BREAKING! Polish Scientists Alarmingly Find That COVID-19 Causes Protein Carbamylation!
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Mar 21, 2025 3 weeks, 2 days, 27 minutes ago
Medical News: A Hidden Molecular Effect of COVID-19 Could Be Triggering Dangerous Health Outcomes
A new and highly concerning medical discovery by a team of Polish scientists has revealed that SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19, may be causing a harmful molecular process in the human body known as protein carbamylation. This alarming finding could provide deeper insights into why many patients, even after recovering from the initial infection, continue to suffer from lingering or new health issues ranging from cardiovascular problems to kidney dysfunction and inflammation-related complications.
 Polish Scientists Alarmingly Find That COVID-19 Causes Protein Carbamylation!
Polish Scientists Alarmingly Find That COVID-19 Causes Protein Carbamylation!
The research was a collaborative effort among experts from Dr. Tytus Chałubiński Specialist Hospital in Radom, the Kazimierz Pułaski University of Technology and Humanities in Radom, and the Medical University of Bialystok, Poland. Led by a team of clinical and biomedical researchers, the study is the first to analyze the relationship between inflammation and protein carbamylation in COVID-19 patients.
This
Medical News report explores how the scientists conducted the study and why the results are critical for understanding long-term complications from COVID-19, including the potential health threats to recovered individuals.
Understanding Protein Carbamylation and Why It Matters
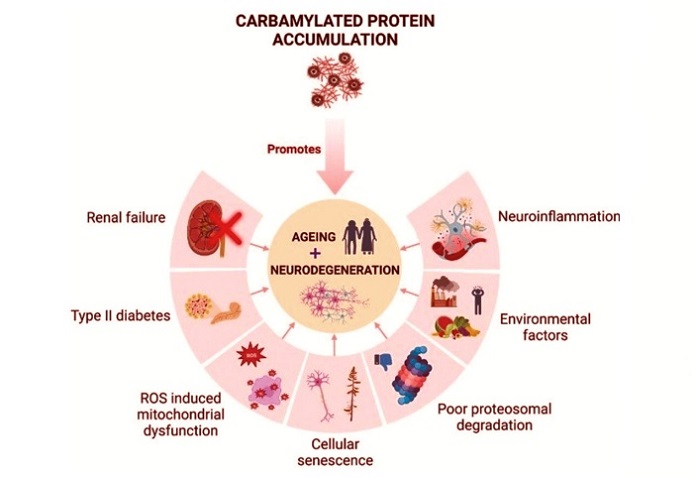
Protein carbamylation is a chemical process in which isocyanic acid - a reactive byproduct derived from urea—binds to amino groups on proteins, particularly on the amino acid lysine. This reaction alters the structure and function of proteins in a non-enzymatic manner, turning them into forms that may no longer function properly or may even trigger harmful effects in the body. The modified amino acid formed is known as carbamyllysine (or homocitrulline).
This process can occur naturally during aging or under certain disease conditions. However, high levels of protein carbamylation are strongly linked to chronic kidney disease, cardiovascular disease, inflammation, and even autoimmune reactions. In healthy individuals, protein carbamylation occurs at low levels, but in the presence of excess urea (as seen in kidney dysfunction) or chronic inflammation, the rate can significantly rise - causing proteins to misbehave and resulting in damage to organs and tissues.
The Study: A Comparison Between COVID-19 Survivors and Victims
The Polish researchers conducted a focused study involving 50 patients who had been admitted to Dr. Tytus Chałubiński Specialist Hospital during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. The group was equally divided into 25 COVID-19 survivors and 25 patients who had unfortunately died due to the infection. Each group consisted of 15 men and 10 women.
Blood samples were analyzed for levels of carbamylated proteins, specifically measuring carbamyl-lysine (CBL), using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits. Additionally, inflammatory biomarkers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), D-dimer
, procalcitonin, and white blood cell (WBC) counts were measured.
The findings revealed a startling difference: patients who had died from COVID-19 had significantly higher levels of serum CBL compared to those who recovered. Statistical analysis using the Mann-Whitney U test showed this result was highly significant (p = 0.0011). Furthermore, higher CBL levels positively correlated with IL-6, D-dimer, and WBC levels - three markers that reflect heightened inflammation and blood clotting activity.
Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis demonstrated that serum CBL levels above 101 ng/mL could moderately differentiate between those who would recover and those who might die from COVID-19, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.76 - indicating decent diagnostic utility.
Why These Findings Are Crucial
The confirmation that COVID-19 can drive up protein carbamylation opens a new door into understanding the disease’s destructive impact on the human body. This molecular alteration affects proteins across various organs and systems, leading to:
-Cardiovascular Damage: Carbamylated LDL cholesterol can damage blood vessels, promote plaque formation, and raise the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Meanwhile, carbamylated HDL loses its protective functions, further compounding vascular harm.
-Kidney Impairment: Protein carbamylation is already a known issue in chronic kidney disease (CKD). COVID-19 may accelerate kidney fibrosis, uremia, and other renal complications through this mechanism.
-Chronic Inflammation and Aging: Carbamylation contributes to molecular aging and prolonged inflammation, possibly explaining the "long COVID" symptoms such as fatigue, memory issues, and pain.
-Autoimmune Risks: Altered proteins due to carbamylation may become immune targets, potentially leading to autoimmune disorders.
-Hematological and Neurological Impact: Carbamylation has been implicated in anemia due to its effect on erythropoietin and is associated with memory deficits, vision disturbances, and coagulation abnormalities.
Conclusions and Implications for Public Health
The discovery that COVID-19 can drive excessive protein carbamylation marks a critical turning point in our understanding of the virus’s long-term effects. By permanently altering protein function, this process can potentially damage multiple organs, trigger immune dysfunction, and lead to chronic conditions even in individuals who initially recovered. It may also help explain the increasing cases of cardiovascular events and kidney issues reported in post-COVID patients worldwide.
These findings stress the urgent need for deeper monitoring of recovered COVID-19 patients, not just for recurring symptoms, but for hidden biochemical and molecular changes that might be silently progressing. Future therapies may need to focus not only on treating inflammation and the virus itself but also on limiting or reversing protein carbamylation to prevent irreversible health consequences.
The study findings were published as an abstract in the journal: Frontiers in Medicine.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/medicine/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1561670/abstract
For the latest COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-alters-drug-effects-through-cyp3a4-enzyme-dysregulation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/visual-complications-linked-to-covid-19-infection
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-studies-show-sars-cov-2-infections-can-lead-to-irritable-bowel-syndrome
https://www.thailandmedical.news/pages/thailand_doctors_listings
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/hospital-news
