BREAKING! Hong Kong Study Finds That COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines Activates CD57+ NK Cells That Leads To Acute Myocarditis!
Nikhi Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Mar 23, 2024 1 year, 1 month, 3 days, 9 hours, 47 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: As the world continues its battle against the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccination campaigns have been claimed to have played a pivotal role in curbing the spread of the virus and reducing severe illness. Among the various types of COVID-19 vaccines, those based on mRNA technology have come under close scrunity due to a variety of emerging adverse effects. However, alongside their 'claimed effectiveness', reports of 'rare' adverse effects with fatal outcomes have emerged, prompting scientific scrutiny and investigation.
 Graphical Abstract - COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines Activates CD57+ NK Cells That Leads To Acute Myocarditis
Graphical Abstract - COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines Activates CD57+ NK Cells That Leads To Acute Myocarditis
One such adverse event that has garnered attention is acute myocarditis, particularly following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination. Acute myocarditis refers to inflammation of the heart muscle, which can lead to symptoms such as chest pain, abnormal heart rhythms, and in severe cases, heart failure. While instances of vaccine-related myocarditis are claimed to be relatively 'rare', occurring in a small fraction of vaccinated individuals- the number of people dying form sudden heart failures is increasing at a worrisome rate, understanding the immunological mechanisms driving these events is crucial for vaccine safety and public health.
One past study has shown that the overall incidence of acute myocarditis/pericarditis was 18.52 (95% confidence interval [CI], 11.67–29.01) per 100 000 persons vaccinated.
https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/75/4/673/6445179
However, it now believed that the actual figures could be far much higher as many such cases of vaccine induced myocarditis is not detected in the initial cases due to lack of detailed health screenings or check-ups.
It should also be noted that SARS-CoV-2 infections alone can also increase the risk of myocarditis and various other cardiac issues.
Thailand
Medical News would like to stress that having the combination of exposure to the virus and having been vaccinated can actually further increase the risk of myocarditis and the severity of the condition and also the usage of drugs that induce arrhythmias and QT prolongation such as SSRIs inhibitors like Fluvoxamine, can actually create a ‘ripe situation’ for a potential heart failure!
Background and Significance of the Study
Against this backdrop, a groundbreaking study that is covered in this
COVID-19 News report, conducted by researchers from esteemed institutions including the University of Hong Kong, Princess Margaret Hospital Authority, Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital, Macau University of Science and Technology, China, and Aston University, Birmingham, UK, aimed to unravel the immune signatures and genetic factors associated with acute myocarditis following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination.
>
The significance of this study lies in its potential to shed light on the underlying immune responses triggered by mRNA vaccines, particularly focusing on natural killer (NK) cells and their role in mediating vaccine-related myocarditis. By elucidating these mechanisms, the research could pave the way for improved vaccine designs, targeted medical interventions, and enhanced safety monitoring protocols.
Study Design and Methodology
The study involved a meticulous analysis of samples obtained from 60 adolescents diagnosed with vaccine-related myocarditis. These individuals, previously in good health, experienced myocarditis within a few days after receiving mRNA COVID-19 vaccination. Samples were collected from various public hospitals in Hong Kong SAR, encompassing clinical data, blood samples for cytokine analysis, genetic testing for NK cell-related polymorphisms, and immunophenotyping of immune cell subsets.
Additionally, control groups were included in the study for comparative analysis. These control groups comprised vaccinated individuals without myocarditis and age-matched healthy controls who had not received any COVID-19 vaccination. By comparing immune profiles, genetic predispositions, and clinical outcomes across these groups, the researchers aimed to pinpoint specific immune signatures and genetic factors associated with vaccine-related acute myocarditis.
