BREAKING COVID-19 News! Study Shows That SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Has DNA-Melting And Strand-Annealing Properties!
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 09, 2023 1 year, 5 months, 6 days, 12 hours, 34 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: Since the emergence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in December 2019, the world has been grappling with the devastating impacts of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The virus has not only posed a significant threat to global health but has also wreaked havoc on the global economy. As researchers strive to understand the molecular intricacies of SARS-CoV-2, a groundbreaking study covered in this
COVID-19 News report conducted by Zunyi Medical University in China and Guizhou University in Guiyang sheds light on the unique biochemical activities of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (CoV-2 N). This discovery holds immense importance for drug design and development, offering potential insights into antiviral drug development.
 SARS-CoV-2: An Overview
SARS-CoV-2: An Overview
SARS-CoV-2 belongs to the beta coronavirus family and is characterized by its spherical, encapsulated structure with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome. The virus's genetic makeup includes 11 predicted genes, encoding around 20 functional proteins. Among these proteins, the SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural protein 13 (CoV-2 Nsp13) and nucleocapsid protein (CoV-2 N) exhibit high conservation across different mutants and coronaviruses.
CoV-2 Nsp13, a helicase involved in viral replication, has been extensively studied for its role in inhibiting type I interferon signaling and blocking immune activation during infection. On the other hand, CoV-2 N, the nucleocapsid protein, is essential for viral replication and regulation of cell signaling pathways. Recent studies have proposed CoV-2 N as a potential vaccine candidate due to its high immunogenicity and the ability to induce a robust immune response.
The Unprecedented Discovery
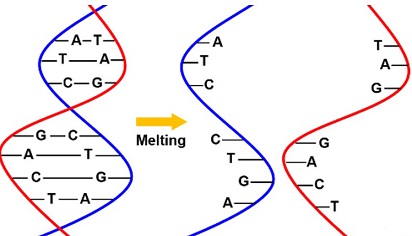
The research focused on unraveling the biochemical characteristics of CoV-2 N, leading to an unexpected revelation. While CoV-2 N has traditionally been known for its role in binding to genomic RNA in the nucleocapsid, the study discovered that it possesses DNA-melting and strand-annealing activities.
Distinguishing Features of CoV-2 N Activities
Compared to CoV-2 Nsp13, CoV-2 N's DNA-melting activity was found to be more than 22 times weaker, and it exhibited a unique independence from nucleoside triphosphates and Mg2+. Intriguingly, at low concentrations, CoV-2 N demonstrated stronger annealing activity than CoV-2 Nsp13, while at high concentrations, it promoted the melting of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). These findings present a paradigm shift in our understanding of CoV-2 N and open new avenues for antiviral drug development.
Biochemical Insights into CoV-2 N
To comprehend the implications of CoV-2 N's newfound activities, the researchers delved into the biochemical functions of this protein. CoV-2 N was observed to efficiently unwind dsDNA involved in DNA replication, repair, and recombination.
Notably, the protein did not exhibi
t typical helicase characteristics, and its unwinding activity did not rely on essential cofactors such as ATP and Mg2+. Instead, CoV-2 N displayed a more nuanced behavior, resembling the helix-destabilizing activity of replication protein A (RPA) rather than a traditional helicase.
Divergent Unwinding Substrates
While both CoV-2 N and CoV-2 Nsp13 share the same unwinding polarity, they differ significantly in their substrates. CoV-2 N displayed a strict requirement for a 5' overhang of 16 nucleotides, emphasizing its dependence on single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) length. This contrasts with CoV-2 Nsp13, which exhibited properties more aligned with typical helicases, requiring a minimum single-stranded bubble structure of 12 nucleotides.
Annealing and Unwinding Dynamics
The study revealed a concentration-dependent duality in CoV-2 N's activities. At low concentrations, CoV-2 N showcased robust ssDNA annealing, while at higher concentrations, unwinding of dsDNA prevailed. This suggests a dynamic role for CoV-2 N in regulating the transition between annealing and unwinding, possibly influencing different stages of viral replication.
Implications for Drug Development
The unprecedented findings regarding CoV-2 N's DNA-melting and strand-annealing activities present a unique opportunity for antiviral drug development. Understanding the multifaceted functions of CoV-2 N could pave the way for targeted therapies that exploit the protein's role in viral replication and host cell interaction. As the world continues to combat the COVID-19 pandemic, this breakthrough study opens new doors for innovative approaches in drug design and development, offering hope for more effective antiviral interventions.
Conclusion
The discovery of DNA-melting and strand-annealing activities in the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein adds a new dimension to our understanding of the virus's molecular mechanisms. This breakthrough study conducted by Zunyi Medical University and Guizhou University not only deepens our knowledge of CoV-2 N but also provides crucial insights for the development of antiviral drugs. As the scientific community continues to unravel the mysteries of SARS-CoV-2, this research marks a significant step forward in the quest for effective interventions against COVID-19.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Frontiers in Microbiology.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2022.851202/full
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
