COVID-19 News: SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Forms Intracellular Aggregates, Inhibiting IFNγ-Induced Antiviral Gene Expression In Lung Epithelial Cells
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 09, 2023 2 years, 1 month, 3 weeks, 5 days, 15 hours, 57 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: The relentless march of the global COVID-19 pandemic has prompted researchers to delve into the intricacies of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) to better understand the mechanisms behind the significant lung tissue damage observed in COVID-19 patients. A recent study covered in this
COVID-19 News report which was conducted by researchers from the Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago-USA, Northwestern University, University of Chicago-USA, and Jesse Brown Veterans Affairs Medical Center-USA sheds light on the elusive role of the open reading frame 8 (ORF8) protein of SARS-CoV-2.
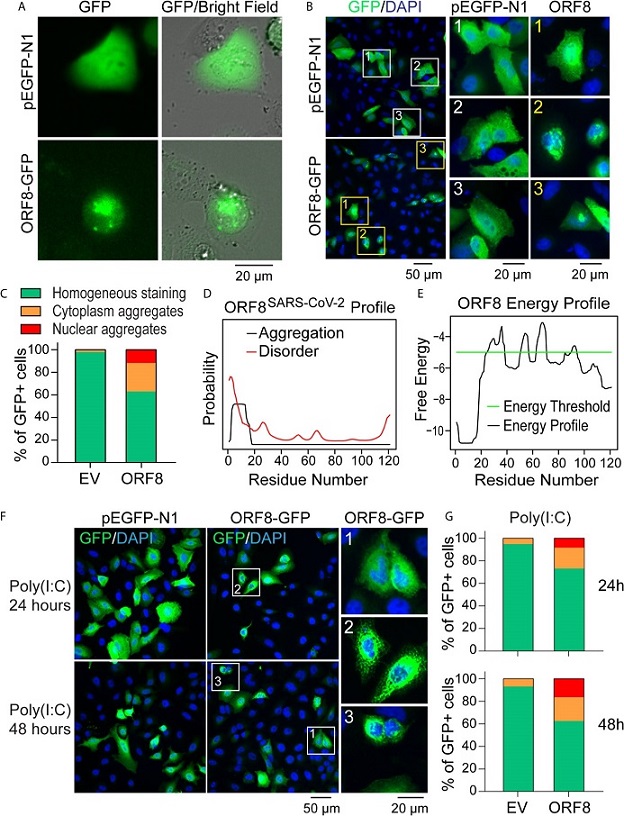 ORF8SARS-CoV-2 forms intracellular aggregates in human lung epithelial cells. (A-C) Aggregation of ORF8SARS-CoV-2 protein in A549 cells viewed by fluorescent microscopy. Human lung epithelial A549 cells were transfected with pEGFP-N1 (empty vector; EV) or pEGFP-ORF8SARS-CoV-2. After 24 h, fluorescent microscopy was performed on either live cells (A) or paraformaldehyde-fixed cells that were stained with anti-GFP antibody (B). In the anti-GFP antibody-stained cells, quantitative analysis of nuclear-cytoplasmic distribution pattern of aggregated ORF8SARS-CoV-2 was performed (C). (D, E) Prediction of aggregation based on the ORF8SARS-CoV-2 protein primary structure using the PASTA 2.0 algorithm (https://protein.bio.unipd.it/pasta2/). Aggregation disorder profile (D) and aggregation-free energy profile (E) showing that N-terminal residues 1-18 have the lowest aggregation free energy and thus is the most aggregation-stabilizing region underlying the propensity for ORF8SARS-CoV-2 aggregates formation. (F, G) The intracellular distribution pattern of ORF8SARS-CoV-2 aggregates is not affected by a poly (I:C)-induced inflammatory response. A549 cells were treated with poly (I:C) during transfection with pEGFP-N1 (EV) or pEGFP-ORF8SARS-CoV-2. After the indicated times, cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde followed by immunofluorescent staining with anti-GFP antibody. The stained cells were viewed by fluorescent microscopy (F) and processed for analysis of nuclear-cytoplasmic distribution pattern of ORF8SARS-CoV-2 aggregates (G). 1 indicates homogenous distribution; 2, cytoplasmic aggregates; and 3, nuclear aggregates.
