COVID-19 News: Indonesian Researchers Uncover Biosurfactant Potential And Antiviral Activity Of Multistrain Probiotics Against SARS-CoV-2!
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 25, 2023 1 year, 4 months, 3 weeks, 6 days, 16 hours, 29 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, continues to present unprecedented challenges to global health. As the scientific community races to find effective treatments, a team of researchers at the Faculty of Biotechnology, University of Surabaya in Indonesia, has embarked on a groundbreaking study to investigate the biosurfactant potential and antiviral activity of multistrain probiotics against SARS-CoV-2. In the face of evolving viral variants and the need for safe and orally administered medications, this research covered in this
COVID-19 News report represents a significant step forward in the quest for innovative COVID-19 treatments.
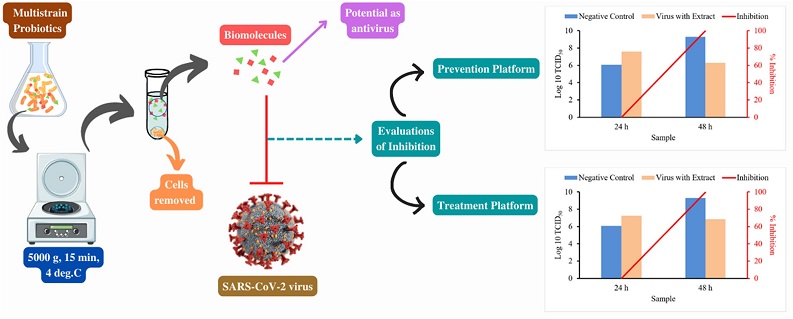 Graphical abstract
Current Treatment Landscape and Challenges
Graphical abstract
Current Treatment Landscape and Challenges
The available treatments for COVID-19, including remdesivir and molnupiravir, have limitations and potential side effects. The World Health Organization has highlighted the absence of a universally accepted and safe oral medication for COVID-19 treatment, emphasizing the urgency of finding effective solutions. Intravenous administration of existing medications further complicates the treatment landscape, prompting researchers to explore alternative avenues.
Biosurfactant Potential of Multistrain Probiotics
The research team focused on leveraging the biosurfactant potential of multistrain probiotics, specifically targeting Lactobacillus spp. and Rhodopseudomonas palustris. These probiotics are known for their beneficial properties, and the researchers hypothesized that their biosurfactant activity could be harnessed to disrupt the lipid membrane of the virus, rendering it inactive and preventing infection. Biosurfactants, with detergent-like properties, have the unique ability to safely dissolve lipids, making them suitable for in vivo use.
Probiotics Extract Evaluation Methods
To comprehensively assess the biosurfactant potential activity of the multistrain probiotics extract, the researchers employed three distinct evaluation methods: oil spreading, drop collapse, and emulsification. These techniques provided nuanced insights into the interaction between the probiotics extract and lipid membranes, shedding light on the extract's ability to exhibit biosurfactant activity effectively.
Discussion on Probiotics and Biosurfactants
Probiotics, such as Lactobacillus spp. and R. palustris, have long been recognized for their ability to regulate immune responses. In this study, the researchers explored the symbiotic relationship between these microorganisms, aiming to en
hance the production of metabolites, including biosurfactants. The biosurfactant activity of these compounds can potentially interact with the lipid membranes of pathogens, presenting a novel avenue for antiviral therapy with low cytotoxicity.
Evaluation of Cytotoxicity
Ensuring the safety of the probiotics extract, the researchers conducted meticulous cytotoxicity evaluations on Vero E6 cells. These evaluations revealed that concentrations of 20% and 16.6% v/v were non-toxic, paving the way for further exploration of the extract's safety profile and potential therapeutic applications.
In vitro Antiviral Activity Against SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant
The researchers utilized the SARS-CoV-2 delta variant as a model for their antiviral experiments, reflecting the virus's ongoing evolution. In both prevention and treatment platforms, the probiotics extract demonstrated remarkable antiviral activity. Within 48 hours, the extract inhibited virus growth by an impressive 99.9% in the prevention platform and 99.6% in the treatment platform. These findings underscore the potential of the multistrain probiotics extract as a potent antiviral agent against SARS-CoV-2.
Implications and Future Directions
The discovery of the biosurfactant potential and antiviral activity of multistrain probiotics against SARS-CoV-2 opens new horizons in the search for effective COVID-19 treatments. However, the researchers emphasize the need for further studies, including extensive clinical trials and long-term investigations, to assess the extract's safety, efficacy, and potential resistance development in human COVID-19 treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the research conducted at the University of Surabaya, represents a significant advancement in the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic. The biosurfactant potential and antiviral activity of multistrain probiotics, particularly Lactobacillus spp. and R. palustris, offer a promising avenue for the development of safe and effective antiviral agents. As the world grapples with the ongoing challenges posed by SARS-CoV-2, this breakthrough research brings hope for a new class of oral medications that could revolutionize the treatment landscape and contribute to the global effort to overcome the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Heliyon.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405844023100454
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
