Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jun 04, 2024 1 year, 7 months, 2 weeks, 6 days, 5 hours, 12 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: In a groundbreaking study, scientists from Southwest Medical University and its affiliated hospital in Luzhou, China, have unveiled the complex mechanisms behind how COVID-19 triggers arrhythmia, a severe and life-threatening heart rhythm disorder. This research covered in this
COVID-19 News report, sheds light on the intricate interplay of factors that lead to arrhythmias in COVID-19 patients, aiming to equip clinicians with the knowledge needed to prevent and treat these complications effectively.
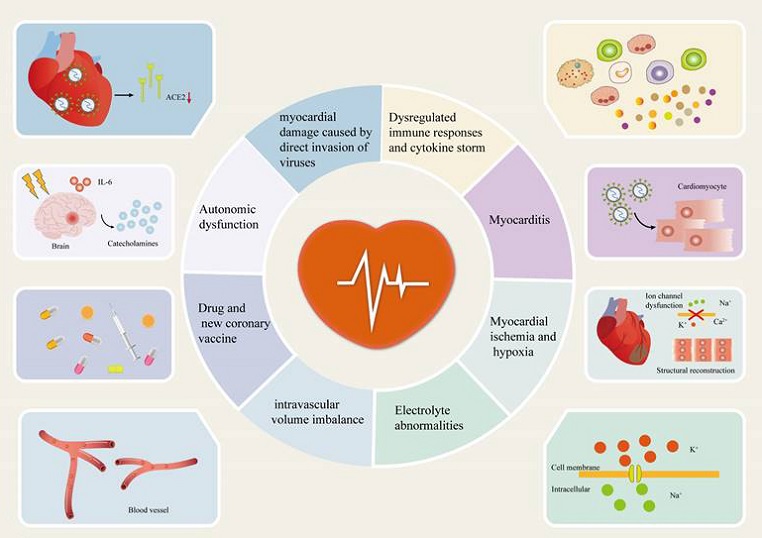 Potential mechanisms of arrhythmia in patients with COVID-19. Potential mechanisms of arrhythmia in patients with COVID-19 include myocardial damage caused by direct invasion of viruses, myocarditis, immune response dysregulation and cytokine storm, myocardial ischemia/hypoxia, electrolyte abnormalities, intravascular volume imbalances, drug interactions, COVID-19 vaccines and autonomic nervous dysfunction.
The Global Impact of COVID-19
Potential mechanisms of arrhythmia in patients with COVID-19. Potential mechanisms of arrhythmia in patients with COVID-19 include myocardial damage caused by direct invasion of viruses, myocarditis, immune response dysregulation and cytokine storm, myocardial ischemia/hypoxia, electrolyte abnormalities, intravascular volume imbalances, drug interactions, COVID-19 vaccines and autonomic nervous dysfunction.
The Global Impact of COVID-19
Since its emergence in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) has rapidly escalated into a global pandemic, affecting millions of lives and overwhelming healthcare systems worldwide. While the primary focus has been on respiratory symptoms, it has become evident that COVID-19 also poses significant risks to the cardiovascular system.
Cardiovascular Complications of COVID-19
COVID-19 can lead to severe cardiovascular complications, including myocardial injury, acute coronary syndrome, and most notably, arrhythmias. Studies have shown that 20-40% of hospitalized COVID-19 patients exhibit evidence of myocardial injury, with arrhythmias being a major complication. The prevalence of arrhythmias in intensive care units (ICUs) is alarmingly high, reaching 44.4%.
Understanding Arrhythmias in COVID-19 Patients
The exact mechanisms by which COVID-19 triggers arrhythmias are complex and not yet fully understood. Factors such as direct viral invasion of the heart, myocarditis, immune response dysregulation, cytokine storms, myocardial ischemia/hypoxia, electrolyte abnormalities, drug interactions, and autonomic nervous system dysfunction all play roles. The following sections delve into these potential mechanisms in detail.
SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2
SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, enters human cells by binding to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors. These receptors are abundant in the lungs and heart, making these organs particularly vulnerable. Once the virus binds to ACE2, it disrupts the balance of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), leading to increased levels of angiotensin II, which can cause inflammation and damage to the heart muscle.
Myocardial Injury from Direct Viral Invasion
The virus can directly invade myocardial tissue, causing damage. Autopsy analyses have confir
med the presence of SARS-CoV-2 particles in the heart tissue of COVID-19 patients. This invasion disrupts the balance of ACE2 expression, leading to myocardial injury and increasing the risk of arrhythmias. The virus can also induce cell degeneration and necrosis in myocardial cells, further exacerbating the condition.
Dysregulated Immune Response and Cytokine Storm
COVID-19 triggers an overactive immune response, leading to a cytokine storm characterized by the excessive release of proinflammatory cytokines. This heightened inflammatory state can directly impact the heart, causing arrhythmias. Inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α have been shown to disrupt ion channel function in cardiomyocytes, leading to prolonged action potentials and promoting arrhythmias.
Myocarditis
Myocarditis, or inflammation of the heart muscle, is another significant complication of COVID-19. SARS-CoV-2 can cause myocarditis through both direct viral damage and immune-mediated mechanisms. This condition can lead to various arrhythmias, including malignant ones, posing a severe threat to patients' lives.
Myocardial Ischemia and Hypoxia
COVID-19 often leads to hypoxemia and acute respiratory failure, resulting in myocardial hypoxia and ischemia. The inflammatory response triggered by the virus can also cause vascular endothelial damage and promote thrombosis, leading to myocardial infarction. These conditions disrupt the normal electrical activity of the heart, increasing the risk of arrhythmias.
Electrolyte Abnormalities and Intravascular Volume Imbalance
Electrolyte imbalances are common in COVID-19 patients due to factors such as RAAS system dysregulation, renal dysfunction, and excessive inflammatory responses. These imbalances can affect the electrophysiological function of cardiomyocytes, leading to arrhythmias. Intravascular volume imbalances, often seen in severe COVID-19 cases, can further exacerbate these issues.
Drug Toxicity and Interactions
Various drugs used to treat COVID-19, including chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, and azithromycin, can prolong the QT interval and increase the risk of ventricular arrhythmias. These drugs can also interact with other medications, leading to toxic effects on the heart. Additionally, some antiviral drugs and monoclonal antibodies used in COVID-19 treatment can have similar adverse effects.
Autonomic Nervous System Dysfunction
COVID-19 can cause autonomic nervous system dysfunction, leading to arrhythmias. This dysfunction is often due to stress-related conditions, mental health issues, and the effects of medications. The overactivation of the sympathetic nervous system and inflammatory responses can contribute to the development of arrhythmias.
Potential Targets and Treatment Strategies
Understanding the mechanisms behind COVID-19-induced arrhythmias can help identify potential targets for treatment. ACE2, TMPRSS2, and other viral entry pathways are potential targets for therapeutic intervention. Additionally, managing the immune response and cytokine storm, as well as addressing electrolyte imbalances and myocardial ischemia, are crucial for preventing and treating arrhythmias.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the intricate relationship between viral infections and cardiovascular health. Arrhythmias are a significant and life-threatening complication of COVID-19, and understanding the underlying mechanisms is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. Continued research and clinical vigilance are necessary to protect the heart health of COVID-19 patients and improve their prognosis and survival rates.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed International Journal of Medical Sciences.
https://www.medsci.org/v21p1366.htm
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/atrial-fibrillation-significantly-increases-mortality-risk-in-severe-covid-19-cases-
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-45-percent-of-individuals-who-get-hospitalized-for-heart-arrhythmia-typically-die-within-the-next-ten-years
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/u-s-fda-warns-that-high-strength-lidocaine-skin-creams-can-trigger-seizures-arrhythmia-and-breathing-issues
