BREAKING! German Study Published In Peer Reviewed Journal Indicates That COVID-19 Shots Can Induce CD8 T-Cell Dominant Hepatitis!
Source: Medical News - Hepatitis - COVID-19 Apr 29, 2022 3 years, 8 months, 3 weeks, 5 days, 20 hours, 12 minutes ago
A new study led by researchers from the University of Freiburg-Germany has found that current COVID-19 shots can induce CD8 T-cell dominant hepatitis!
 Study Graphical Abstract
Study Graphical Abstract
It should be noted that there was never any hepatitis safety signal in the trials of COVID19 shots, however several reports have recently associated autoimmune hepatitis (AIH)-like conditions with COVID-19 shots.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34528278/
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(21)00237-3/fulltext
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8219312/
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(21)01904-8/fulltext
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(21)00417-7/fulltext
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(21)01896-1/fulltext
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(21)00412-8/fulltext
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(21)01953-X/fulltext
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(21)00424-4/fulltext
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(21)02093-6/fulltext
Thailand
Medical News would however like to highlight however that to date, no severe case of liver failure requiring liver transplantation has ever been reported with regards to post COVID-19 shot issues.
Liver injury was observed after both, mRNA and vector-based shots, while time from shot administration to symptom onset ranged between 4 days after the first dose to 6 weeks after the second dose.
One patient was re-exposed to the shot which led to
a worsening of liver injury.
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(21)02093-6/fulltext
However, it remained unclear whether the reported association of autoimmune hepatitis with COVID-19 jabs is coincidental, might reflect transient drug-induced liver injury, or could involve unique SARS-CoV-2-induced antigen-specific immune activation.
https://www.journal-of-hepatology.eu/article/S0168-8278(21)01965-6/fulltext
However, the fact that autoimmune hepatitis or AIH-like conditions also occurred after SARS-CoV-2 infection suggests that the latter could be a driving factor for the sporadic cases.
https://europepmc.org/article/pmc/pmc8662284
Numerous autoimmune hepatitis episodes have been described following SARS-CoV-2 infection and jabs but their pathophysiology remains unclear.
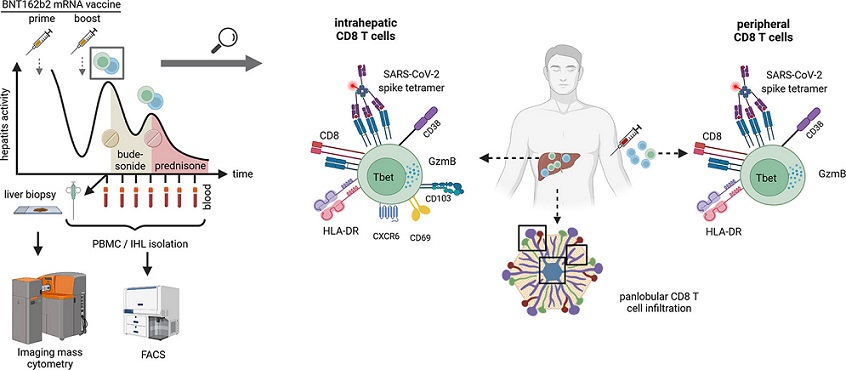
In this new study in Germany, the study team reported the case of a 52-year-old male, presenting with bimodal episodes of acute hepatitis, each occurring 2-3 weeks after BNT162b2 mRNA jabs and sought to identify the underlying immune correlates. The patient received first oral budesonide, relapsed, but achieved remission under systemic steroids.
A detailed imaging mass cytometry for spatial immune profiling was performed on liver biopsy tissue. Flow cytometry was performed to dissect CD8 T cell phenotypes and identify SARS-CoV-2-specific and EBV-specific T cells longitudinally. Jab-induced antibodies were determined by ELISA. Data was correlated with clinical labs.
The study findings showed that detailed analysis of the hepatic tissue revealed an immune infiltrate quantitatively dominated by activated cytotoxic CD8 T cells with panlobular distribution.
Furthermore, an enrichment of CD4 T cells, B cells, plasma cells and myeloid cells was also observed compared to controls.
The intrahepatic infiltrate showed enrichment for CD8 T cells with SARS-CoV-2-specificity compared to the peripheral blood. Notably, hepatitis severity correlated longitudinally with an activated cytotoxic phenotype of peripheral SARS-CoV-2-specific, but not EBV-specific CD8+ T cells or jab-induced immunoglobulins.
The study findings concluded that COVID-19 jabs can elicit a distinct T cell-dominant immune-mediated hepatitis with a unique patho-mechanism associated with jab induced antigen-specific tissue-resident immunity requiring systemic immunosuppression.
It has already been known that liver inflammation is sometimes observed during SARS-CoV-2 infection.
However, liver inflammation can also occur in some individuals after COVID-19 jabs and shares some typical features with autoimmune liver disease.
The study findings show that highly activated T cells accumulate and are evenly distributed in the different areas of the liver in a patient with liver inflammation following SARS-CoV-2 shots.
Moreover, within these liver infiltrating T cells, it was also observed an enrichment of T cells that are reactive to SARS-CoV-2, suggesting that these jab-induced cells can contribute to the liver inflammation in this context.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed Journal of Hepatology. (Science Direct-Elsevier)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168827822002343
Thailand
Medical News would however like to note that the current reports of kids developing hepatitis in various countries might not be linked to this study findings as many had never received the COVID-19 shots and some never contracted COVID-19 according to some of these reports. However, we do have our own hypothesis which we have indicated in blue in the linked article.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/what-they-are-not-telling-you-about-the-covid-19-pandemic,-about-the-sars-cov-2-virus,-its-emerging-variants-and-long-covid
For more on
Hepatitis and SARS-CoV-2, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/researchers-alarmingly-find-that-metabolic-associated-fatty-liver-disease-mafld-may-be-a-prevalent-long-covid-manifestation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-sars-cov-2-infection-induces-increase-of-gp73-that-causes-dysglycaemia-increased-gp73-could-also-imply-future-liver-disease-and-liver-cancer