The Puzzle of Lung Injury
ORF8SARS-CoV-2 forms intracellular aggregates in human lung epithelial cells. (A-C) Aggregation of ORF8SARS-CoV-2 protein in A549 cells viewed by fluorescent microscopy. Human lung epithelial A549 cells were transfected with pEGFP-N1 (empty vector; EV) or pEGFP-ORF8SARS-CoV-2. After 24 h, fluorescent microscopy was performed on either live cells (A) or paraformaldehyde-fixed cells that were stained with anti-GFP antibody (B). In the anti-GFP antibody-stained cells, quantitative analysis of nuclear-cytoplasmic distribution pattern of aggregated ORF8SARS-CoV-2 was performed (C). (D, E) Prediction of aggregation based on the ORF8SARS-CoV-2 protein primary structure using the PASTA 2.0 algorithm (https://protein.bio.unipd.it/pasta2/). Aggregation disorder profile (D) and aggregation-free energy profile (E) showing that N-terminal residues 1-18 have the lowest aggregation free energy and thus is the most aggregation-stabilizing region underlying the propensity for ORF8SARS-CoV-2 aggregates formation. (F, G) The intracellular distribution pattern of ORF8SARS-CoV-2 aggregates is not affected by a poly (I:C)-induced inflammatory response. A549 cells were treated with poly (I:C) during transfection with pEGFP-N1 (EV) or pEGFP-ORF8SARS-CoV-2. After the indicated times, cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde followed by immunofluorescent staining with anti-GFP antibody. The stained cells were viewed by fluorescent microscopy (F) and processed for analysis of nuclear-cytoplasmic distribution pattern of ORF8SARS-CoV-2 aggregates (G). 1 indicates homogenous distribution; 2, cytoplasmic aggregates; and 3, nuclear aggregates.
The Puzzle of Lung Injury
While SARS-CoV-2 infects epithelial cells and macrophages in the lungs, leading to severe inflammation and alveolar damage, the molecular mechanisms causing lung injury remain unclear. Accessory proteins encoded in the CoV genome have been shown to disrupt host signaling pathways and cell function. The study focuses on ORF8SARS-CoV-2, a unique accessory protein with little-known cellular functions.
Unveiling ORF8SARS-CoV-2's Cellular Activities
The researchers conducted a comprehensive investigation into the cellular distribution and function of ORF8SARS-CoV-2 in human lung epithelial cells. Through live imaging and immunofluorescent staining analyses, they discovered that ectopically expressed ORF8SARS-CoV-2 forms aggregates in the cytosol and nuclear compartments of lung epithelial cells.
Bioinformatic analysis revealed an intrinsic aggrega
tion characteristic in the N-terminal residues 1-18 of ORF8SARS-CoV-2. Strikingly, these aggregates did not impact lung epithelial cell proliferation and cell cycle progression. However, the study found that ORF8SARS-CoV-2 significantly inhibited the baseline expression of various antiviral molecules, including DHX58, ZBP1, MX1, and MX2.
Interplay with the Immune Response
Moreover, the researchers observed that the expression of ORF8SARS-CoV-2 attenuated the induction of antiviral molecules by interferon-gamma (IFNγ) but not interferon-beta (IFNβ) in lung epithelial cells. This suggests that ORF8SARS-CoV-2's unique characteristics may enable the virus to evade the host antiviral innate immune response during early infection.
Looking Ahead: Implications for COVID-19 Patients
The study proposes an intriguing question: Do COVID-19 patients exhibit persistent ORF8SARS-CoV-2 expression after recovering from the infection? If so, the pathogenic effects of prolonged ORF8SARS-CoV-2 expression and its potential association with post-COVID symptoms warrant further investigation.
