Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jul 27, 2024 1 year, 4 months, 3 weeks, 4 days, 2 hours, 56 minutes ago
Arthritis News: A collaborative team of researchers from Beirut Arab University, the American University of Beirut, and Abu Dhabi Women’s College has shed new light on the potential treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a debilitating autoimmune disease affecting millions worldwide. This
Arthritis News report delves into their recent findings, which have revealed the promising effects of Galangin, a natural flavonoid compound, in alleviating the symptoms of RA.
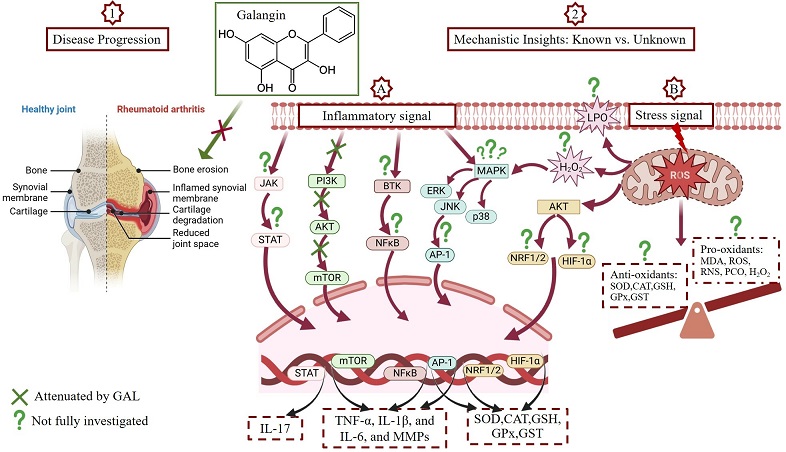 Graphical Abstract - Galangin shows promise in treating rheumatoid arthritis
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
Graphical Abstract - Galangin shows promise in treating rheumatoid arthritis
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily targets joints, causing inflammation, pain, and eventual joint damage. Affecting about 1% of the global population, RA is more prevalent among women, possibly due to hormonal influences. The complexity of RA, coupled with the significant role of oxidative stress in its progression, makes it a challenging disease to treat effectively.
The study explores the detailed mechanisms by which Galangin (GAL), a naturally occurring flavonoid, may serve as a potent therapeutic agent for RA. Sourced from plants and honeybee products, GAL has exhibited various bioactive properties, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects.
Galangin: A Multifaceted Bioactive Compound
GAL is derived from several sources, including honey, propolis, bee pollen, and various plants. Its diverse pharmacological effects make it a subject of interest for treating numerous conditions, particularly RA. The researchers from Beirut Arab University, the American University of Beirut, and Abu Dhabi Women’s College focused on elucidating the mechanisms through which GAL can impact RA.
Mechanisms of Action
The study highlighted several key mechanisms through which GAL exerts its effects:
-Anti-Inflammatory Properties: GAL has been shown to inhibit key inflammatory pathways, such as NF-κB, MAPK, and JAK/STAT. These pathways are crucial in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which play significant roles in RA progression.
-Antioxidant Effects: The presence of hydroxyl groups in GAL’s structure enables it to function as a potent antioxidant. GAL enhances the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). It also reduces oxidative stress markers such as malondialdehyde (MDA) and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE).
-Immunomodulatory Effects: GAL influences various immune cells, reducing the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the joints and modulating the activity of macrophages and dendritic cells. This leads to a decrease in the production of inflammatory mediators and promotes a more balanced immune response.
Study Findings
The researchers conducted a series of in vivo and in vitro studies to assess the impact of GAL on RA. Their findings revealed that GAL significantly reduced inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune dysregulation in RA models. Key results included:
-Reduction of Inflammatory Cytokines: GAL treatment led to a marked decrease in TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 levels in RA models. This reduction was associated with an improvement in joint inflammation and damage.
-Enhanced Antioxidant Defense: GAL increased the activity of antioxidant enzymes, thereby reducing oxidative stress in affected tissues. This was evidenced by lower levels of oxidative stress markers and higher antioxidant capacity.
-Modulation of Immune Response: GAL influenced the behavior of immune cells, promoting the differentiation of regulatory T cells and reducing the activity of pro-inflammatory cells. This helped in achieving a more regulated immune response, mitigating the autoimmune attack on joints.
Potential and Future Directions
The promising results from this study suggest that GAL could be a valuable addition to the arsenal of treatments for RA. However, the researchers emphasize the need for further clinical trials to confirm these findings in human subjects and to better understand the optimal dosing and delivery methods for GAL.
Conclusion
The study findings highlight the therapeutic potential of Galangin in treating rheumatoid arthritis. By targeting inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune dysregulation, GAL offers a comprehensive approach to managing RA symptoms and improving patient outcomes.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Pharmaceuticals.
https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/17/7/963
For the latest
Arthritis News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/the-role-of-traf1-in-rheumatoid-arthritis
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/melatonin-a-potential-game-changer-in-arthritis-treatment
