Combining Hormone Therapy and Radiation Offers New Hope for High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Apr 10, 2025 2 days, 16 hours, 57 minutes ago
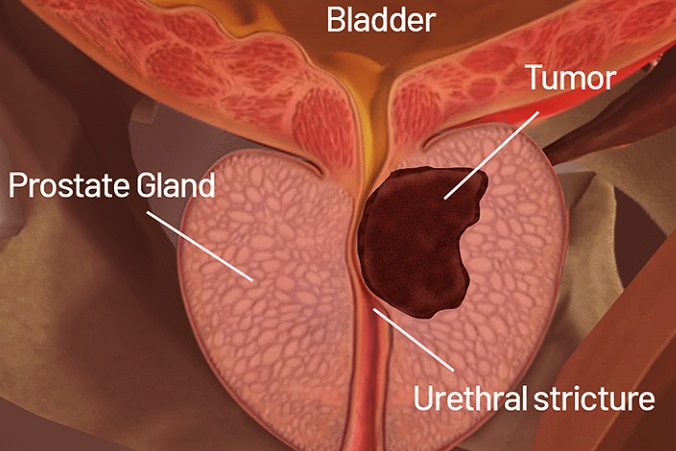
Medical News: In an important breakthrough for the treatment of high-risk prostate cancer, researchers from Taibah University in Saudi Arabia have found that a powerful combination of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) and radiation therapy (RT) significantly improves survival outcomes compared to ADT alone.
 Combining Hormone Therapy and Radiation Offers New Hope for High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
Combining Hormone Therapy and Radiation Offers New Hope for High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
The findings are based on a detailed meta-analysis involving over 18,000 patients across eight clinical studies, making it one of the most comprehensive assessments of this treatment strategy to date.
ADT, often referred to as hormone therapy, works by reducing the levels of male hormones, or androgens, that fuel the growth of prostate cancer. It has long been a first-line treatment for men with advanced forms of the disease. However, its long-term effectiveness has remained questionable, especially for patients with locally advanced or node-positive cancers. In this
Medical News report, the researchers explored whether adding radiation therapy — a treatment that directly targets tumors — could offer improved chances of survival.
Significant Survival Advantages for Specific Patient Groups
The results are compelling. The combination of ADT and RT led to a 25 percent reduction in overall mortality risk, a nearly 60 percent decrease in cancer-specific deaths, and a dramatic 59 percent improvement in progression-free survival — the period during which the cancer does not worsen.
The benefits were especially noticeable in patients with locally advanced prostate cancer or those whose cancer had spread to nearby lymph nodes. These individuals showed an even more pronounced survival advantage, with a 34 percent reduction in death from any cause and a 57 percent drop in cancer-specific mortality.
Importantly, the researchers also examined whether patient characteristics such as baseline PSA levels and Gleason scores — both indicators of cancer severity — influenced outcomes. Patients with lower PSA levels and Gleason scores below eight appeared to benefit the most from the combination treatment.
Increased Complications a Tradeoff for Better Outcomes
While the survival benefits are promising, the combined therapy also comes with higher risks of complications. Patients undergoing both ADT and RT were nearly twice as likely to experience genitourinary issues like bladder problems or urinary frequency. Gastrointestinal complications such as diarrhea and rectal bleeding were four times more common. Moreover, sexual dysfunction — including erectile problems and reduced libido — was also slightly more prevalent.
The authors stress that despite these complications, the overall trade-off leans in favor of combination therapy, particularly for patients at high risk. However, they caution that treatment decisions should be tailored to individual patients, taking into account their overall health, age, and perso
nal preferences.
Why the Combination Therapy Works
The researchers believe that combining systemic androgen suppression with localized radiation may attack the cancer from two fronts. Hormone therapy weakens cancer cells by cutting off their hormonal fuel, while radiation delivers a localized hit to the tumor mass. Some evidence even suggests that ADT can make cancer cells more sensitive to radiation by changing their environment and making them more prone to cell death.
Conclusions and Future Directions
This landmark study strongly supports using ADT in combination with radiation therapy for patients with locally advanced or node-positive prostate cancer. While there is a tradeoff in terms of increased side effects, the improved survival rates make it a compelling option. Physicians should engage in thorough discussions with patients, balancing the survival benefits with quality-of-life considerations.
The study also highlights the need for further research to fine-tune treatment timing, explore which subgroups benefit most, and develop ways to reduce side effects. More precise and personalized treatment protocols could soon be on the horizon.
The study findings were published on a preprint server and are currently being peer reviewed.
https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-6206964/v1
For the latest on Prostate Cancer, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/heavy-metals-and-prostate-cancer-unveiling-a-new-connection
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/the-overlooked-role-of-fat-in-prostate-cancer
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/alcohol-and-prostate-cancer-risk
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/cancer
https://www.thailandmedical.news/pages/thailand_doctors_listings
