Expression Of IFI6, OAS1 And IRF9 Genes Was Associated With Lower Risk Of Mortality And Need For Mechanical Ventilation In COVID-19
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Apr 27, 2024 10 months, 5 days, 16 hours, 35 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: SARS-CoV-2 infections have unveiled a spectrum of clinical complexities influenced by various factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and genetic predispositions. A recent study, conducted by researchers from Universidad de La Laguna-Spain, Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias Ismael Cosío Villegas-Mexico, and Instituto de Salud Carlos III-Spain, that is covered in this
COVID-19 News report, delves into the differential expression of seven key genes - IRF9, CCL5, IFI6, TGFB1, IL1B, OAS1, and TFRC in COVID-19 patients with varying disease severities. Through a meticulous analysis using two-step RT-qPCR on whole-blood samples from 160 individuals, the study aims to unravel crucial insights into COVID-19 prognosis and potential biomarkers for improved diagnosis and treatment strategies.
 Expression Of IFI6, OAS1 And IRF9 Genes Was Associated With Lower Risk Of Mortality
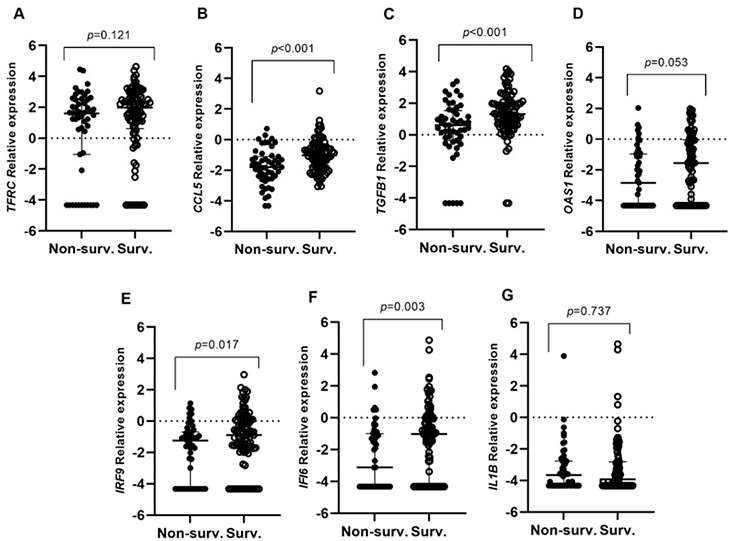
Differential gene expression among patients who underwent hospitalization in relation to survival (Surv vs. Non-surv.). Lines represent the median with an interquartile range (25th–75th pc). (A) TFRC, (B) CCL5, (C) TGFB1, (D) OAS1, (E) IRF9, (F) IFI6, and (G) IL1B. p-values < 0.05 were considered significant.
Factors Influencing COVID-19 Severity
Expression Of IFI6, OAS1 And IRF9 Genes Was Associated With Lower Risk Of Mortality
Differential gene expression among patients who underwent hospitalization in relation to survival (Surv vs. Non-surv.). Lines represent the median with an interquartile range (25th–75th pc). (A) TFRC, (B) CCL5, (C) TGFB1, (D) OAS1, (E) IRF9, (F) IFI6, and (G) IL1B. p-values < 0.05 were considered significant.
Factors Influencing COVID-19 Severity
COVID-19 severity hinges on a multitude of factors encompassing age, gender, and underlying health conditions. Advanced age, typically beyond 60 years, amplifies the risk of severe disease manifestation. Moreover, males exhibit higher rates of ICU admissions and mortality compared to females. Comorbidities like obesity, diabetes, and cardiorespiratory ailments further escalate the risk of developing acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in COVID-19 patients. However, despite these established risk factors, the precise phenotypic variability in SARS-CoV-2 infection remains inadequately understood, necessitating a deeper exploration into the genetic underpinnings of host susceptibility and disease outcomes.
The Role of Gene Expression in COVID-19 Prognosis
An in-depth analysis of gene expression related to antiviral activity and inflammatory responses emerges as a pivotal tool for prognosticating COVID-19 outcomes. Perturbations in gene expression have been correlated with unfavorable disease trajectories in respiratory viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2, with a notable emphasis on pathways involving interferons such as IRF9 and IFI6. Notably, previous studies have demonstrated the discriminatory potential of IFI6 expression in discerning infected individuals from healthy controls during respiratory viral infections.
