Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Dec 20, 2024 3 months, 3 weeks, 4 days, 53 minutes ago
Medical News: Siglecs, or sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectins, are critical components in the immune system, playing a pivotal role in distinguishing "self" from "non-self." Found on the surface of immune cells, these glycan-binding proteins interact with complex carbohydrates called glycans, which are present on the cell surface. The intricate interaction between Siglecs and glycans helps modulate immune responses, preventing unnecessary attacks on healthy tissues and maintaining overall immune balance.
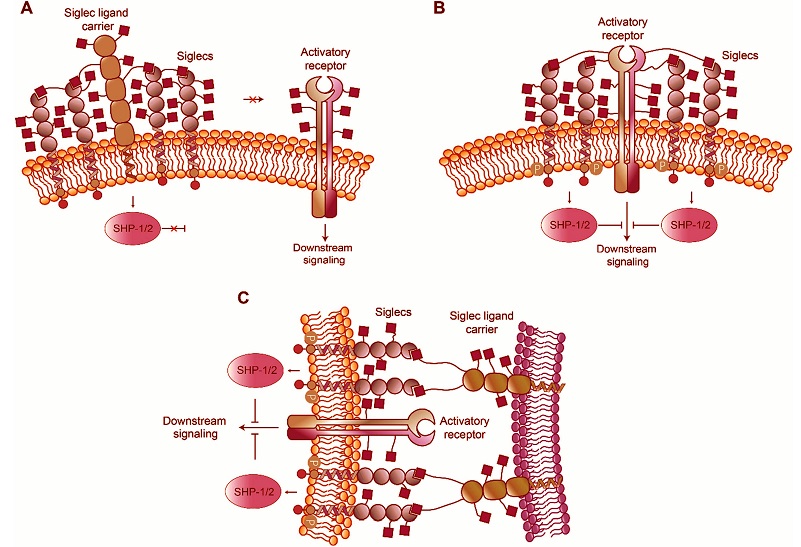 Exploring the Role of Siglecs in Immune Cell Regulation
Exploring the Role of Siglecs in Immune Cell Regulation
The University of Alberta in Canada has been at the forefront of research into Siglecs. Researchers from the Departments of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Chemistry, and the Neuroscience and Mental Health Institute have delved into the complexities of these molecules. Their work highlights the importance of Siglec-glycan interactions in regulating both the innate and adaptive arms of the immune system.
The Architecture of Siglecs
All Siglecs share a similar structure, comprising a V-set domain responsible for recognizing sialic acids, a variable number of C2-set domains that dictate their distance from the cell surface, and a cytoplasmic tail containing signaling motifs. These motifs can either inhibit or activate immune responses depending on the specific Siglec and its associated ligands.
Interestingly, Siglecs can interact with ligands either on the same cell (cis interactions) or on different cells (trans interactions). This
Medical News report explores how these interactions influence immune cell behavior, particularly in the context of health and disease.
Adaptive Immunity and Siglecs
B cells, essential players in adaptive immunity, express Siglecs like CD22 and Siglec-G/10. These molecules help maintain immune tolerance by preventing overactivation of B cells, which could lead to autoimmune conditions. For example, CD22 clusters on the B cell surface, binding to sialic acid-containing glycans and modulating B cell receptor (BCR) signaling. This clustering mechanism is crucial for controlling the activation and differentiation of B cells into antibody-producing cells.
Studies have shown that disrupting CD22’s ability to bind glycans leads to hyperactive BCR signaling, emphasizing the importance of these interactions. Additionally, the shift from one type of sialic acid to another during B cell maturation - from Neu5Gc to Neu5Ac - illustrates how glycan remodeling can fine-tune immune responses.
Siglec-G/10, expressed on B cells and other immune cells, also plays a role in maintaining tolerance. Research indicates that these molecules inhibit calcium signaling in B cells, reducing the likelihood of autoimmunity. In experimental models, the absence of Siglec-G leads to an increased risk of diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), highlighting their protective role.
Innate Immunity and Siglecs
The innate immune system relies
on Siglecs to regulate the activity of cells like macrophages, neutrophils, and natural killer cells. For instance, Siglec-9, found on neutrophils and macrophages, helps dampen inflammatory responses. This is particularly relevant in conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), where excessive inflammation can exacerbate disease progression.
Siglec-8, predominantly expressed on eosinophils and mast cells, has garnered attention for its potential in treating allergic conditions. Targeting Siglec-8 with specific antibodies has been shown to reduce the activation of these cells, offering therapeutic promise for diseases like asthma and eosinophilic esophagitis. Clinical trials with anti-Siglec-8 antibodies have demonstrated significant reductions in eosinophil levels and inflammation, paving the way for new treatments.
Implications for Cancer and Autoimmune Diseases
Siglec expression patterns can change in the tumor microenvironment, where they often contribute to immune suppression. For example, Siglec-9 on T cells in tumors inhibits their ability to attack cancer cells, allowing tumors to evade the immune system. This finding has led researchers to explore ways to block Siglec-9 interactions, thereby enhancing anti-tumor immunity.
In autoimmune diseases like SLE and rheumatoid arthritis, alterations in Siglec expression or function can disrupt immune tolerance. Research has shown that mutations in Siglec genes or their ligands can exacerbate these conditions. Understanding these mechanisms is critical for developing targeted therapies to restore balance.
Therapeutic Potential and Future Directions
The therapeutic potential of Siglecs is vast. By targeting Siglec-ligand interactions, researchers aim to modulate immune responses in a range of diseases. For example, synthetic Siglec ligands have been designed to inhibit inflammation by mimicking natural interactions. These ligands have shown promise in preclinical studies, particularly in reducing macrophage activation and promoting the resolution of inflammation.
Nanoparticles and liposomes decorated with Siglec ligands represent another innovative approach. These particles can selectively deliver drugs or modulate immune cell activity by engaging Siglecs. In cancer immunotherapy, strategies to block inhibitory Siglecs or enhance their activation have shown potential in boosting the effectiveness of existing treatments.
Conclusion
The study of Siglecs and their interactions with glycans is shedding light on fundamental mechanisms that govern immune regulation. These molecules act as gatekeepers, balancing activation and inhibition to maintain health. Disruptions in Siglec function can lead to a host of diseases, from cancer to autoimmunity, underscoring their importance as therapeutic targets.
As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of Siglec-glycan interactions, new opportunities for intervention are emerging. Whether through synthetic ligands, targeted antibodies, or nanoparticle-based therapies, the potential to harness Siglecs for therapeutic benefit is immense.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Seminars in Immunology.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1044532324000630
For the latest on Siglecs, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/rbd-of-sars-cov-2-omicron-sub-lineages-targets-siglec-9-to-decrease-its-immunogenicity-by-preventing-macrophage-phagocytosis
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-study-finds-that-sars-cov-2-impairs-natural-killer-nk-cells-functions
