BREAKING! COVID-19 News: SARS-CoV-2 ORF3A Protein Damages Renal Tubules Via TRIM59 Induced STAT3 Activation Causing Acute Kidney Injury!
COVID-19 News - SARS-CoV-2 ORF3A - Acute Kidney Injury Dec 17, 2022 2 years, 4 months, 3 days, 1 hour, 4 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: Researchers from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York-USA have shockingly discovered that the SARS-CoV-2 viral protein ORF3A injures and damages the renal tubules of human host by interaction with TRIM59 to induce STAT3 activation, which typically results in acute kidney injury.
This kidney damage occurs to most people who have been exposed to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, irrespective if they were asymptomatic or even mildly symptomatic.
Thailand Medical News has been warning for a long time through our various
COVID-19 News coverages that millions of people are now walking around not even being aware that they have acute kidney injury (AKI) till when conditions are far too late.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/university-of-queensland-study-warns-that-millions-of-sars-cov-2-infected-individuals-are-not-aware-that-they-may-have-undiagnosed-acute-kidney-injury
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/warning-covid-19-latest-researchers-warn-of-epidemic-of-post-covid-19-kidney-disease-and-study-shows-many-will-die-or-never-recover-from-aki
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/good-news-study-finds-that-most-recovered-covid-19-patients-even-with-mild-infections-will-ultimately-develop-virus-induced-kidney-damage
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/more-great-news-even-those-that-initially-had-mild-covid-19-symptoms-can-develop-kidney-disease-as-part-of-many-manifestations-of-long-covid
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/university-of-washington-study-confirms-that-sars-cov-2-can-directly-invade-human-kidney-cells-causing-a-range-of-kidney-issues-including-acute-kidney
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/dutch-and-german-study-shows-that-sars-cov-2-directly-infects-the-kidneys-and-causes-tissue-scarring-which-ultimately-leads-to-kidney-damage-and-failu
/acute-kidney-injury-study-shows-that-acute-kidney-injury-(aki)-predominant-among-covid-19-patients">https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/acute-kidney-injury-study-shows-that-acute-kidney-injury-(aki)-predominant-among-covid-19-patients
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-attacks-kidney-proximal-tubular-cells-causing-acute-fanconi-syndrome-according-to-french-study
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-clinical-care-kidney-failure-emerging-as-a-common-occurrence-from-covid-19-infections
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/study-finds-that-covid-19-induced-acute-kidney-injury-similar-to-sepsis-caused-kidney-injury-and-that-mitochondrial-dysfunction-may-play-a-key-role
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-more-emerging-chinese-research-studies-shows-that-the-sars-cov-2-coronavirus-also-attacks-the-kidneys,-pancreas-and-liver
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-study-latest-autopsy-study-by-imperial-college-london-shows-extensive-blood-clots,-massive-lung-and-kidney-injuries-along-with-new-findings
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-u-s-cdc-reports-high-incidences-of-kidney-failure,-clots,-diabetes-and-heart-issues-in-post-covid-children-and-teenagers
According to one meta-analysis study in 2020, the incidence of acute kidney injury or AKI in COVID-19 was 8.9%.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9014846/
However more recent studies are showing the that the actual figures could be as high as between 31 to 46% of all individuals who have been exposed to the SARS-CoV-2 virus!
https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1003969
https://jasn.asnjournals.org/content/32/1/151
AKI or acute kidney injury occurs frequently in COVID-19 patients infected by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and infection of kidney cells by this virus has been frequently reported.
To date however, little is known about the direct impact of the SARS-CoV-2 infection upon the renal tubular cells.
The study team found that SARS-CoV-2 activated Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling and caused cellular injury in the human renal tubular cell line (HK-2).
