BREAKING NEWS! Study Reveals SARS-CoV-2 Causes Gastrointestinal Lesions Of Various Kinds And Also Gastrointestinal Bleeding!
COVID-19 News - Gastrointestinal Lesions Jun 03, 2023 2 years, 6 months, 3 weeks, 5 days, 1 hour, 8 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: In a study conducted by researchers from Chongqing Three Gorges University in China, it has been discovered that the SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, not only invades the respiratory system but also wreaks havoc on the digestive system. The research has shed light on the various gastrointestinal diseases caused by the virus, including
gastrointestinal inflammatory lesions, ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal thrombotic lesions, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
While many past studies, clinical case series and
COVID-19 News reports have covered on various gastrointestinal manifestations as a result of exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, many are unaware of the serious gastrointestinal damage that SARS-CoV-2 can really cause and many are even unaware of the damage that is silently taking place in their gastrointestinal tracts even after asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic exposures to the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
These worrying study findings have significant implications for understanding and treating the gastrointestinal complications arising from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
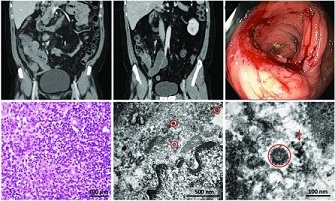
Gastrointestinal inflammatory lesions have been identified as one of the consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection. The spike protein (S Pro) of the virus binds to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which is not only found in alveolar cells but also in gastrointestinal epithelial cells. This binding initiates a cascade of events leading to gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases such as erosive gastritis and hemorrhagic gastritis, ultimately resulting in gastrointestinal bleeding.
Surprisingly, a study has revealed that more than 40% of COVID-19 patients with gastrointestinal symptoms develop severe forms of the disease. Abdominal pain, one of the common symptoms, has been associated with an increased risk of severe COVID-19 infection. These findings highlight the importance of monitoring and addressing gastrointestinal inflammation in the clinical management of COVID-19 patients.
Another alarming discovery from the study is the occurrence of
ulcerative lesions in the gastrointestinal tract caused by the interaction between ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2. Gastrointestinal ulcerative lesions have been observed in various parts of the digestive system, including the tongue, palate, lips, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, and large intestine. Endoscopic evaluations have confirmed the presence of these ulcers, underscoring the need for close monitoring and timely diagnosis of COVID-19 patients. Moreover, severe cases have been reported where large, deep, and non-hemorrhagic gastric ulcers have led to fatal outcomes. The study urges healthcare professionals to remain vigilant in identifying and treating ulcerative lesions in COVID-19 patients.
Gastrointestinal bleeding has emerged as a concerning complication in critically ill COVID-19 patients. With reported proportions varying from 2% to 3%, gastrointestinal bleeding can occur due to gastrointestinal ulceration, inflammation, direct damage to mucous membranes, or the use of certain medications. Recognizing the causes and implementing appropriate interventions a
re essential to prevent and manage gastrointestinal bleeding in COVID-19 patients effectively.
Perhaps one of the most alarming findings of the study is
the gastrointestinal thrombotic lesions associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. In severe COVID-19 cases, abnormal coagulation and thrombotic diseases have been observed, leading to thrombosis in various parts of the gastrointestinal system. Patients with COVID-19 have shown longer prothrombin time, higher plasma D-dimer levels, and elevated inflammatory factors, which contribute to coagulation disorders and potentially fatal thrombotic events. Disturbingly, cases of intestinal ischemia, acute mesenteric thrombosis, and intestinal obstruction have been reported in COVID-19 patients, underscoring the need for prompt identification and treatment of these gastrointestinal thrombotic complications.
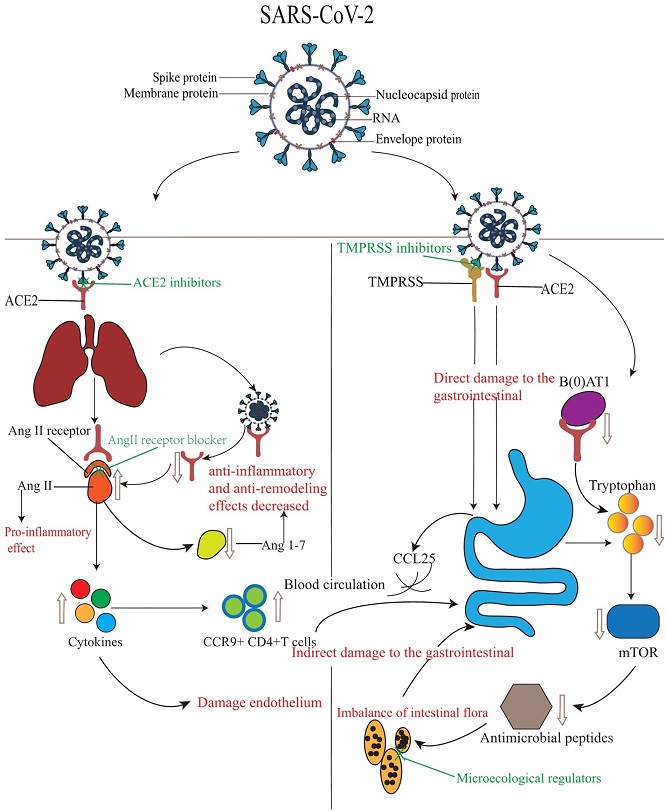 The mechanisms and treatment of gastrointestinal injury induced by SARS-CoV-2
The mechanisms and treatment of gastrointestinal injury induced by SARS-CoV-2
As the COVID-19 pandemic persists, it is becoming increasingly clear that the virus extends its impact beyond the respiratory system. Gastrointestinal symptoms are now being recognized as a significant aspect of the disease, necessitating a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. The study conducted by Chongqing Three Gorges University emphasizes the importance of understanding the mechanisms of gastrointestinal damage caused by SARS-CoV-2, which will aid in developing targeted therapies to alleviate the symptoms and complications associated with COVID-19.
By specifically targeting the pathways involved in viral replication, inflammation, and tissue damage, researchers may be able to mitigate the gastrointestinal symptoms associated with COVID-19. Further research is needed to explore these mechanisms in greater detail and translate the findings into effective clinical interventions.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Frontiers in Microbiology.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1177741/full
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-millions-unknowingly-harbor-sars-cov-2-in-their-gut-with-viral-persistence-contributing-to-long-covid
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/there-is-no-such-thing-as-long-covid-sars-cov-2-exposure-causes-persistent-infections-along-with-continuous-presence-of-short-viral-rnas-svrnas

