COVID-19 Inhibits cytochrome P450 enzymes that metabolize drugs like antipsychotics, leading to higher blood levels
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jul 15, 2024 1 year, 3 months, 2 days, 6 hours ago
COVID-19 News: Surprising Rise in Antipsychotic Levels
A recent study reveals that COVID-19 infection can significantly increase antipsychotic drug concentrations in hospitalized patients with mental disorders. This
COVID-19 News report will delve into the details of this intriguing study and its implications for mental health care. Researchers from Beijing Anding Hospital, Zhangjiakou Shalingzi Hospital, Shunyi Women’s & Children’s Hospital, and Beijing HuiLongGuan Hospital in China conducted the study.
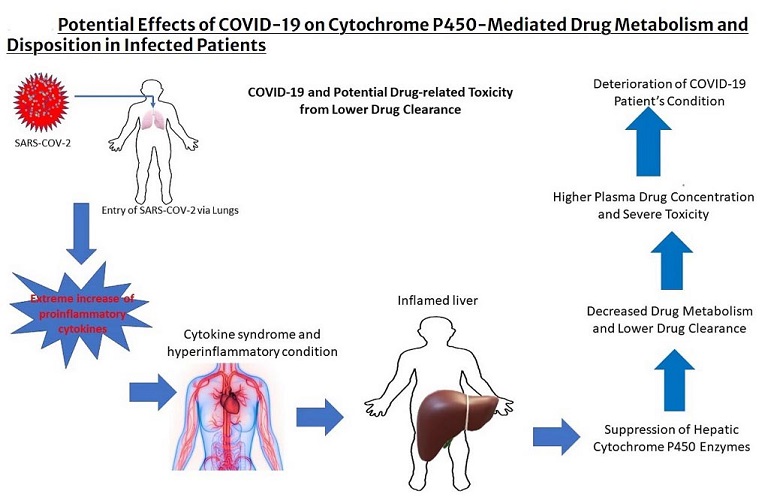 COVID-19 Inhibits cytochrome P450 enzymes that metabolize drugs like antipsychotics, leading to higher blood levels
The Study and Its Purpose
COVID-19 Inhibits cytochrome P450 enzymes that metabolize drugs like antipsychotics, leading to higher blood levels
The Study and Its Purpose
The primary aim of the study was to examine the changes in antipsychotic drug concentrations among patients with mental disorders who were hospitalized and later infected with COVID-19. The researchers sought to understand the factors influencing these changes and to offer recommendations for managing medication dosages during such infections.
Methodology
The study included data from inpatients at Beijing Huilongguan Hospital between December 12, 2022, and January 11, 2023. A total of 329 patients with mental disorders were considered, though three with incomplete data were excluded. The focus was on patients diagnosed with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and other mental disorders according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5).
Key Findings
-Increased Drug Concentrations: The study found significant increases in the concentrations of several antipsychotic drugs post-COVID-19 infection. These drugs included clozapine, aripiprazole, quetiapine, olanzapine, risperidone, and paliperidone.
-Clozapine Leads the Pack: Clozapine showed the highest increase in concentration post-infection, with a notable number of patients requiring dosage adjustments. Approximately 50.4% of clozapine users had to adjust their doses compared to 17.5% of olanzapine users and fewer for other antipsychotics. Clozapine metabolism is heavily mediated by the cytochrome CYP1A2 enzyme, which is inhibited during inflammation.
-Influence of Traditional Medicines and Antibiotics: The use of traditional Chinese patent medicines and antibiotics during COVID-19 was associated with reductions or withdrawal of antipsychotic drugs, highlighting the interaction between these treatments and antipsychotic drug levels.
Why the Increase?
The increase in drug concentrations is believed to be related not only to the COVID-19 infection itself but also to the use of traditional Chinese medicines during treatment. Inflammation caused by COVID-19 can inhibit the cytochrome P450 enzymes responsible for metabolizing these drugs, leading to higher blood levels.
Thailand Medical News
had previously warned that doctors, pharmacists and the medical community need to conduct more urgent studies on how COVID-19 is affecting the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of many existing drugs and pharmaceuticals based on the findings of a past study that showed that COVID-19 affects cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP34A)-mediated drug metabolism and drug interactions.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-a-must-for-all-doctors-to-read-scientists-warn-that-covid-19-affects-cytochrome-p450-3a4-mediated-drug-metabolism-and-drug-interactions
For all we know, the existing dosage recommendations of certain drugs could be currently be killing patients!
Factors Affecting Drug Levels
The study identified several factors influencing the increased drug levels:
-Pre-Infection Drug Levels: Patients with higher baseline drug levels were more likely to see a significant increase post-infection.
-Type of Antipsychotic: Different drugs showed varying degrees of concentration increases.
-Gender: Males were more likely to need dose adjustments compared to females.
Concurrent Use of Traditional Medicines: These medicines, commonly used during COVID-19 treatment, were linked to higher drug levels.
Implications for Treatment
Given these findings, the study suggests that health care providers need to closely monitor antipsychotic drug levels in patients with mental disorders who contract COVID-19. Adjustments to medication dosages should be made cautiously, taking into account the type of antipsychotic and the patient’s pre-infection drug levels.
Conclusion
The study highlights a critical area of concern for mental health care during the ongoing pandemic. The significant increase in antipsychotic drug levels post-COVID-19 infection necessitates vigilant monitoring and potential dose adjustments to prevent adverse effects.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Frontiers in Psychiatry.
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/molnupiravir--what-wrong-with-america-why-is-the-american-government-and-agencies-funding-and-pushing-potentially-toxic-drugs-to-treat-covid-19
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/common-medications-that-can-harm-your-kidneys
