COVID-19 Induces Hypertriglyceridemia That Prolongs Time To Death And Length Of Hospital Stay!
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Feb 24, 2024 1 year, 1 month, 3 weeks, 14 hours, 2 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: Since its emergence in late 2019, the COVID-19 pandemic has posed unprecedented challenges to global healthcare systems. Beyond its primary respiratory effects, the disease has demonstrated a propensity to affect multiple organ systems, leading to diverse clinical manifestations. Among these, hypertriglyceridemia, characterized by elevated levels of triglycerides in the bloodstream, has emerged as a notable complication, particularly in severe cases requiring intensive care unit (ICU) admission. This
COVID-19 News report delves into the intricate relationship between COVID-19 and hypertriglyceridemia, exploring its prevalence, clinical implications, underlying mechanisms, and treatment strategies.
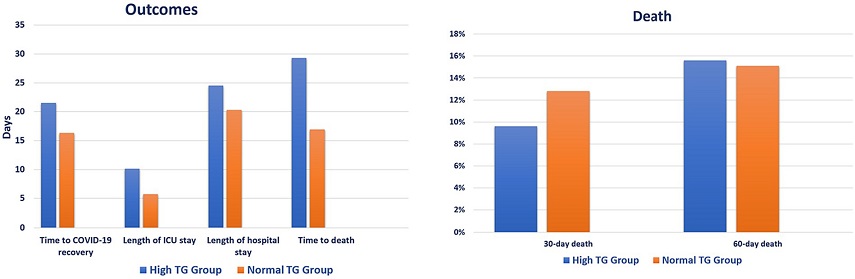 Clinical outcomes based on triglycerides levels. ICU, intensive care unit; TG, triglyceride.
Understanding the Landscape of COVID-19 and Hypertriglyceridemia
Clinical outcomes based on triglycerides levels. ICU, intensive care unit; TG, triglyceride.
Understanding the Landscape of COVID-19 and Hypertriglyceridemia
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, has inflicted significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. While the majority of cases present with mild respiratory symptoms, a subset of patients progresses to severe illness characterized by acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and multi-organ dysfunction. In this context, the association between COVID-19 and hypertriglyceridemia has garnered attention due to its potential impact on disease severity and clinical outcomes.
Epidemiological studies have revealed a high prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia among COVID-19 patients, particularly those admitted to ICUs. In Qatar, a retrospective observational cohort study conducted at various medical facilities including the Heart Hospital, Hamad Medical Corporation, Doha, Qatar, revealed that approximately 82.3% of ICU-admitted patients exhibited hypertriglyceridemia. These findings underscore the importance of understanding the clinical implications of elevated triglyceride levels in the context of COVID-19.
Clinical Implications and Impact on Patient Outcomes
The presence of hypertriglyceridemia in COVID-19 patients has been associated with a myriad of clinical implications, ranging from prolonged hospital stays to delayed recovery and, notably, a prolonged time to death. Patients with hypertriglyceridemia exhibited a significantly longer time to COVID-19 recovery, extended ICU, and hospital stays compared to their counterparts without hypertriglyceridemia. Despite the absence of a significant difference in mortality rates between the two groups, the prolonged time to death highlights the complex interplay between hypertriglyceridemia and disease progression in severe COVID-19 cases.
Furthermore, the impact of treating hypertriglyceridemia on clinical outcomes remains a topic of debate. While fibrates and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are traditional therapies for lowering triglyceride levels, their efficacy in improving COVID-19 outcomes is uncertain. A retrospective analysis revealed that treating hypertriglyceridemia did not translate into improved clinical outcomes, including mortality rates. These findings underscore the need for further research to elucidate the o
ptimal management strategies for hypertriglyceridemia in the context of COVID-19.
Exploring the Underlying Mechanisms
The underlying mechanisms driving COVID-19-induced hypertriglyceridemia are complex and multifactorial. Infection with SARS-CoV-2 triggers an immune response that disrupts lipid metabolism, leading to elevated triglyceride levels. Several factors contribute to this dysregulation, including increased secretion of very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) from the liver, decreased removal of VLDL and triglycerides, and alterations in inflammatory markers such as TNF-α.
Moreover, the severity of infection appears to correlate inversely with VLDL elimination, further exacerbating hypertriglyceridemia in critically ill patients. Inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6, play a pivotal role in lipid metabolism and contribute to the dysregulation observed in severe COVID-19 cases. Additionally, increased adipose tissue lipolysis and potential upregulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression further contribute to the hypertriglyceridemic state.
Treatment Strategies and Future Directions
The management of hypertriglyceridemia in COVID-19 patients poses unique challenges, necessitating tailored approaches to address both the underlying disease and its associated complications. While fibrates and omega-3 fatty acids remain cornerstone therapies for lowering triglyceride levels, their efficacy in improving COVID-19 outcomes requires further investigation.
Recent studies have suggested potential therapeutic avenues, including the use of fenofibrate, a fibrate, which has been shown to reduce SARS-CoV-2 infectivity in vitro. However, the clinical implications of fenofibrate therapy in COVID-19 patients warrant further exploration through randomized controlled trials.
Additionally, ongoing research is investigating the role of plasmapheresis in removing proinflammatory cytokines and toxins associated with hypertriglyceridemia in severe COVID-19 cases. Targeting lipid metabolism pathways may hold promise in mitigating disease severity and improving clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients with hypertriglyceridemia.
Conclusion
In conclusion, COVID-19-induced hypertriglyceridemia represents a complex interplay between viral infection, immune dysregulation, and altered lipid metabolism. While associated with prolonged hospital stays and delayed recovery, the impact of hypertriglyceridemia on mortality rates remains inconclusive. Treatment strategies aimed at lowering triglyceride levels have yet to demonstrate significant improvements in clinical outcomes.
Moving forward, a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms driving hypertriglyceridemia in COVID-19, coupled with innovative treatment approaches, is essential to optimize patient management and improve outcomes. Continued research efforts, including randomized controlled trials and mechanistic studies, will be critical in elucidating the pathophysiology of COVID-19-induced hypertriglyceridemia and informing evidence-based treatment strategies in the ongoing battle against the pandemic.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Frontiers in Medicine.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1326156/full
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
