COVID-19 Supplements: Cleveland Clinic Study Highlights Efficacy Of Melatonin To Help Treat COVID-19
Source: COVID-19 Supplements Nov 10, 2020 5 years, 2 months, 3 weeks, 4 days, 5 hours, 55 minutes ago
COVID-19 Supplements: Researchers from Cleveland Clinic in a new study have found that melatonin, a hormone that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and is commonly used as an over-the-counter sleep aid, may be a viable treatment option for COVID-19.
.jpg)
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: PLOS Biology.
https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3000970
Most Western doctors who initially despised Eastern approaches to treating COVID-19 by using supplements, herbs and cheap generic repurposed drugs are now turning back to them after discovering the drug scams perpetrated by large American and European pharmaceutical and biotech companies and also by the Trump administration, Dr Anthony Fauci and private clandestine business groups lead by individuals like Tom Cahill.
Currently all the extremely expensive U.S. FDA and NIH touted drugs like remdesivir, tocilizumab and certain antibody treatments have all failed to treat COVID-19 despite all the efforts by the perpetrators to buy unethical researchers and create manipulated studies and also paid coverage in certain leading medical journals.
When Thailand Medical News published an article about melatonin as a possible adjuvant to treat COVID-19 in early May this year, numerous American media, so called American and European science writers and American social media platforms termed us as fake news and misinformation despite having a lot of scientific data to back our claims.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-supplements-melatonin-helps-lessen-severity-risk-in-covid-19-patients-by-preventing-cytokine-storms
Hopefully many of these garbage and their loved ones have perished in this COVID-19 pandemic in a painful manner as they are threat to the lives of millions. (Shocking? As a privately owned and Eastern based medical news website we do not need to be politically correct and hypocritical like most Western media, if you do not like our site, please leave and follow your Western medical sites and become one the fatality figures eventually!) It is also interesting to note that it is currently America and many European countries that are worse hit by the COVID-19 pandemic and many of their citizens are sadly dying despite the so called claims of medical prowess of these countries. Their U.S. FDA approved remdesivir, tocilizumab and certain antibody treatments are not are helping to reduce the death rates in these countries so far or even help prevent the numbers of infected from increasing.
In this Cleveland Clinic led study, a novel artificial intelligence platform developed by Lerner Research Institute researchers to identify possible drugs for COVID-19 repurposing has revealed melatonin as a promising candidate.
Detailed analysis of patient data from Cleveland Clinic's COVID-19 registry also revealed that melatonin usage was associated with a nearly 30 percent reduced likelihood of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) after adjusting for age, race, smoking history and various disease comorbi
dities. Notably, the reduced likelihood of testing positive for the virus increased from 30 to 52 percent for African Americans when adjusted for the same variables.
The study team further explored drug–disease outcome relationships for melatonin using a large-scale COVID-19 patient registry database. They found that among individuals who received testing for SARS-CoV-2, melatonin usage was associated with a 28% and 52% reduced likelihood of a positive laboratory test result for SARS-CoV-2 in the all combined population and black Americans , respectively, after adjusting for age, sex, race, smoking, and various disease comorbidities. Using user active comparator design, they further found that melatonin usage was associated with a reduced likelihood of a positive laboratory test result for SARS-CoV-2 compared to use of ARBs and ACEIs as well. Exogenous melatonin may be of benefit in older patients with COVID-19, given the aging-related reduction of endogenous melatonin and the greater vulnerability of older individuals to mortality from SARS-CoV-2 , the latter potentially due to declining immunity, i.e., immunosenescence . Moreover, melatonin suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation induced by cigarette smoking and attenuates pulmonary inflammation, not only via reduction of NF-κB p65 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) expression, but also via increase in anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 or IL-6, which can also have anti-inflammatory effects. Thus, large-scale observational studies and randomized controlled trials are needed to validate the clinical benefit of melatonin for patients with COVID-19. It would be important, however, that the trials be designed with the understanding of the mechanism of the drug to be repurposed. For example, it would be obvious that drugs that decrease viral entry, e.g., part of melatonin’s action, would be beneficial in preventing infection or very early in the COVID-19 course, but may be inconsequential when utilized in severe or end-stage infection. Several randomized controlled trials are being performed to test the clinical benefits of melatonin in patients with COVID-19 (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04409522 and NCT04353128). In addition, the Selective Estrogen Modulation and Melatonin in Early COVID-19 (SENTINEL) trial is underway to test the combination therapy of melatonin with toremifene (an approved selective estrogen receptor modulator) for patients with early and mild COVID-19 (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04531748).
