COVID-19 News: Study Shows That COVID-19 Patients With Myocardial Injury Had Elevated IL6 Expression And Decreased Lymphocyte Counts
COVID-19 News - Myocardial Injury - Elevated IL6 Expression - Decreased Lymphocyte Counts Jul 29, 2023 1 year, 8 months, 6 days, 11 hours, 12 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: Since the emergence of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 in late 2019, the world has been grappling with the devastating impact of COVID-19. Among its numerous complications, myocardial injury has emerged as a serious concern, contributing to adverse outcomes and increased mortality rates.
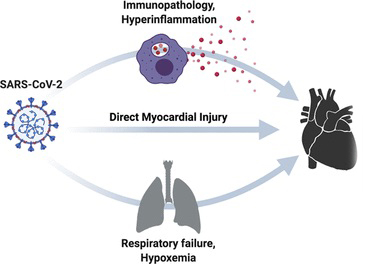
Myocardial injury in COVID-19 patients presents a complex scenario involving excessive immune inflammation, cellular hypoxia, and compromised functional contractility of the heart. Researchers from The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University and the Key Laboratory of Integrative Chinese and Western Medicine for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Circulatory Diseases of Zhejiang Province in China embarked on a mission to identify key regulatory molecules responsible for myocardial injury in COVID-19 patients. Their study aimed to shed light on the underlying mechanisms, ultimately paving the way for improved treatment strategies and enhanced patient prognoses.
The Complexity of Myocardial Injury in COVID-19
SARS-CoV-2 infection causes not only respiratory distress but also myocardial injury, with approximately 12-41% of COVID-19 patients experiencing this complication. Myocardial injury is an independent risk factor for mortality, making it crucial to unravel its mechanisms for timely intervention.
Previous studies and
COVID-19 News reports have pointed to various mechanisms contributing to myocardial injury, such as inflammatory activation and immune cell infiltration.
Cardiomyocytes infected with SARS-CoV-2 exhibit defensive responses involving excessive immune inflammation, leading to cell hypoxia and functional impairment. Post-mortem examinations of deceased COVID-19 patients have shown that infective myocardial injury results from local inflammation with interstitial edema.
Identifying Key Regulatory Molecules
To identify crucial regulatory molecules and pathways responsible for myocardial injury in COVID-19, the researchers employed cutting-edge bioinformatics tools and data analysis. The team conducted Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) on COVID-19 datasets, revealing the interleukin signaling pathway and GPCR ligand binding pathway as common disordered pathways associated with myocardial injury. Further analysis led to the identification of seven key genes (IL6, NFKBIA, CSF1, CXCL1, IL1R1, SOCS3, and CASP1) related to the interleukin pathway, signifying its central role in myocardial injury.
The Involvement of Inflammation-Related Pathways
The comprehensive analysis also highlighted the involvement of multiple inflammation-related pathways in myocardial injury caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection. These pathways included cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, TNF signaling pathway, JAK-STAT signaling pathway, and NF-κB signaling pathway. The NF-κB signaling pathway, known for its role in inflammation regulation, appeared to significantly impact the inflammatory state of COVID-19 patients. Furthermore, IL6 emerged as a critical pro-inflammatory cytokine controlling the proliferation, survival, and orientation of T cells, and its elevated expression was found to be ass
ociated with severe COVID-19 cases.
Clinical Verification and Immune Cell Imbalance
To verify the findings, the researchers analyzed clinical samples from COVID-19 patients. Through hierarchical clustering of the seven key genes, patients with myocardial injury could be distinguished from those without. Immune cell analysis revealed imbalances in the proportions of B cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and NK cells in COVID-19 patients with myocardial injury. These results reinforced the notion that myocardial injury was closely linked to altered immune cell proportions and aberrant interleukin pathways.
The Role of Interleukin 6 (IL6)
As a pro-inflammatory cytokine, IL6 plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection-related myocardial injury. Its levels were found to be significantly elevated in COVID-19 patients with myocardial injury, indicating its involvement in the inflammatory response. Monitoring IL6 levels could serve as an important biomarker for identifying severe COVID-19 cases, and inhibiting its expression might offer potential therapeutic benefits.
Conclusion
The study findings have shed new light on the complex mechanisms underlying myocardial injury in COVID-19 patients. By identifying key regulatory molecules and pathways, such as the interleukin signaling pathway and IL6, this research paves the way for targeted treatment strategies and enhanced prognoses for COVID-19 patients with myocardial injury. The findings emphasize the critical role of inflammation in myocardial injury and highlight the importance of closely monitoring immune cell imbalances and cytokine levels in COVID-19 patients.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Frontiers In Immunology.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1190644/full
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
