Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Oct 22, 2024 1 year, 3 months, 3 weeks, 4 days, 19 hours, 12 minutes ago
Medical News: In a breakthrough study, researchers from Aix-Marseille University, CNRS, in France, have uncovered new insights into how a protein, known as Complement C5a, plays a vital role in nerve regeneration after injury. This discovery could pave the way for future treatments for spinal cord injuries and other nerve-related damage.
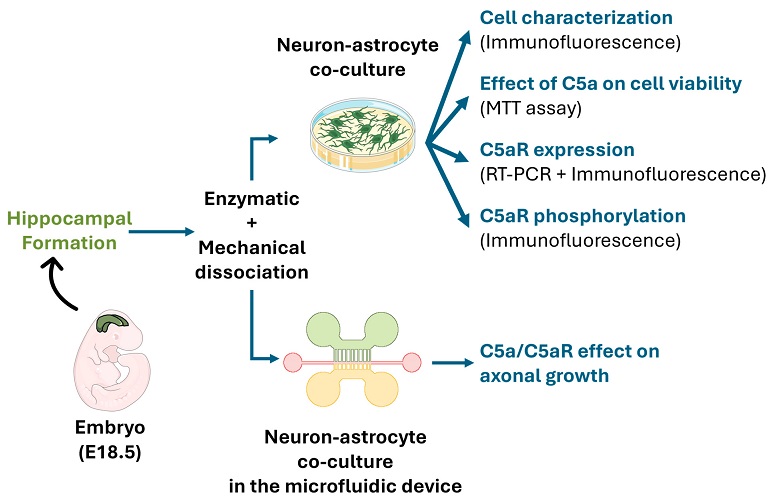 A schematic view of the experimental design. Cells were obtained from the hippocampal formation of rat embryos (E18.5) using enzymatic and mechanical dissociation methods. Neuron-astrocyte co-cultures were used to investigate C5aR expression/activation and the effect of C5a on cell viability. The microfluidic device was used to quantify the C5a effect on axonal growth.
A schematic view of the experimental design. Cells were obtained from the hippocampal formation of rat embryos (E18.5) using enzymatic and mechanical dissociation methods. Neuron-astrocyte co-cultures were used to investigate C5aR expression/activation and the effect of C5a on cell viability. The microfluidic device was used to quantify the C5a effect on axonal growth.
Complement C5a, a key component of the body’s immune system, has long been known for its role in triggering inflammation. However, researchers have found that it also has a unique ability to stimulate nerve growth, offering new hope for those suffering from central nervous system injuries, for which no effective treatment currently exists.
The Complement System and C5a
The Complement system, comprising over 35 proteins, is a crucial part of the body's immune response, helping to eliminate pathogens and repair tissues after injury. Complement C5a is a particularly potent protein in this system, known for its ability to increase blood vessel permeability and recruit immune cells to damaged areas. This
Medical News report sheds light on a new function of C5a in nerve repair, a finding that could revolutionize treatments for nerve injuries.
The Role of C5a in Axonal Growth
The research team focused on axonal growth - the process where nerve fibers, known as axons, regenerate after being damaged. Axons are crucial for transmitting signals in the nervous system, and their regrowth is essential for restoring function after nerve injuries.
The study demonstrated that applying C5a to injured nerve cells increased both the speed and length of axonal regrowth. This was done using a sophisticated 3D-printed microfluidic device, which allowed researchers to observe the effects of C5a on axonal growth in real-time.
The findings are particularly exciting because, to date, there has been no successful pharmacological treatment for regenerating damaged axons. The potential use of C5a as a therapeutic agent could open new doors for treating injuries of the central nervous system.
The Study: Axonal Regrowth in Detail
Researchers conducted experiments using primary cultures of hippocampal neurons isolated from embryonic Wistar rats. These neurons were placed in a specially designed microfluidic device that mimicked the environment of injured nerve cells. By introducing C5a into this system, they were able to observe its effects on nerve regeneration over a 48-hour period.
Results showed a significant increase in axonal growth, both in terms of length and speed, when C5a was applied. Without C5a, axonal growth was relatively slow, with an average speed
of around 13 micrometers per hour. However, with C5a, the speed of regrowth more than doubled, reaching approximately 35 micrometers per hour.
Moreover, the length of the regrown axons was also significantly longer in the presence of C5a. Researchers measured this growth by imaging the neurons and their extensions at multiple time points, noting a clear increase in growth compared to the control group that did not receive C5a.
Understanding C5a's Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which C5a stimulates axonal growth is related to its interaction with its receptor, C5aR, found on the surface of neurons. When C5a binds to this receptor, it triggers a series of intracellular processes that lead to the phosphorylation of the receptor. This phosphorylation is a signal that activates pathways within the cell that promote axonal growth.
Interestingly, when researchers introduced a C5aR inhibitor known as PMX53, the effects of C5a were blocked, and axonal growth returned to baseline levels. This indicates that the interaction between C5a and its receptor is essential for the observed increase in nerve regeneration.
These findings also suggest that targeting the C5a-C5aR pathway could be a viable strategy for developing new treatments for nerve injuries. However, further research is needed to fully understand how C5a works in more complex systems, such as the human body, where inflammation and immune responses are also at play.
Implications for Spinal Cord Injuries
One of the most significant potential applications of this research is in the treatment of spinal cord injuries. Currently, there are no effective treatments to repair the damage caused by such injuries, which often lead to permanent loss of function.
Previous studies have shown that C5a can have both beneficial and harmful effects, depending on the timing of its application. For example, administering C5a too soon after an injury can exacerbate inflammation, leading to worse outcomes. However, when given at the right time, it has been shown to improve nerve regrowth and functional recovery.
This new study reinforces the idea that C5a could be used to enhance recovery after spinal cord injury, but only if its use is carefully timed and controlled. Researchers are now planning further studies to explore how C5a could be delivered in a way that maximizes its benefits while minimizing any potential harmful effects.
Future Directions and Therapeutic Potential
While this study was conducted in vitro, using isolated neurons in a controlled environment, the results are encouraging for future research in living organisms. The next step for the research team will be to test C5a in animal models of nerve injury to determine whether the effects observed in the lab can be replicated in a more complex system.
If successful, this could lead to the development of new therapies for a range of conditions that involve nerve damage, including spinal cord injuries, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
In addition to its potential for treating nerve injuries, C5a may also have broader applications in tissue regeneration. Previous studies have shown that C5a can promote the healing of other tissues, including liver, muscle, and bone. By understanding how C5a works at the molecular level, researchers hope to unlock new ways to harness its regenerative potential for a variety of medical conditions.
Conclusion
The discovery that Complement C5a can enhance axonal growth after nerve injury offers a promising new avenue for research into treatments for central nervous system injuries. By targeting the C5a-C5aR pathway, it may be possible to develop therapies that help to regenerate damaged nerves and restore lost function in patients with spinal cord injuries and other neurodegenerative conditions.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Cells.
https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/13/20/1729
For the latest on Nerve Regeneration, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/new-hope-for-nerve-repair-breakthrough-in-axon-regeneration
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/new-hope-for-nerve-injury-recovery-combining-traditional-chinese-medicine-with-modern-biomaterials
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-a-new-approach-to-nerve-regeneration-utilizing-developmental-genes
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/medical-news-swiss-and-british-scientists-discover-that-axonal-regeneration-and-repair-is-regulated-by-the-circadian-clock
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/glaucoma-news-pou3f1-identified-as-a-regulator-of-contralateral-retinal-ganglion-cells-transcription-a-breakthrough-in-optic-nerve-regeneration