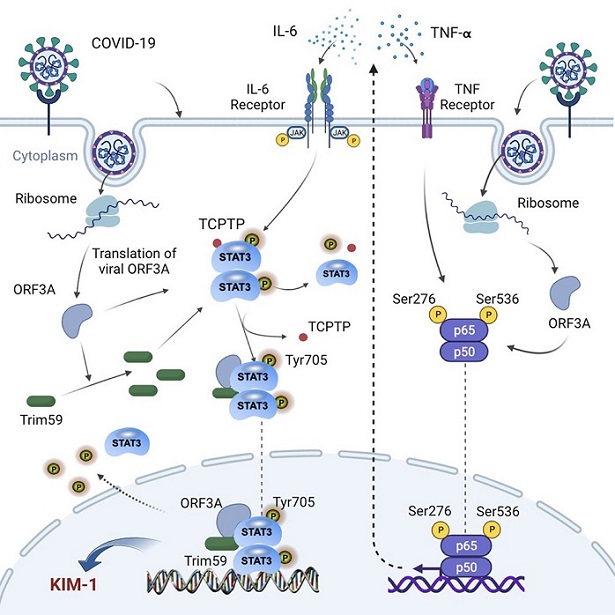
Mechanistically, the viral protein ORF3A of SARS-CoV-2 augmented both NF-κB and STAT3 signaling and increased the expression of kidney injury molecule 1(KIM-1).
Interestingly, it was found that SARS-CoV-2 infection or expression of ORF3A alone elevated the protein level of Tripartite motif-containing protein 59 (TRIM59), a ubiquitin E3 ligase, which interacts with both ORF3A and STAT3.
The excessive TRIM59 in turn dissociated the phosphatase TCPIP from binding to STAT3 and hence inhibited the dephosphorylation of STAT3, leading to persistent STAT3 activation.
Animal model studies showed that ORF3A induced renal injury in zebrafish and mice.
Furthermore, it was found that expression of TRIM59 was elevated in the kidney autopsies of COVID-19 patients with AKI.
Hence, the aberrant activation of STAT3 signaling by TRIM59 plays a significant role in the renal tubular cell injury caused SARS-CoV-2, which suggest a potential targeted therapy for the renal complications of COVID-19.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Molecular Therapy.
https://www.cell.com/molecular-therapy-family/molecular-therapy/fulltext/S1525-0016(22)00712-2
The study team employed both in vitro and in vivo model systems to uncover a previously unrecognized pathogenic mechanism of kidney injury associated with COVID-19, in which dysregulation of STAT3 signaling plays a central role.
Previous study findings about increased STAT3 phosphorylation in COVID-19 patient kidney biopsy suggests that aberrant STAT3 signaling due to the SARS-CoV-2 infection could be one of the patho-mechanisms underlying the renal injury in COVID patients given that STAT3 activation in kidney cells has been implicated in various kidney diseases.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33942030/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34626364/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30943069/
To date however, how the STAT3 signaling pathway in kidney cells is perturbed by SARS-CoV-2 infection remains unclear.
It has been known that a massive secretion of cytokines is elicited by SARS-CoV-2 infection in COVID-19 patients, including IL-6, a potent activator of STAT3 signaling, so the systematic cytokine response to the viral infection is one of the triggers to activate the STAT3 signaling.
However, recent reports about the detection of viral mRNA and proteins in kidney biopsies of COVID-19 patients and infection of human kidney organoids by SARS-CoV-2 viruses in vitro suggest that kidney cells could be infected directly by the virus.
Hence, this opens up a new question whether direct viral infection by SARS-CoV-2 can alter STAT3 signaling and modulate the severity of kidney injury due to the exposure to massive cytokines.
In order to address this question, the study team found that in vitro cultured HK-2 cells infected by SARS-CoV-2 had an elevated level of phosphorylated STAT3 and KIM-1expression, demonstrating that direct infection of SARS-COV-2 can disturb the STAT3 signaling and cause renal tubular epithelial cell injury.
Importantly, this is consistent with a recent report showing that the JAK-STAT pathway was solely activated in the proximal tubule cells infected by the virus.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35032430/
To fully comprehend the mechanism for the renal cell injury caused by direct infection of SARS-CoV-2, the study team generated a number of transgenic zebrafish to express individual viral proteins of SARS-CoV-2 in the embryonic pronephric tubular epithelial cells and found that the viral protein ORF3A could induce renal tubular injury in zebrafish.
The ORF3A, protein is one of the largest accessory proteins of SARS-CoV-2, encodes a viroporin with ion channel activities that is localized to plasma membrane and lysosomes and is involved in viral release.
Similar to SARS-CoV ORF3A, SARS-CoV-2 ORF3A has been shown to induce apoptosis, necrosis and pyroptosis in HEK293T and Vero E6cells and can activate NF-kB and NLRP3 inflammatory pathways in HEK293T and A549 cells.
The pathogenic role of ORF3A has however not been characterized in the context of kidney cells or STAT3 signaling.
