COVID-19 News: Groundbreaking Taiwanese Research Suggests Phytochemicals From Antrodia Cinnamomea As A Promising Solution For COVID-19
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Oct 27, 2023 1 year, 5 months, 3 weeks, 3 days, 15 hours, 24 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: In the ongoing battle against the global COVID-19 pandemic, a recent study conducted in Taiwan has unveiled a groundbreaking discovery. The research explores the potential of a phytochemical compound known as Dehydrosulphurenic Acid, derived from the medicinal fungus Antrodia Cinnamomea (AC), in aiding the fight against COVID-19. The findings from this study, conducted by a collaborative team of researchers from Taipei City Hospital, National Ilan University, ALPS Biotech Co. Ltd, China Medical University Hospital, and China Medical University, offer a glimpse of hope in the quest for effective COVID-19 treatments and prevention.
As the world grapples with widespread transmission of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), several challenges have emerged. Concerns about vaccine side effects, diminishing vaccine efficacy over time, and vaccine hesitancy rooted in religious beliefs have underscored the need for alternative pharmacological approaches. The study covered in this
COVID-19 News report, therefore, delves into the impact of the ethanol extract of Antrodia Cinnamomea on COVID-19, examining both in vitro and in vivo aspects to understand the potential of this native Taiwanese medicinal fungus.
The Role of ACE2 in COVID-19
At the heart of this research lies the significance of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a crucial host receptor for the spike protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which is responsible for causing COVID-19. It's widely known that the initial step in SARS-CoV-2 infection involves the binding of the viral spike protein to ACE2. Importantly, studies have demonstrated that individuals with underlying health conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, or chronic obstructive lung disease tend to exhibit significantly elevated levels of ACE2 expression in their lung tissues. This heightened ACE2 expression is believed to contribute to the severity of COVID-19 in patients with these comorbidities.
Moreover, patients with heart failure have shown increased ACE2 expression within myocardial tissues, making them more susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection in the heart, which can lead to severe complications. These findings suggest that reducing ACE2 expression might decrease an individual's susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and improve disease outcomes. However, it's crucial to strike a balance when modulating ACE2, as complete blockade may lead to unintended adverse effects, including increased inflammation and cardiovascular damage.
The Quest for Effective COVID-19 Therapies
In the fight against COVID-19, vaccines have taken center stage as the primary strategy. Researchers and pharmaceutical companies have invested extensive efforts in developing effective SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. However, challenges have emerged, including concerns about vaccine side effects, declining efficacy over time, and vaccine hesitancy driven by religious beliefs. These challenges have underscored the need for additional therapeutic or preventive measures.
One promising approach in the search for effective COVID-19 treatments involves the repurposing of FDA-approved drugs. These repurposed drugs can expedite
the availability of medications and reduce costs. Notably, drugs such as Teriflunomide, initially approved for multiple sclerosis; Forodesine, effective against T-cell malignancies; and Didanosine, used in managing HIV/AIDS, have shown potential in combating SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
In addition to repurposed drugs, synthetic compounds and natural products have come under scrutiny for their potential in countering SARS-CoV-2. Some natural compounds, like Cordycepin and compounds found in pineapple and ginger, have shown promise against SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the virus's RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Furthermore, the protein-protein interaction between ACE2 and the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, as well as the targeting of ACE2 using small molecules, has gained traction as novel approaches to reduce SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Antrodia Cinnamomea: A Natural Solution
Antrodia Cinnamomea, also known as Taiwanofungus camphoratus, is a unique medicinal mushroom that thrives exclusively within the inner recesses of the native tree species Cinnamomum kanehirae Hayata. This indigenous Taiwanese fungus has a rich history in ethnomedicine and has been utilized for various health benefits, including immune modulation, liver protection, neuroprotection, anticancer properties, anti-inflammatory effects, and assistance in managing diabetes. One of the key bioactive components found in AC is a group of well-defined ergostane-type triterpenoids known as antcins. These antcins have demonstrated promise in reducing ACE2 expression in epithelial cells, suggesting a potential therapeutic role in the context of COVID-19.
Another phytochemical found in Antrodia Cinnamomea called Dehydrosulphurenic Acid or DA was also found to possess unique properties to aid in preventing and treating COVID-19.
