French Doctors Find That Therapeutic Plasma Exchange Can Enhance Immune Recovery in Severe COVID-19 Patients
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jan 18, 2025 2 months, 4 weeks, 2 hours, 48 minutes ago
Medical News: As the world continues to grapple with the consequences of COVID-19, researchers are looking into innovative methods to improve outcomes for critically ill patients. One such approach, therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE), has shown promise in helping to restore immune function in individuals suffering from severe COVID-19. This
Medical News report focuses on findings from a clinical trial led by an international team of researchers from institutions including the French National Institute of Health and Medical Research (INSERM), University of Lyon-France, and Assistance Publique- Hôpitaux de Paris-France.
 French Doctors Find That Therapeutic Plasma Exchange Can Enhance Immune Recovery in Severe COVID-19 Patients
French Doctors Find That Therapeutic Plasma Exchange Can Enhance Immune Recovery in Severe COVID-19 Patients
The study sheds light on the potential of TPE to combat immune dysregulation, a key factor in the progression of severe COVID-19. By removing harmful substances from the blood, TPE aims to correct the immune system's response, offering new hope for patients.
The Role of the Immune System in Severe COVID-19
In severe cases of COVID-19, immune disturbances such as lymphopenia (low lymphocyte levels), overproduction of cytokines, and the presence of autoantibodies against type I interferon (IFN) exacerbate the disease. These issues often result in complications like acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), prolonged oxygen dependency, and, in some cases, death. Traditional treatments, including corticosteroids and oxygen therapy, address symptoms but do little to resolve underlying immune dysfunction.
The study set out to test whether adding TPE to standard treatments could improve immune recovery and reduce the severity of symptoms. Researchers enrolled 21 patients with severe COVID-19 from multiple French hospitals, including Lyon’s Centre Hospitalier Croix-Rousse and Paris’ Hôpital de la Pitié-Salpêtrière.
How Therapeutic Plasma Exchange Works
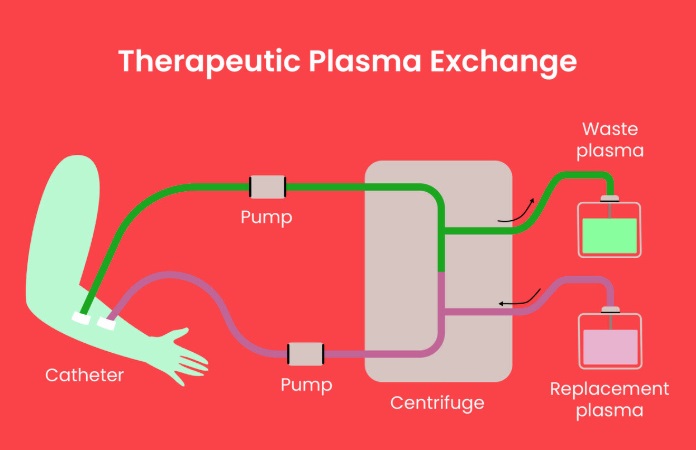
Therapeutic plasma exchange involves replacing a patient’s plasma, which contains inflammatory molecules and autoantibodies, with healthy donor plasma. This process aims to remove harmful substances from circulation while preserving the patient's ability to fight infection.
Patients in the trial were divided into two groups. Ten patients received three TPE sessions along with standard treatments (corticosteroids and high-flow oxygen), while the remaining 11 received standard treatment alone. Blood samples were collected to measure changes in immune cell counts, cytokine levels, and other parameters.
Key Findings from the Study
The study revealed several important outcomes:
-Reduction in Autoantibodies: TPE effectively removed type I IFN autoantibodies, which are known to impair antiviral responses. This removal could play a crucial role in restoring immune balance.
;
-Lower Inflammatory Marker Levels: Patients undergoing TPE showed significant reductions in inflammatory markers such as IL-7, IL-18, and C-reactive protein. These reductions suggest that TPE may help mitigate the cytokine storm often observed in severe COVID-19.
-Improved Immune Cell Recovery: TPE accelerated the recovery of lymphocyte counts, including CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, which are vital for mounting a proper immune response. Patients who responded well to TPE exhibited better T-cell function and a higher number of virus-specific T cells, indicating enhanced antiviral immunity.
-Clinical Outcomes: While TPE did not drastically alter the course of ARDS or reduce the need for intubation, patients with favorable immune responses to TPE experienced shorter durations of oxygen dependency.
Implications and Future Directions
The findings suggest that TPE may offer a targeted approach to correct immune dysfunction in severe COVID-19 cases. Unlike corticosteroids, which broadly suppress the immune system, TPE allows for the removal of harmful substances while preserving adaptive immunity. This characteristic makes it particularly valuable in managing immune complications without compromising the body’s ability to fight infections.
However, the study's authors emphasize that TPE's benefits were most pronounced in a subset of patients with favorable respiratory outcomes, suggesting that its effectiveness may depend on individual factors. Additional research with larger cohorts is needed to identify which patients are most likely to benefit from TPE.
Conclusions
This groundbreaking research highlights therapeutic plasma exchange as a potential adjunct to standard treatments for severe COVID-19. By targeting the root causes of immune dysregulation, TPE could pave the way for more effective management of critically ill patients. The study findings underscore the importance of personalized treatment strategies, as not all patients responded equally well to the therapy.
The researchers concluded that "the addition of TPE sessions to standard treatment accelerates immune cell recovery and contributes to the development of appropriate antiviral T-cell responses in some patients with severe COVID-19 disease." While TPE may not be a universal solution, its ability to restore immune function holds significant promise for improving outcomes in selected cases.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Frontiers in Immunology.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1492672/full
For the latest COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/new-findings-on-plasmablasts-and-autoantibodies-in-covid-19
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-news-study-find-that-covid-19-causes-decreased-plasma-cartilage-acidic-protein-1-crtac1-with-implications-for-long-covid-and-cancer
https://www.thailandmedical.news/articles/coronavirus