Unraveling the Mysteries of ORF8SARS-CoV-2
The findings of this study shed light on the biological and immunobiological effects of the SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 accessory protein in lung epithelial cells. The N-terminal sequence of ORF8SARS-CoV-2 was identified as favoring the formation of protein aggregates, which were observed in both cytoplasmic and nuclear compartments of lung epithelial cells.
Contrary to expectations, the aggregates did not exert cytotoxic effects on the cells. This challenges the conventional understanding that intracellular protein aggregates during viral infections are necessarily detrimental. Instead, the study suggests that ORF8SARS-CoV-2 aggregates may play a role in evading cellular degradation machinery or promoting viral functions without inducing cellular stress responses.
Impact on Antiviral Immunity
The study found that ORF8SARS-CoV-2 selectively attenuated the basal expression of key antiviral molecules in lung epithelial cells, potentially compromising the host's ability to sense and respond to viral infections. Notably, the expression of ORF8SARS-CoV-2 hindered IFNγ-mediated antiviral gene expression, suggesting a targeted interference with the host's immune response.
The Complexity of ORF8SARS-CoV-2's Actions
While the exact mechanisms underlying the formation of ORF8SARS-CoV-2 aggregates remain unclear, the study highlights the importance of specific residues in ORF proteins in driving the aggregation process. The intricate interplay between ORF8SARS-CoV-2 and the host immune response, especially the disruption of IFNγ-induced antiviral immunity, adds complexity to our understanding of the pathogenic roles of SARS-CoV-2 accessory proteins.
Implications for Future Research and Therapeutics
The study calls for further research into the molecular mechanisms behind ORF8SARS-CoV-2's actions, aiming to elucidate its role in COVID-19 pathogenesis fully. The potential persistence of ORF8SARS-CoV-2 expression in recovered COVID-19 patients opens avenues for investigating its association with long-haul COVID-19 symptoms.
In conclusion, the Chicago study significantly advances our understanding of the elusive ORF8SARS-CoV-2 and its impact on lung epithelial cells. The intricate dance between this viral accessory protein and the host's immune response adds another layer of complexity to the ongoing battle against the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Frontiers in Immunology.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.679482/full
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-news-scientist-from-india-find-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-possesses-complement-inhibitory-properties
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/u-s-study-reveals-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-triggers-inflammatory-response-in-immune-cells-through-myd88-independently-of-the-il-17-receptor
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/unique-sites-of-immune-regulation-discovered-in-sars-cov-2-orf8
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-sublineages-lacking-orf8-protein-do-not-replicate-in-upper-respiratory-tract,-reducing-transmission-but-increasing-inflammation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/study-finds-orf8-protein-of-sars-cov-2-induces-endoplasmic-reticulum-stress-like-responses-and-facilitates-virus-replication-by-triggering-calnexin
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-study-discovers-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-exhibits-complement-inhibitory-properties-and-damages-innate-immunity
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-yale-study-shows-that-omicron-subvariants-are-evolving-further-through-mutations-on-orf8-proteins-to-escape-from-mhc-i-recognition
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-french-scientists-uncover-how-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-causes-dysregulation-of-gene-expression-in-infected-cells
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/mayo-clinic-researchers-discover-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-protein-is-the-key-factor-that-is-causing-covid-19-disease-severity
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-study-discovers-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-encoded-protein-contains-a-histone-mimic-that-disrupts-human-host-cell-epigenetic-regulation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-research-university-of-california-scientist-identify-rapidly-evolving-immune-evasion-protein-sars-cov-2-orf8-
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-research-briefs-anti-androgens-and-covid-19,-possible-cytotoxic-t-cell-therapy-for-covid-19,-immune-evasion-by-evolving-orf8-protein-in-sars-
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-accessory-proteins-orf6,-orf8,-orf9b,-orf9c-have-the-ability-to-trigger-inflammatory-and-profibrotic-processes-through-il11-signaling