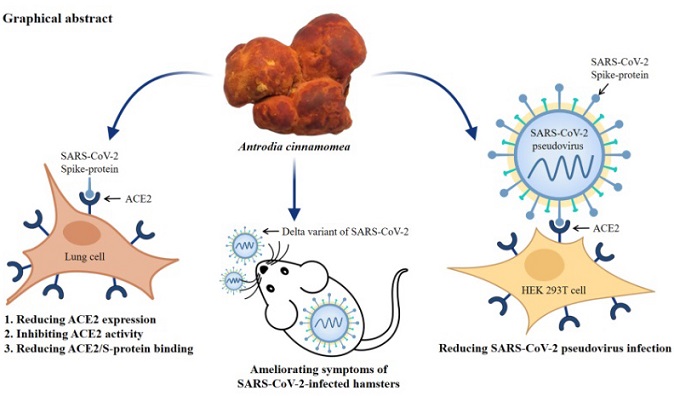
The research study conducted by the collaborative team delved deeper into the therapeutic and preventive potential of the ethanol extract from Antrodia Cinnamomea (AC) and its pure compounds. The investigation encompassed several critical aspects, including the impact of AC on ACE2 expression in human lung cells, the interaction between ACE2 and the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, in vitro experiments involving SARS-CoV-2 pseudotyped lentivirus infection, and in vivo assessments using a SARS-CoV-2-infected hamster model.
Promising Results
The results from this comprehensive study revealed several key findings:
-AC Reduces ACE2 Expression: AC effectively decreased ACE2 mRNA and protein levels in human lung cells, which are critical host receptors for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
-DA Inhibits ACE2 Protease Activity: Dehydrosulphurenic acid (DA), an isolate from AC, directly inhibited ACE2 protease activity, indicating its potential as a therapeutic agent.
-
AC and DA Reduce SARS-CoV-2 Infections: In vitro experiments demonstrated that both AC and dehydrosulphurenic acid significantly reduced the infection rate of SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus.
-AC Mitigates Lung Injury: In hamsters infected with the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2, oral administration of AC reduced body weight loss and improved lung injury.
-Reduction in IL-1β Expression: AC also inhibited IL-1β expression in both macrophages and the lung tissues of SARS-CoV-2-infected hamsters.
-Potential Nutraceutical: The research suggests that AC could serve as a nutraceutical for reducing the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection by disrupting the interaction between ACE2 and the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, as well as for preventing COVID-19-associated lung inflammation.
Discussion
The search for effective COVID-19 treatments and preventive measures has led researchers to explore various avenues, including targeting specific viral proteins, inhibiting viral replication, and modulating the immune response. While numerous compounds have shown promise as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, only a few have demonstrated effectiveness in vivo. The study highlights the importance of exploring natural products like Antrodia Cinnamomea as potential solutions for COVID-19.
A. cinnamomea stands out as a valuable medicinal fungus with a history of use in traditional medicine. Its anti-inflammatory properties have gained recognition, making it a potential candidate for mitigating the cytokine storms associated with severe COVID-19. The research found that AC significantly inhibited the NLRP3 inflammasome, which is responsible for the release of proinflammatory cytokines like IL-1β. This suggests that AC has the potential to reduce the severity of COVID-19 by modulating the body's cytokine response.
Conclusion
The findings from this study are nothing short of remarkable. Antrodia Cinnamomea, a native Taiwanese medicinal fungus, has shown significant promise in the context of COVID-19. By reducing ACE2 expression and interfering with the interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and ACE2-expressing lung cells, AC has the potential to reduce SARS-CoV-2 infections without causing severe adverse effects associated with complete ACE2 blockade.
Moreover, AC's ability to mitigate lung injuries and reduce inflammation in COVID-19 patients provides hope for the development of effective treatments and preventive measures. As the world continues to combat the COVID-19 pandemic, the research conducted by this collaborative team sheds light on the potential of Antrodia Cinnamomea as a functional food or nutritional supplement in the future. Such utilization could enhance the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines and reduce the risk of severe disease among patients. While further research is needed to explore the full extent of AC's capabilities and its efficacy against different SARS-CoV-2 variants, these findings offer a glimpse of optimism in the ongoing fight against the global pandemic.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Cureus.
https://www.dovepress.com/antrodia-cinnamomea-may-interfere-with-the-interaction-between-ace2-an-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-JIR
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Check Out Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/covid-19-herbs
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/covid-19-supplements
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/covid19-drugs
