Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jun 07, 2024 1 year, 6 months, 1 week, 5 days, 18 hours, 46 minutes ago
Cardiology Updates: A Simple Amino Acid with a Big Impact
Glycine, the simplest amino acid with a single hydrogen atom as its side chain, is more than just a building block for proteins. This tiny molecule plays crucial roles in various metabolic functions and has significant therapeutic potential, particularly for cardiovascular health. A recent study by researchers from the Autonomous University of Nuevo León-Mexico and Research Center in Optics, Loma del Bosque-Mexico that is covered in this
Cardiology Updates news report
highlights its broad spectrum of benefits, ranging from reducing the risk of heart attacks to improving outcomes in conditions like aortic aneurysms and insulin resistance.
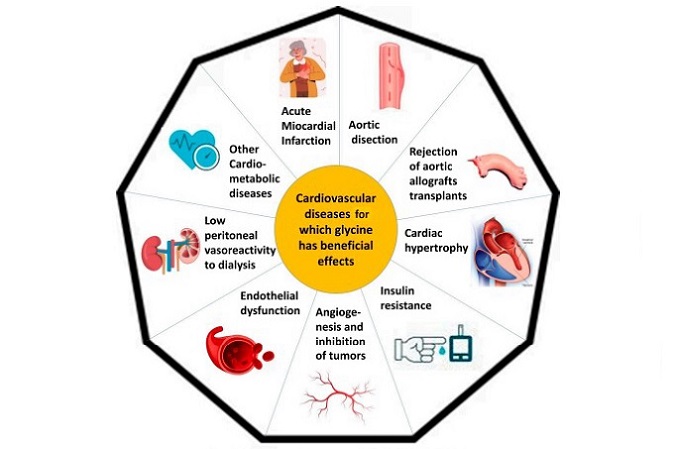 Glycine’s main positive impacts on cardiovascular health
The Essential Role of Glycine
Glycine’s main positive impacts on cardiovascular health
The Essential Role of Glycine
Humans can synthesize glycine from multiple sources such as glucose and glyoxylate. Despite this, studies indicate that the body's production may not always meet metabolic demands, making dietary intake of glycine essential. An intake of 1.5-3 grams per day is recommended to maintain optimal health.
Glycine and Cardiovascular Health
Glycine’s benefits extend significantly to cardiovascular health. It has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties, enhance insulin response, and stimulate glutathione biosynthesis, crucial for antioxidant protection. Notably, low levels of glycine have been linked to conditions like acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and aortic aneurysms.
Glycine and Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI)
Acute myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, is a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Research by Ding et al. involving over 4,000 participants revealed that higher plasma glycine levels are associated with a lower risk of AMI. Glycine's role in lipid metabolism and cholesterol transport is believed to contribute to this protective effect. In animal studies, glycine supplementation reduced myocardial fibrosis and inhibited apoptosis of heart cells, further showcasing its potential in heart attack prevention and treatment.
Aortic Conditions and Glycine
The aorta, the body’s main artery, can suffer from various conditions such as aneurysms and dissections. Studies have shown that glycine levels are significantly lower in patients with acute aortic dissection. Glycine supplementation has demonstrated promising results in reducing atherosclerosis and mitigating chronic rejection in aortic transplants by promoting glutathione biosynthesis and reducing immune responses.
Glycine in Angiogenesis and Tumor Inhibition
Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is a c
ritical process in both health and disease. Glycine influences angiogenesis in a dose-dependent manner; low doses promote while high doses inhibit blood vessel formation. This dual role makes glycine a potential therapeutic agent for conditions requiring angiogenesis, like wound healing, and for inhibiting tumor growth. Glycine's ability to decrease VEGF-mediated angiogenesis highlights its potential as an anti-cancer agent.
Dietary Glycine for Endothelial Dysfunction
Endothelial dysfunction, a precursor to many cardiovascular diseases, can be improved with glycine supplementation. Research on aged rats showed that glycine enhanced endothelial function by increasing eNOS expression and reducing oxidative stress. This suggests that glycine could be beneficial in treating conditions like hypertension and atherosclerosis.
Combating Cardiac Hypertrophy with Glycine
Cardiac hypertrophy, the thickening of the heart muscle, can lead to heart failure if untreated. Glycine has been found to prevent the overproduction of collagens in cardiac cells, thus combating hypertrophy. Studies in animal models have demonstrated that glycine supplementation can significantly reduce cardiac hypertrophy and improve heart function.
Glycine’s Role in Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Diseases
Insulin resistance is a major factor in metabolic diseases like type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Glycine has shown potential in improving insulin sensitivity and reducing symptoms of these conditions. Supplementation with glycine has led to reduced plasma free fatty acids, lower blood pressure, and improved metabolic profiles in animal studies. These findings suggest that glycine could play a critical role in managing and preventing metabolic disorders.
Conclusion: A Versatile Therapeutic Agent
Glycine’s extensive benefits across various aspects of health, particularly cardiovascular health, highlight its potential as a versatile therapeutic agent. From reducing the risk of heart attacks and improving outcomes in aortic conditions to enhancing endothelial function and combating cardiac hypertrophy, glycine stands out as a crucial nutrient with significant health benefits. Future research will undoubtedly uncover more about this small but mighty amino acid, solidifying its place in medical therapy and disease prevention.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed Journal of Vascular Diseases.
https://www.mdpi.com/2813-2475/3/2/16
For the latest
Cardiology Updates, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/study-finds-that-glycine-and-n-acetylcysteine-glynac-supplementation-can-treat-cognitive-decline-and-improve-brain-health-in-the-aged-
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-study-shows-that-sars-cov-2-infections-lead-to-increased-levels-of-oxidative-stress,-oxidant-damage-and-glutathione-deficiency
