Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Feb 18, 2024 1 year, 10 months, 1 week, 5 days, 1 hour, 29 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, has had a profound impact on global health systems, necessitating swift and coordinated responses to mitigate its spread and impact. Amidst the multifaceted strategies employed, vaccination has emerged as a pivotal tool in controlling the transmission and severity of the disease. However, as the global vaccination effort progresses, emerging reports have highlighted a potential association between COVID-19 mRNA vaccines and the development of new-onset acute interstitial nephritis (AIN), adding a layer of complexity to the clinical landscape. In this
COVID-19 News report, we delve into the clinical manifestations, immunological mechanisms, treatment modalities, and long-term implications of AIN post-SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 vaccination based on a study by researchers from Department of Nephrology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Jiangxi, China.
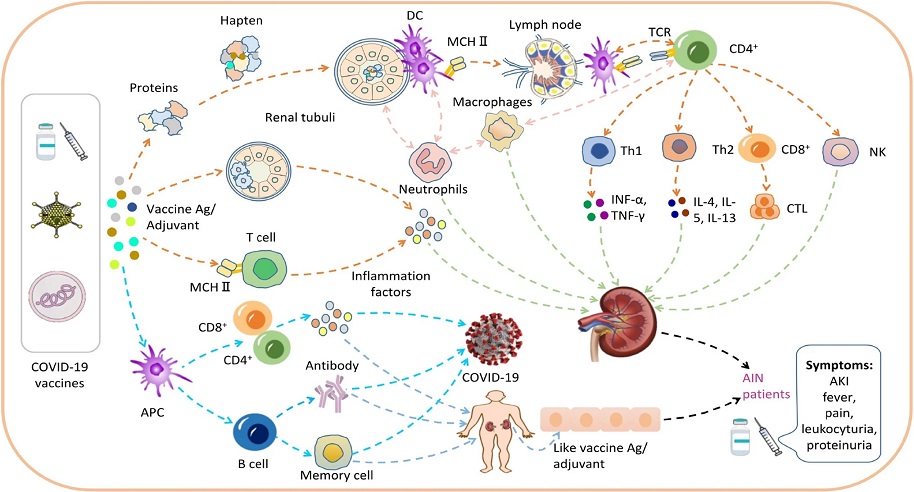 New-Onset Acute Interstitial Nephritis After COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines.
The assumed mechanisms of AIN post COVID-19 vaccination. Hypothesis of AIN caused by COVID-19 vaccination. Haptens: The vaccine may bind to proteins to form protein complexes called "hapten", which are recognized and presented by DCs, causing a subsequent T-cell-mediated toxic response, as well as activation of intrinsic immune cells in the renal stroma, and further amplification of the inflammatory response by crosstalk between different immune cells. P-i concept: some specific structures of the vaccine may stimulate T cells, thus allowing binding to the major histocompatibility peptide complexes and causing inflammatory factor production. Direct injury: vaccines and their products may cause direct renal tubular injury. Molecular mimicry: some structures of vaccines or adjuvants may be homologous to human proteins, and exposure to vaccines triggers antigenic epitopes of cross-reactive antibodies and thus disrupts immune tolerance.
New-Onset Acute Interstitial Nephritis After COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines.
The assumed mechanisms of AIN post COVID-19 vaccination. Hypothesis of AIN caused by COVID-19 vaccination. Haptens: The vaccine may bind to proteins to form protein complexes called "hapten", which are recognized and presented by DCs, causing a subsequent T-cell-mediated toxic response, as well as activation of intrinsic immune cells in the renal stroma, and further amplification of the inflammatory response by crosstalk between different immune cells. P-i concept: some specific structures of the vaccine may stimulate T cells, thus allowing binding to the major histocompatibility peptide complexes and causing inflammatory factor production. Direct injury: vaccines and their products may cause direct renal tubular injury. Molecular mimicry: some structures of vaccines or adjuvants may be homologous to human proteins, and exposure to vaccines triggers antigenic epitopes of cross-reactive antibodies and thus disrupts immune tolerance.
Acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) is a kidney lesion that typically causes a decline in kidney function and is characterized by an inflammatory infiltrate in the kidney interstitium. If not treated and if the condition progresses, it can cause kidney damage and lead to kidney failure without treatment.