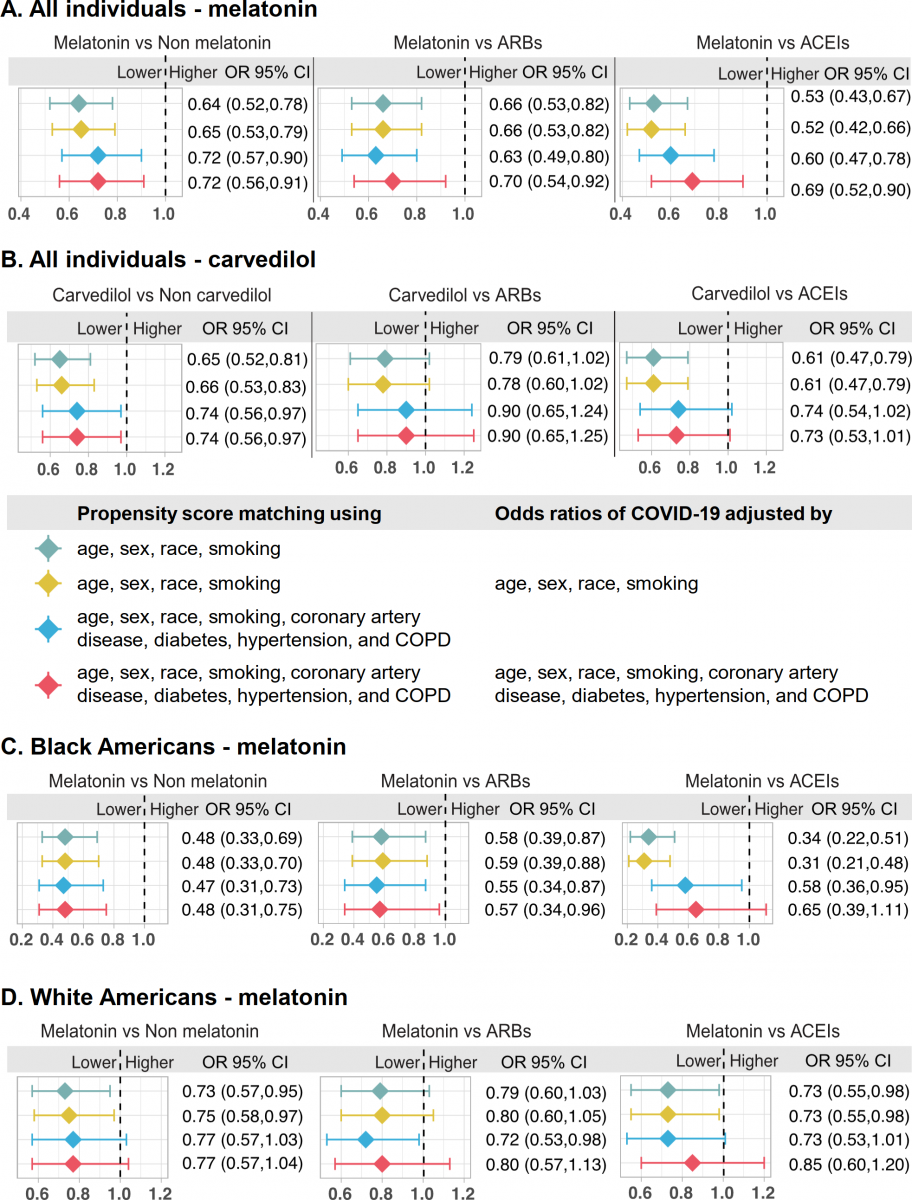
Patient-based validation of drug repurposing for COVID-19.Validation for (A) melatonin and (B) carvedilol using the whole COVID-19 registry (all combined population). Validation for melatonin (C) in the black American (African American) subgroup and (D) in the white American subgroup. Patient groups were matched using propensity score matching. Four models were evaluated: (1) model 1 was matched using age, sex, race, and smoking without adjustment for the odds ratio; (2) model 2 was matched using age, sex, race, and smoking, and the odds ratio of COVID-19 was adjusted by age, sex, race, and smoking; (3) model 3 was matched using age, sex, race, smoking, coronary artery disease, diabetes, hypertension, and COPD without adjustment for the odds ratio; and (4) model 4 was matched using age, sex, race, smoking, coronary artery disease, diabetes, hypertension, and COPD, and the odds ratio of COVID-19 was adjusted by age, sex, race, smoking, coronary artery disease, diabetes, hypertension, and COPD. These models were adjusted for different variables using the propensity score matching approach (see Materials and Methods—Patient data validation of the network-identified drugs using a COVID-19 registry). ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; OR, odds ratio
Dr Feixiong Cheng, Ph.D., assistant staff in Cleveland Clinic's Genomic Medicine Institute and lead author on the study told Thailand Medical News, "It is very important to note these study findings do not suggest individuals should start to take melatonin without consulting their physician. Large-scale observational studies and randomized controlled trials are critical to validate the clinical benefit of melatonin for patients with COVID-19, but we are excited about the associations put forth in this study and the opportunity to further explore them."
The study team harnessed network medicine methodologies and large-scale electronic health records from Cleveland Clinic patients to identify clinical manifestations and pathologies common between COVID-19 and other diseases.
Most importantly, they measured the proximity between host genes/proteins and those well-associated with 64 other diseases across several disease categories (malignant cancer and autoimmune, cardiovascular, metabolic, neurological and pulmonary diseases), where closer proximity indicates a higher likelihood of pathological associations between the diseases.
The study team found, for example, that proteins associated with respiratory distress syndrome and sepsis, two main causes of death in patients with severe COVID-19, were highly connected with multiple SARS-CoV-2 proteins.
Dr Cheng explained, "This signals to us, then that a drug already approved to treat these respiratory conditions may have some utility in also treating COVID-19 by acting on those shared biological targets."
The study team determined that autoimmune (e.g., inflammatory bowel disease), pulmonary (e.g., chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pulmonary fibrosis) and neurological (e.g., depression and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder) diseases showed significant network proximity to SARS-CoV-2 genes/proteins and identified 34 drugs as repurposing candidates, melatonin chief among them.
Dr Cheng further added, "Recent studies suggest that COVID-19 is a systematic disease impacting multiple cell types, tissues and organs, so knowledge of the complex interplays between the virus and other diseases is key to understanding COVID-19-related complications and identifying repurposable drugs. Our study provides a powerful, integrative network medicine strategy to predict disease manifestations associated with COVID-19 and facilitate the search for an effective treatment."
The study team concluded that melatonin was the most ideal drug candidate out of list of 34 identified drug candidates and suggest that more detailed research and randomized trials be conducted.
For more on
COVID-19 Supplements, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
.jpg)