Key Findings and Immunological Insights
The study's findings revealed several key insights into the immunological mechanisms underlying vaccine-related acute myocarditis:
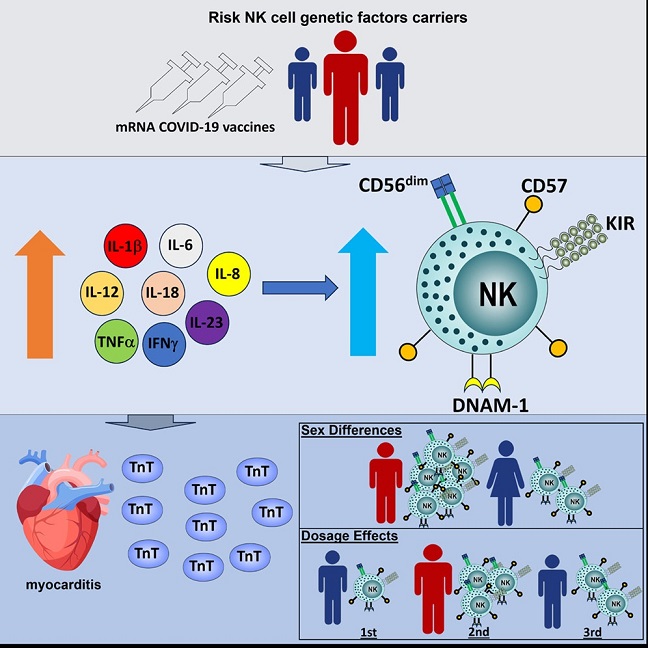
-Elevated Cytokine Levels: Patients diagnosed with vaccine-related myocarditis exhibited significantly elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines crucial for NK cell activation. These cytokines included interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interferon α2 (IFN-α2), IL-12, and IFN-γ. Importantly, these cytokines were found to be markedly higher in patients with myocarditis compared to both vaccinated individuals without myocarditis and healthy controls.
-NK Cell Activation: A notable observation was the increased prevalence of CD57+ NK cells in the blood of patients with vaccine-related myocarditis. The CD57+ NK cell subset, known for its cytotoxic and inflammatory properties, showed a positive correlation with elevated levels of cardiac troponin T (cTnT), a marker of myocardial injury. This correlation suggested a direct link between NK cell activation and myocarditis severity.
-Genetic Risk Factors: Genetic analysis revealed specific killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genotypes and NK cell-specific expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) associated with increased susceptibility to vaccine-related myocarditis. Polymorphisms in KIR genes and eQTLs related to NK cell activity were identified as potential genetic determinants of myocarditis risk post-vaccination.
Genotypically, killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) KIR2DL5B(−)/KIR2DS3(+)/KIR2DS5(−)/KIR2DS4del(+) was a risk haplotype, in addition to single-nucleotide polymorphisms related to the NK cell-specific expression quantitative trait loci DNAM-1 and FuT11, which also correlated with cardiac troponin T levels in post-vaccination patients with myocarditis.
Implications for Vaccine Safety and Future Research Directions
The implications of these findings are manifold and hold significant implications for vaccine safety, design, and clinical management:
-Refining Vaccine Designs: Insights into the immune pathways and genetic factors associated with vaccine-related myocarditis could inform the development of safer and more targeted mRNA vaccines. By understanding how NK cells and cytokines contribute to myocardial inflammation, researchers can explore strategies to mitigate these adverse effects while preserving vaccine efficacy.
-Targeted Medical Interventions: For individuals with a history of post-vaccination myocarditis or identified genetic susceptibilities, personalized medical advice and close monitoring may be warranted. Early detection and intervention strategies could help mitigate the severity of myocarditis and improve clinical outcomes.
-Enhanced Safety Monitoring: Incorporating immune profiling and genetic screening into vaccine safety monitoring protocols could enhance the early detection of individuals at risk of vaccine-related adverse events. This proactive approach to safety monitoring is crucial for maintaining public trust in vaccination programs.
Moving forward, further research is warranted to validate these findings, explore additional immune pathways involved in vaccine-related myocarditis, and assess long-term outcomes in affected individuals. Collaborative efforts between researchers, healthcare providers, and regulatory agencies are essential to ensure vaccine safety while maximizing the benefits of COVID-19 vaccination for global public health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study's in-depth analysis of immune responses, genetic factors, and clinical outcomes in vaccine-related acute myocarditis represents a significant step forward in understanding and addressing vaccine safety concerns. The study found that CD57+ NK cell abundance positively correlates with the elevated cTnT level and that CD57+ NK cells are more frequent in males and after second vaccine dose administration. By unraveling the complex interplay between NK cells, cytokines, and genetic predispositions, researchers are paving the way for safer and more effective COVID-19 vaccination strategies. These insights underscore the importance of ongoing research, vigilance in safety monitoring, and targeted interventions to mitigate rare adverse events.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Med (Cell Press)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666634024000801
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News