A number of cases reports and studies have already validated the new-onset of acute interstitial nephritis after the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
https://www.revistanefrologia.com/en-a-case-acute-interstitial-nephritis-articulo-S2013251423000081
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/21645515.2022.2059308
https://www.tandfonline.com/do
i/full/10.2147/IJNRD.S345898
https://ecevr.org/DOIx.php?id=10.7774/cevr.2024.13.1.68
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40620-022-01519-2
https://academic.oup.com/ckj/article/15/1/174/6377315
https://search.bvsalud.org/global-literature-on-novel-coronavirus-2019-ncov/resource/zh/covidwho-1854257
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/internalmedicine/62/16/62_1631-23/_article/-char/ja/
https://www.cureus.com/articles/224971-a-case-of-combination-of-iga-nephropathy-and-interstitial-nephritis-after-covid-19-vaccination#!/
https://www.mdpi.com/2076-393X/10/11/1783
https://journals.lww.com/ijcm/fulltext/2023/48020/renal_complications_following_covid_19.3.aspx
https://europepmc.org/article/pmc/8899450
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2451993623000774
https://karger.com/ajn/article/53/4/325/827394/New-Onset-Biopsy-Proven-Nephropathies-after-COVID
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2468024921014480
https://casereports.bmj.com/content/15/5/e246841
https://www.dustri.com/article_response_page.html?artId=189190&doi=10.5414/CN110753&L=0
https://utsouthwestern.elsevierpure.com/en/publications/late-onset-granulomatous-interstitial-nephritis-after-booster-dos
A past coverage by Thailand
Medical News also shows that that the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines can also cause IgA Nephropathy and kidney failures!
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-news-gene-study-reveals-how-covid-19-mrna-vaccine-leads-to-high-risk-of-iga-nephropathy-eventual-kidney-failure-and-possible-cancers
Clinical Evidence of AIN Post-SARS-CoV-2 Infection
A retrospective analysis of 22 cases of AIN following SARS-CoV-2 infection unveils intriguing insights into the demographic and clinical profiles of affected individuals. Notably, the median age of patients was 15 years, with a notable predominance of male representation. Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis (TINU) were observed in 45.5% of cases, further complicating the clinical picture. The median onset of AIN post-infection was 14.5 days, highlighting the acute nature of renal involvement. While the majority of patients responded favorably to treatment modalities, a solitary case progressed to chronic kidney disease, underscoring the potential long-term sequelae of AIN.
Baseline Demographics and Clinical Characteristics of Patients with AIN Post-COVID-19 Vaccination
Exploring 36 cases of AIN subsequent to COVID-19 vaccination provides valuable insights into the diverse clinical presentations and vaccine-specific associations. The demographic distribution reveals a predominance of patients of European descent, with a spectrum of mRNA vaccines implicated, including BNT162b2 (Pfizer), mRNA-1273 (Moderna), AstraZeneca, and Sinovac. Clinical manifestations encompassed AKI, proteinuria, hematuria, and leukocyturia, with varying degrees of severity. Follow-up assessments indicated a generally positive response to treatment, albeit with a subset of severe cases resulting in mortality, highlighting the importance of vigilant monitoring and prompt intervention.
Immunological Mechanisms of AIN Induced by COVID-19 Vaccination
In-depth exploration of the immunological underpinnings of AIN post-COVID-19 vaccination unveils a complex interplay between vaccine components and host immune responses. Central to this paradigm is the formation of haptens, wherein vaccines conjugate with proteins, triggering dendritic cell activation and subsequent immune cascade activation culminating in AIN. Noteworthy is the potential role of vaccine constituents, such as polyethylene glycol, in eliciting hypersensitivity-like reactions, underscoring the need for heightened awareness of AIN as an allergic response to vaccines.
AIN and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Unraveling Viral-Induced Mechanisms
The intricate relationship between SARS-CoV-2 infection and AIN is elucidated through an exploration of viral-induced mechanisms. Evidence suggesting the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in renal tissue, coupled with monocyte cell infiltration, underscores the plausibility of viral-induced renal pathology. Furthermore, hypotheses regarding molecular mimicry mechanisms, wherein viral antigens trigger cross-reactive antibodies, offer insights into the potential immunological basis of AIN post-SARS-CoV-2 infection, necessitating further investigation to unravel the complexities of viral-induced renal injury.
Treatment Modalities and Prognosis
Timely diagnosis and intervention are paramount in the effective management of AIN post-SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 vaccination. Steroid therapy emerges as a cornerstone in the treatment armamentarium, with a majority of patients demonstrating favorable responses. However, a subset of severe cases underscores the importance of vigilant monitoring and individualized therapeutic approaches. Long-term prognosis remains a subject of ongoing exploration, necessitating comprehensive follow-up assessments to delineate the trajectory of renal function and potential sequelae of AIN.
Conclusion
In conclusion, AIN post-SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 vaccination present multifaceted clinical scenarios, underscoring the intricate interplay between viral pathogens, vaccine constituents, and host immune responses. This extensive exploration sheds light on the demographic, clinical, and immunological nuances of AIN, offering valuable insights into the pathogenesis, treatment modalities, and long-term implications of renal complications in the context of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. As vaccination efforts continue to evolve, a nuanced understanding of AIN is imperative for informed decision-making and optimal patient care in the realm of nephrology and beyond.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed Journal of Epidemiology and Global Health.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s44197-023-00159-4
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
