Covid-19 Diagnostics: Adjusted CT Scoring Criteria For Faster Diagnosis And Treatment Of Covid-19 Disease
Source: Covid-19 Diagnostics Apr 02, 2020 5 years, 9 months, 3 weeks, 6 days, 6 hours, 53 minutes ago
Covid-19 Diagnostics: According to a new study by Chinese researchers from Wuhu Public Hospitals In Anhui, updated CT scan scoring criteria that considers lobe involvement, as well as changes in CT scan findings, could quantitatively and accurately evaluate the progression of theCovid-19 pneumonia.
https://www.ajronline.org/doi/10.2214/AJR.20.23078
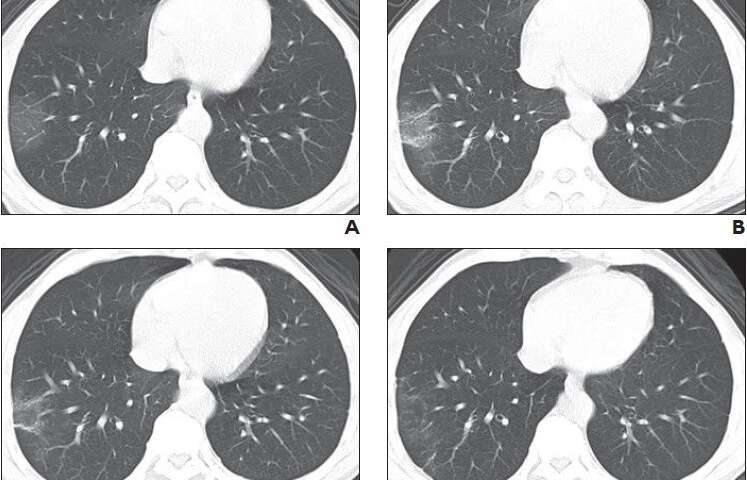 CT scoring criteria were applied to images from sequential chest CT examinations.A, Initial chest CT image obtained 2 days after onset of symptoms shows small region of subpleural ground-glass opacities in right lower lobe, for CT score of 1. B, Chest CT image obtained on day 3 of treatment shows slightly enlarged region of subpleural ground-glass opacities with partial crazy-paving pattern and consolidation, for CT score of 3. C, Chest CT image obtained on day 5 of treatment shows partial resolution of consolidation, for CT score of 2. D, Chest CT image obtained on day 14 of treatment shows continued resolution of consolidation with minimal residual ground-glass opacities, for CT score of 1. Credit: American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR)
CT scoring criteria were applied to images from sequential chest CT examinations.A, Initial chest CT image obtained 2 days after onset of symptoms shows small region of subpleural ground-glass opacities in right lower lobe, for CT score of 1. B, Chest CT image obtained on day 3 of treatment shows slightly enlarged region of subpleural ground-glass opacities with partial crazy-paving pattern and consolidation, for CT score of 3. C, Chest CT image obtained on day 5 of treatment shows partial resolution of consolidation, for CT score of 2. D, Chest CT image obtained on day 14 of treatment shows continued resolution of consolidation with minimal residual ground-glass opacities, for CT score of 1. Credit: American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR)
Lead author, Dr Guoquan Huang of Wuhu Second People's Hospital in China told Thailand Medical News, "The earlier that Covid-19 is diagnosed and treated, the shorter the time to disease resolution and the lower the highest and last CT scores are."
By assigning CT scores to 25 patients according to CT findings and lung involvement, Dr Huang and colleagues recorded the time from symptom onset to diagnosis and treatment for each patient.
The patients with Covid-19 were divided into two groups: (patients for whom this interval was less than 3 days) and group 2 (those for whom the interval was > 3 days).
Utilizing a Lorentzian line-shape curve to show the variation tendency during treatment, the fitted tendency curves for group 1 and group 2 were significantly different. Peak points showed that the estimated highest CT score was 10 and 16 for each group, respectively, and the time to disease resolution was 6 and 13 days, respectively.
The nonparametric Mann-Whitney test showed that the last CT scores were lower for group 1 than for group 2 (p = 0.025), although the chi-square test found no difference in age and sex between the groups. The time from symptom onset to diagnosis and treatment had a positive correlation with the time to disease resolution (r = 0.93; p = 0.000), as well as with the highest CT score (r = 0.83; p = 0.006).
Dr Huang explained, "Sequential chest CT examinations enable qualitative investigation of alterations in COVID-19 infection during the course of treatment."
As previously proposed CT scoring criteria regarding lobe involvement gave no consideration to changes in CT features (i.e., the change from observation of GGO to a crazy-paving pattern and then consolidation), Dr Huang suggest that such a rubric is not sufficiently accurate to assess the progression of pneumonia.
Dr Huang further added, "In the present study, we propose a new version of CT scoring criteria that considers both lobe involvement and changes in CT findings, in an attempt to more comprehensively evaluate C
OVID-19 pneumonia on sequential chest CT examinations."
For the latest developments on
Covid-19 Diagnostics, keep logging on to
Thailand Medical News.
PLEASE HELP. URGENT APPEAL: Please help support our site and our initiatives to propel and aid research by making a donation to help sustain the site. Donations are accepted via paypal:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/p/sponsorship
