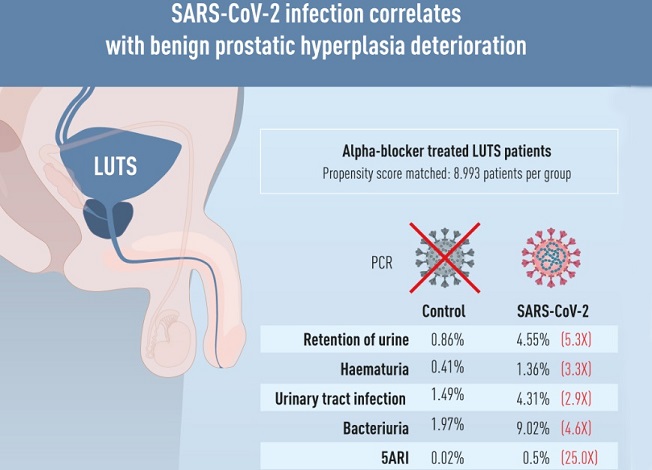
For this study, the research team gathered data from male patients receiving alpha-blocker monotherapy for lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) within the public healthcare system in Hong Kong from 2021 to 2022. The researchers divided these patients into two groups: those with positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests for SARS-CoV-2 (the exposure group) and those without (the control group). Propensity score matching was employed to ensure that the two groups were balanced in terms of baseline characteristics. Subsequently, the study team compared BPH complications and conducted subgroup analyses to gain deeper insights.
Results
Following propensity score matching, the study team analyzed data from 17,986 patients, half of whom had confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection (n = 8,993). The SARS-CoV-2 group exhibited statistically significant higher incidences of urinary retention (4.55% vs. 0.86%, p < 0.001), hematuria (1.36% vs. 0.41%, p < 0.001), clinical urinary tract infections (UTI) (4.31% vs. 1.49%, p < 0.001), culture-proven bacteriuria (9.02% vs. 1.97%, p < 0.001), and the addition of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (5ARI) for combination therapy (0.50% vs. 0.02%, p < 0.001) when compared to the control group. Subgroup analysis demonstrated similar differences across different age groups. There were no statistically significant differences in the incidence of retention, hematuria, or the addition of 5ARI a
cross different COVID-19 severities.
This study conclusively shows that SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with an increased incidence of urinary retention, hematuria, UTI, and the addition of combination therapy in the short term, irrespective of the severity of COVID-19. This research represents the largest study to date demonstrating the negative impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection on urological health.
Understanding the Mechanism
The link between SARS-CoV-2 and male prostate health is complex. The virus enters cells by engaging angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as an entry receptor, along with the surface protease TMPRSS2. Many organ systems in the human body express both ACE2 and TMPRSS2, allowing SARS-CoV-2 to exert its effects in multiple areas. Notably, prostate epithelial cells also express ACE2 and TMPRSS2, suggesting that the male lower urinary tract is a target for the virus.
Beyond the ACE2 pathway, recent systematic reviews have revealed additional pathophysiological pathways through which the prostate is affected by SARS-CoV-2. These pathways include androgen-receptor-dependent TMPRSS2 expression, the inflammatory cascade, and metabolic dysregulation associated with SARS-CoV-2. Metabolic syndrome and disorders such as diabetes mellitus are known risk factors for LUTS and are believed to affect the prostate gland by increasing sympathetic tone, promoting insulin-mediated prostate growth, and inducing chronic inflammation. SARS-CoV-2 infection has been linked to new-onset metabolic complications, including hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis, and diabetes. These metabolic dysregulations could potentially exacerbate LUTS.
Investigating BPH Complications
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition that affects the quality of life of aging men. It can lead to complications such as urinary retention, urinary tract infections, hematuria, and bladder stone formation. BPH prevalence increases with age, with more than 80% of patients over the age of 70 affected. Interestingly, older male patients are also more significantly affected by COVID-19.
This study aimed to investigate how SARS-CoV-2 infection might affect male LUTS associated with BPH. Previous research included small-scale case series and observational studies that hinted at a connection between COVID-19 and worsening male LUTS. However, this new research contributes to our understanding by using large-scale real-world data to explore the correlation between SARS-CoV-2 infection and BPH outcomes.
The research began with 192,435 male patients prescribed alpha-blocker monotherapy in Hong Kong's public healthcare system in 2021. After applying the necessary exclusion criteria, 17,986 patients were included in the final analysis, with 8,993 patients in each group. Before propensity score matching, there were some imbalances between the two groups, which were corrected after matching.
The results of the study revealed statistically significant differences in the incidence of primary outcomes between the two groups. Patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 had significantly higher rates of urinary retention, hematuria, clinical UTIs, bacteriuria, and the addition of 5ARIs for combination therapy during follow-up.
These findings indicated that SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with a higher risk of BPH complications, including a 5.31-fold risk for urinary retention, a 3.30-fold risk for hematuria, a 2.90-fold risk for clinical UTI, and a 4.58-fold risk for bacteriuria.
Subgroup analysis, stratified by age, consistently demonstrated higher incidence of BPH complications and outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 patients across various age groups, with the exception of younger patients. The incidence of these BPH-related outcomes increased with age, mirroring the known age-related progression of BPH.
Notably, even patients with asymptomatic or mild COVID-19 infection, which represents the majority of cases, exhibited an increased risk of BPH complications. The research also suggested that concomitant psychological and environmental stress during a SARS-CoV-2 infection could contribute to lower urinary tract dysfunction.
Conclusion
This study offers valuable insights into the connection between SARS-CoV-2 infection and male prostate health. It is evident that the virus can exacerbate benign prostatic hyperplasia, leading to complications such as urinary retention, urinary tract infections, hematuria, and the addition of combination therapy. Importantly, these effects are observed regardless of the severity of the COVID-19 infection.
While this study has limitations, such as its retrospective nature and relatively short follow-up duration, it highlights the significance of understanding the urological manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 in male patients. Clinicians should be aware of the higher incidence of BPH complications among COVID-19 patients and the fact that these complications can occur even in asymptomatic cases. Further research with longer follow-up periods is needed to explore the long-term effects and potential interventions for individuals affected by this unique relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and male prostate health.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed Journal of Internal Medicine.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/joim.13719
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
