Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Feb 10, 2025 2 months, 3 days, 7 hours, 26 minutes ago
Medical News: A Closer Look at the Role of MicroRNAs in Heart Disease
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is one of the most common inherited heart diseases, affecting millions of people worldwide. This condition is characterized by an abnormal thickening of the heart muscle, which can interfere with normal blood flow and lead to complications such as arrhythmias and heart failure. Researchers have been investigating the molecular mechanisms behind HCM, and recent studies have highlighted the role of tiny genetic molecules known as microRNAs (miRNAs), which are carried by exosomes - small extracellular vesicles that transport genetic material between cells.
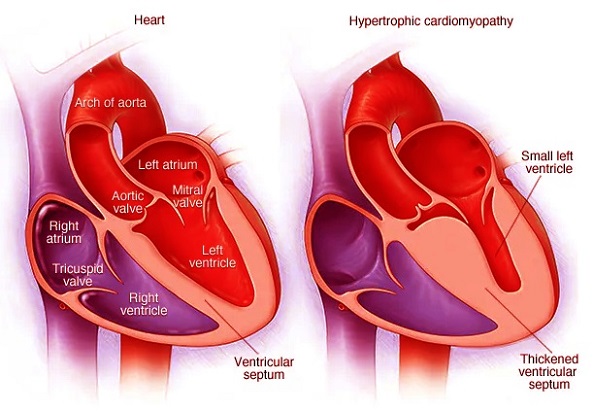 Exosome Derived MicroRNAs in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Exosome Derived MicroRNAs in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
This
Medical News report focuses on the findings of a study conducted by researchers from Jersey General Hospital-UK, who explored how exosome-derived microRNAs influence HCM. Their research sheds light on the potential of these molecules as diagnostic tools and therapeutic targets for managing the condition.
The Key Role of Exosome Derived MicroRNAs in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Exosomes are tiny vesicles secreted by different types of cells, including heart cells. They serve as messengers, carrying important biological molecules such as proteins, lipids, and microRNAs. In the context of HCM, exosome-derived microRNAs play a major role in regulating the cellular processes that contribute to heart muscle thickening.
The study identified several key miRNAs that are significantly altered in patients with HCM. Among the most notable were miR-1, miR-133, and miR-208. These microRNAs are involved in heart cell function, hypertrophy (excessive growth), and fibrosis (scarring of the heart tissue). The research found that in individuals with HCM, these microRNAs are often dysregulated, meaning their normal functions are disrupted, which contributes to the disease progression.
Potential for Diagnosing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
One of the most promising aspects of this research is the potential use of exosome-derived microRNAs as biomarkers for diagnosing HCM. Unlike traditional methods that rely on imaging techniques and genetic testing, detecting specific miRNA patterns in blood samples offers a minimally invasive and highly precise approach.
By analyzing blood samples from HCM patients, researchers found that the expression levels of certain exosomal miRNAs were consistently different from those in healthy individuals. For example, miR-1 and miR-133, which typically suppress excessive heart muscle growth, were found to be downregulated in HCM patients, while miR-208, which promotes hypertrophy, was significantly upregulated. These findings suggest that measuring these miRNA levels could serve as a reliable diagnostic tool.
New Avenues for Treatment
Beyond diagnosis, exosome-derived miRNAs could open new possibilities for treating HCM. Since these molecules directly influence heart muscle growth and remodeling, targeting them with therapies that restore their normal balance coul
d help slow or even reverse disease progression.
Several experimental treatments are currently being explored. One promising approach involves using synthetic molecules known as antagomirs to block the action of harmful miRNAs like miR-208. Another approach is the introduction of miRNA mimics to replenish beneficial miRNAs such as miR-1 and miR-133, potentially reducing heart muscle thickening and preventing fibrosis.
Additionally, researchers are exploring the possibility of engineering exosomes to deliver therapeutic miRNAs directly to heart cells. This targeted approach could enhance the effectiveness of treatment while minimizing side effects.
Conclusion
The growing understanding of exosome-derived microRNAs and their role in HCM represents a major step forward in the fight against this complex heart disease. The discovery that these molecules can serve as both biomarkers and therapeutic targets offers new hope for early diagnosis and more effective treatments. While further research is needed to translate these findings into clinical applications, the potential impact on patients' lives is significant. With continued advancements, miRNA-based therapies could revolutionize how HCM is diagnosed and managed, offering a more personalized and precise approach to treatment.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Cardiogenetics.
https://www.mdpi.com/2035-8148/14/4/19
For the latest on Exosomes, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breakthrough-research-on-exosomes-and-their-role-in-oral-cancer
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-study-finds-that-covid-19-accelerates-liver-cancer-growth-and-spread-via-exosomes-derived-from-syncytia
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/exosomes-and-their-role-in-cancer-progression-and-cancer-therapy