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
The study findings presented both in vitro evidence with HK-2 cells and in vivo evidence with transgenic zebrafish that ORF3A in kidney cells is indeed able to modulate the NF-kB pathway and increase cytokine production in kidney cells, including TNF-Alpha and IL-6, which are NF-kB target genes and strongly associated with the severity of COVID-19 patient outcomes.
Thus, the study findings support that, upon viral infection, certain viral proteins such as ORF3A affect the inflammatory pathways triggering cytokine release to activate the STAT3 pathway and induce renal cell injury.
Multiple molecular mechanisms have been proposed to mediate the dysregulation of STAT3 signaling by SARS-CoV-2, such as the imbalance between STAT1 and STAT3 activation and the crosstalk between plasminogen activator-inhibitor 1 and STAT3 signaling.
The study findings showed in HK-2 cells, both SARS-CoV-2 infection and expression of SARS-CoV-2 ORF3A alone could upregulate TRIM59, which competitively block the interaction between STAT3 and the phosphatase TCPTP and reduce the dephosphorylation of STAT3, leading to persistent activation of STAT3.
Significantly, this represents a previously unrecognized mechanism of the regulation of STAT3 signaling by a SARS-CoV-2 viral protein downstream to the JAK-mediated STAT3 phosphorylation.
Also, since ORF3A could simultaneously activate NF-kB and STAT3 signaling, the study findings suggest that direct infection by SARS-CoV-2 may create a positive feedback loop to enhance the cellular response to cytokines such as IL-6 in kidney cells and aggravate the injury.
Coincidentally, such simultaneous activation of NF-kB and STAT3 has been observed in clinical samples from patients with other inflammatory diseases as an evidence of IL-6 signaling amplifier, so it is worth while exploring whether this mechanism is applicable to other cell types besides kidney cells, and further studies are needed to test it in other cell types susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection, such as pulmonary alveolar cells and endothelial cell.
The study team discovered that ORF3A of SARS-CoV-2 could interact with TRIM59 and STAT3, but it is unclear whether these interactions are involved in the regulation of STAT3 activation.
ORF3A has been found to be localized to the lysosome-endosome membranes and inhibiting autophagy in cultured cells.
The researchers also found that ORF3A is also present in the nuclei of HK-2 cells, which is consistent with its interaction with STAT3 that translocates to the nuclei when it is phosphorylated.
However, whether nuclear ORF3A also affects activity of other transcriptional factors requires further studies.
In order to corroborate their in vitro findings, the study team also examined the expression TRIM59 in the kidney autopsies of COVID-19 patients with AKI and found that its expression was significantly increased in the renal tubular cells.
It is still unclear however as to how TRIM59 is regulated in the COVID-19-associated nephropathy.
As ORF3A has been shown to inhibit autophagosome/lysosome function, it is possible that TRIM59 degradation is affected by ORF3A, which deserves further investigation.
In order to explore the potential role of ORF3A in COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury, the study team established a murine model with transient ORF3A expression in kidney and showed that ORF3A exacerbated kidney injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion and inhibition of STAT3 activities could ameliorate this effect.
The study findings demonstrate the cytotoxicity of ORF3A in kidney cells in a mammalian animal model and suggest that STAT3 is a critical mediator of renal injury in COVID-19-associated kidney injury.
It was also reported recently, the N protein of SARS-CoV-2 have been reported to cause renal tubular-necrosis in mice by dysregulating the TGF-k-Smad3 pathway.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34813685/
Hence, multiple pathogenic pathways may be involved in the COVID-19-related renal injury.
An appropriate animal model for kidney injury induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection is needed to further confirm these study findings.
The study team concluded, “SARS-CoV-2 ORF3A protein can augment both NF-kB and STAT3 signaling and exacerbate the injury of renal tubular cells in the presence of cytokines induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection. In addition, ORF3A modulates the STAT3 signaling via TRIM59-mediated inhibition of dephosphorylation. Therefore, targeting the aberrant STAT3 activation may serves as a potential therapy for acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients.”
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-are-certain-newer-sars-cov-2-variants-causing-a-rise-in-chronic-kidney-disease-and-kidney-failure-in-countries-like-singapore-and-thailand
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-diagnostics-researchers-uncover-new-protein-biomarker-supar-to-identify-covid-19-patients-at-risk-of-acute-kidney-injury-aki