Interferon-Stimulated Genes: Key Players in COVID-19
Of particular interest among the plethora of genes under scrutiny are interferon-stimulated genes known for their antiviral prowess. OAS1 and IRF9 have emerged as promising biomarkers for COVID-19 pr
ognosis, with in vitro studies hinting at IFI6's inhibitory effect on viral replication. These genes, intricately involved in host defense mechanisms, warrant comprehensive investigation to ascertain their translational relevance in combating SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Chemokines, Cytokines, and Immune Response
Chemokines like CCL5 and cytokines like IL-1β play pivotal roles in orchestrating immune responses during viral infections. While elevated levels of CCL5 have been associated with cytokine storms in severe COVID-19 cases, their nuanced interplay in patient survival necessitates meticulous scrutiny. Additionally, the immunomodulatory role of TGFB1 in COVID-19 pathogenesis, particularly concerning pulmonary fibrosis, underscores the intricate balance within the immune milieu during viral infections.
Study Design and Patient Characteristics
The study cohort comprised 160 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, predominantly male, with varying disease severities. Noteworthy differences in gene expression were observed concerning age, obesity status, and treatment modalities, shedding light on the nuanced interplay between clinical features and genetic signatures in dictating disease outcomes.
Key Findings and Clinical Implications
The study unearthed differential gene expression patterns, notably elevated levels of OAS1, IFI6, and IRF9 in moderate COVID-19 cases, correlating with reduced IMV requirements and enhanced survival rates. Conversely, heightened TGFB1 and CCL5 expression was associated with improved patient survival, underscoring the intricate balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses in mitigating COVID-19 severity.
Discussion: Unraveling Genetic Influences on COVID-19
The intricate interplay between genetic factors and COVID-19 severity underscores the need for a nuanced understanding of host-virus interactions. Noteworthy genes like IFI6, OAS1, IRF9, TGFB1, CCL5, IL1B, and TFRC offer valuable insights into disease prognosis and treatment paradigms, paving the way for tailored therapeutic interventions.
Limitations and Future Directions
Despite its illuminative findings, the study acknowledges certain limitations such as the diverse SARS-CoV-2 variants encompassed within the study period and the need for replication studies in independent cohorts to validate the findings. Future research endeavors should delve deeper into elucidating the genetic intricacies governing COVID-19 outcomes, thereby fostering precision medicine approaches for enhanced patient care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study underscores the pivotal role of gene expression profiling in unraveling the intricate web of factors governing COVID-19 severity and patient outcomes. Genes like IFI6, OAS1, IRF9, TGFB1, CCL5, IL1B, and TFRC emerge as potential biomarkers with translational implications for improved diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic interventions in COVID-19 management. As research in this domain evolves, a deeper comprehension of host genetic factors promises to revolutionize our approach towards mitigating the impact of SARS-CoV-2 on global health.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/9/4632
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/researchers-identify-hub-genes-stat1,-irf7,-isg15,-mx1,-and-oas1-that-increases-covid-19-severity-in-diabetic-kidney-disease-patients
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-german-study-discovers-eight-human-proteins-and-genes-that-determine-covid-19-outcomes-with-the-elf5-gene-being-most-important
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/university-of-college-london-study-shows-that-both-the-oas1-gene-is-a-risk-factor-for-both-alzheimer-s-disease-and-covid-19-severity
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-immuno-genetics-university-of-edinburgh-study-confirms-that-genes-could-be-key-to-new-covid-19-treatments
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-news-scientist-from-china-find-that-oas-genes-play-a-key-role-in-sars-cov-2-induced-heart-failure
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-genetic-risk-variants-significantly-associated-with-the-expression-of-11-protein-coding-genes-that-impact-immune-cell-types-and-disease-sever
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-severity-linked-to-mutations-in-any-13-different-human-genes-involved-with-antiviral-defense-according-to-study-by-rockefeller-university
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-news-washington-university-discover-1,449-human-host-plasma-proteins-altered-by-sars-cov-2-infection-database-useful-for-long-covid
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/blood-proteome-profiling-of-covid-19-patients-revealed-circulating-proteins-mbl2,-mmp3,-il2ra,-fcgr2a,-ccl5,-gp1ba,-vwf,-ang,-sdc4-chl1
