Herb And Phytochemicals: Astragalus and Curcuma Show Promises In Fighting Colon Cancer
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jun 18, 2024 10 months, 1 week, 1 day, 5 hours, 19 minutes ago
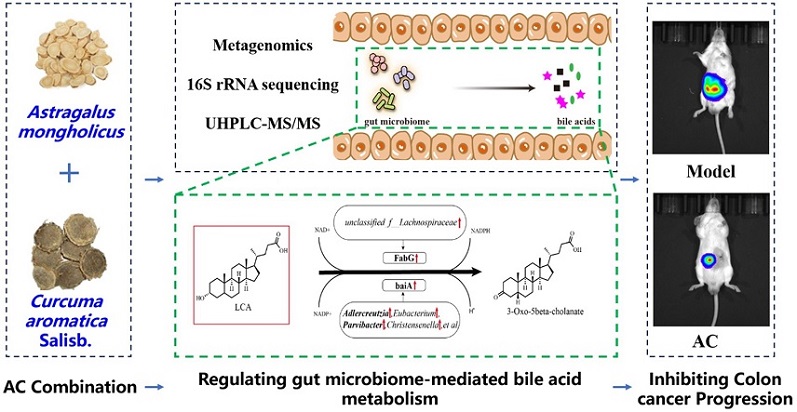
Herb And Phytochemicals: Colon cancer is a serious and common disease that affects many people worldwide. Modern treatments like surgery and chemotherapy can have harsh side effects, leading researchers to explore natural remedies. Recent studies have shown that traditional Chinese medicinal herbs, Astragalus mongholicus Bunge and Curcuma aromatica Salisb., might help fight colon cancer by improving gut health.
 Graphical Abstract- Astragalus and Curcuma Show Promises In Fighting Colon Cancer
The Power of the Gut Microbiome
Graphical Abstract- Astragalus and Curcuma Show Promises In Fighting Colon Cancer
The Power of the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome, which consists of trillions of microorganisms in our digestive tract, plays a crucial role in our health. It affects everything from digestion to immune function and even cancer development. Researchers have found that an imbalance in these gut bacteria can promote cancer growth. Conversely, a healthy and balanced microbiome can help prevent it.
Astragalus and Curcuma: A Potent Pair
Astragalus mongholicus Bunge, often used in traditional Chinese medicine, is known for boosting the immune system and fighting inflammation. Curcuma aromatica Salisb., related to the turmeric we commonly use in cooking, has powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Together, these herbs (referred to as AC) show significant promise in treating colon cancer by modulating the gut microbiome and bile acid metabolism.
Study Design: Testing the Herbs
Researchers from Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine-China, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei-China, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine-China and the Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine-China conducted a
Herb And Phytochemicals study using mice with colon cancer to understand how AC affects tumor growth. The mice were divided into groups, with one group receiving AC treatment. The researchers measured tumor size and analyzed the gut microbiome and bile acids in the mice to determine the herbs' effects.
Results: Tumor Suppression and Microbiome Modulation
The results were promising. Mice treated with AC showed a significant reduction in tumor growth compared to untreated mice. The treatment also led to changes in the gut microbiome, increasing beneficial bacteria and decreasing harmful ones. Specifically, there was an increase in Adlercreutzia and Parvibacter, which are known for their health benefits, and a decrease in pathogenic bacteria like Citrobacter.
Bile Acids: Key Players in Cancer Progression
Bile acids, produced by the liver and modified by gut bacteria, are crucial in cancer development. Some bile acids can promote cancer, while others can inhibit it. The study found that AC treatment altered the bile acid profile in the mice, reducing cancer-promoting bile acids like deoxycholic acid (DCA) and lithocholic acid (LCA) and increasing the concentration of cancer-inhibiting bile acids such as ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA).
Mechanisms-How AC Works
The bene
ficial effects of AC seem to be linked to specific genes and bacterial species in the gut. The treatment upregulated genes like FabG and baiA, which are involved in bile acid metabolism. These changes promoted the breakdown of harmful bile acids and supported a healthier gut environment, which in turn inhibited cancer progression.
Discussion: Implications for Human Health
These findings suggest that Astragalus and Curcuma could be valuable in preventing and treating colon cancer. By improving gut health and modulating bile acids, these herbs offer a natural and less toxic alternative to traditional cancer treatments. This research opens the door to further studies on how dietary supplements and natural products can support cancer therapy.
Conclusion: A Promising Future
The study provides strong evidence that Astragalus mongholicus Bunge and Curcuma aromatica Salisb. can significantly impact gut health and inhibit colon cancer progression. These findings highlight the potential of combining traditional wisdom with modern science to discover new treatments for cancer. As research continues, these herbs might become a valuable part of cancer prevention and therapy strategies, offering hope for safer and more effective treatments.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Frontiers in Microbiology.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/microbiology/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1395634/full
For the latest on
Herbs and Phytochemicals, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/how-an-allergy-medicine-could-fight-colon-cancer
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/study-identifies-early-warning-signs-of-colon-cancer
