COVID-19 News: Study Shows That Phytochemicals From Humulus Lupulus (Common Hop) Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Papain-Like Protease And Virus Replication
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Oct 31, 2023 1 year, 5 months, 2 weeks, 1 day, 6 hours, 2 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: In the wake of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, the global scientific community has been fervently searching for innovative treatments and preventative measures. As vaccination campaigns continue, new SARS-CoV-2 variants with potential immune evasion properties continue to emerge, highlighting the critical need for effective antiviral therapies. In this context, researchers from the University of Hohenheim in Germany, in collaboration with scientists from the University Hospital Tübingen, the University of Freiburg, Dermatologie zum Delfin in Switzerland, and Leiden University Medical Centre in the Netherlands, have unveiled a groundbreaking study. Their research which is covered in this
COVID-19 News report, reveals the remarkable antiviral properties of phytochemicals found in the Humulus lupulus plant, commonly known as hops. The study specifically investigates the effect of these phytochemicals on SARS-CoV-2, focusing on their inhibition of the papain-like protease (PLpro) and virus replication.
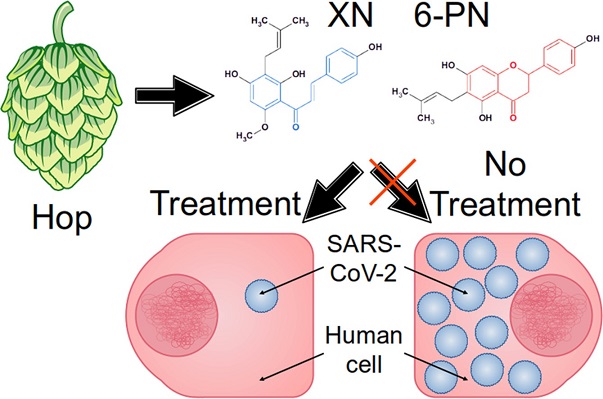 Graphical Abstract
Thailand Medical
Graphical Abstract
Thailand Medical News had also covered a past study in 2021 by Chinese researchers that also showed phytochemicals from Hops had broad spectrum antiviral effectiveness against various coronaviruses including SARS-CoV-2.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-the-phytochemical-xanthohumol-extracted-from-hops-flowers-is-a-potent-broad-spectrum-antiviral-against-most-coronaviruses-including-sars-cov-
Background and Significance
The global COVID-19 pandemic has affected nearly 700 million people, resulting in the tragic loss of approximately seven million lives. Despite extensive vaccination efforts and prior infections, there remains a pressing need for novel antiviral treatments, particularly as immunity against the virus often proves transient. Among the key drug targets for SARS-CoV-2, the main protease (Mpro) and the papain-like protease (PLpro) have been identified as essential components in the viral replication process.
While protease inhibitors like nirmatrelvir and ritonavir have shown promise, their use can lead to severe side effects due to their potent inhibition of CYP3A4. Therefore, alternative therapeutic options are actively sought. PLpro is of particular interest, as it not only aids in viral maturation but also interferes with the ho
st's innate immune system, effectively hindering the antiviral response.
Study Objectives and Methodology
The primary aim of this study was to investigate the impact of specific hop-derived compounds, including xanthohumol (XN), isoxanthohumol (IXN), 6-prenylnaringenin (6-PN), and 8-prenylnaringenin (8-PN), on SARS-CoV-2 PLpro. The research employed a two-fold approach: in silico modeling to predict the binding affinity of these compounds to PLpro and in vitro experiments to validate these predictions. Furthermore, the study sought to ascertain the effects of these hop compounds on the replication of SARS-CoV-2 within host cells.
In Silico Analysis and Binding Affinity
The study's in silico analysis used computational modeling to predict the binding affinity of hop compounds to the active site of SARS-CoV-2 PLpro. The findings suggested that these phytochemicals effectively block PLpro's active site, preventing its interaction with natural substrates.
In Vitro Findings
Following the promising in silico results, the research team conducted in vitro experiments to validate the inhibitory effects of hop-derived compounds on SARS-CoV-2 PLpro. The results were striking, with these phytochemicals demonstrating a potent ability to inhibit PLpro activity, with half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values ranging from 59 to 162 µM.
Antiviral Activity
Crucially, the study extended its investigations to the impact of hop compounds on the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in host cells. The findings revealed that XN and 6-PN, in particular, exhibited remarkable antiviral activity, with IC50 values of 3.3 µM and 7.3 µM, respectively.
Implications and Future Research
The study's outcomes are significant as they expand our understanding of the potential of hop-derived compounds in combating SARS-CoV-2. While XN had previously been recognized as an inhibitor of Mpro, this research sheds new light on its ability to target PLpro, an exciting therapeutic target due to its role in both viral replication and immune system modulation.
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to evolve, the development of novel antiviral drugs remains a top priority. Hop-derived compounds, with their demonstrated inhibitory effects on both Mpro and PLpro, offer promising avenues for drug development and the mitigation of viral diseases. The widespread availability of these compounds in hop-related products further underscores their potential in the fight against COVID-19.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this groundbreaking study conducted by a collaborative team of researchers across Europe unveils the potent antiviral properties of hop-derived phytochemicals, particularly xanthohumol (XN) and 6-prenylnaringenin (6-PN). These compounds exhibit the ability to inhibit the papain-like protease (PLpro) of SARS-CoV-2, thereby hindering viral replication. The implications of this research are profound, suggesting that hop-derived compounds may hold the key to developing effective antiviral drugs against human coronaviruses, particularly in the face of the ever-evolving COVID-19 pandemic. Further investigations and clinical trials are warranted to harness the full potential of these natural compounds in the fight against SARS-CoV-2.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Phytomedicine.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0944711323005354
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep o logging to Thailand Medical News.
