Herbs And Phytochemicals: Erianin From The Orchid Dendrobium Officinale Alleviates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team May 14, 2024 11 months, 1 week, 5 days, 17 hours, 47 minutes ago
Herbs and Phytochemicals: Acute lung injury (ALI) is a severe medical condition that presents significant challenges to global public health. Among various potential treatments, natural compounds derived from medicinal herbs have gained attention for their therapeutic properties. One such phytochemical is erianin, a benzidine compound extracted from Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo, a well-known herb in traditional Chinese medicine. This
Herbs And Phytochemicals news report delves into the potential of erianin in alleviating LPS-induced acute lung injury, exploring its mechanisms of action and therapeutic implications.
 Herbs And Phytochemicals: Erianin From The Orchid Dendrobium
Herbs And Phytochemicals: Erianin From The Orchid Dendrobium
Officinale Alleviates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury
Ethnopharmacological Relevance of Dendrobium Officinale
Dendrobium officinale, a type of Orchid known as "Tiepi Shihu" in traditional Chinese medicine, has a long history of medicinal use. Documented in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia and revered in the classic "Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing," D. officinale is esteemed for its ability to fortify "Yin" and invigorate the five viscera. The pharmacological efficacy of D. officinale is closely linked to its active constituents, among which erianin stands out due to its potent anti-inflammatory properties.
The Threat of Acute Lung Injury
Acute lung injury is characterized by severe inflammation and damage to the lung tissues, leading to significant morbidity and mortality. The condition involves a cascade of pathological events, including the infiltration of inflammatory cells, pulmonary edema, and disruption of the capillary endothelium. ALI can be triggered by various factors, including bacterial infections, sepsis, and, notably, viral infections such as COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the critical need for effective treatments for ALI. The SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for COVID-19, frequently leads to acute lung injury, marked by an excessive inflammatory response and heightened recruitment of neutrophils. This excessive neutrophil infiltration and activation contribute significantly to lung damage and impaired respiratory function.
Exploring Erianin's Therapeutic Potential
The study covered here that was conducted by researchers from The First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University-China, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University-China, The Affiliated Cangnan Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University-China, Wenzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine-China and the State Key Laboratory for Quality Ensurance and Sustainable Use of Dao-di Herbs, Beijing-China, aimed to explore the therapeutic potential of erianin in treating ALI and elucidate the underlying mechanisms. Given the critical role of P-selectin in mediating neutrophil adhesion during acute inflammation, this investigation focuses on the impact of erianin on P-selectin-mediated neutrophil adhesion and its potential to mitigate ALI.
Experimental Design and M
ethodology
To assess the protective effects of erianin against ALI, comprehensive histopathological and biochemical analyses were conducted on lung tissues and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) in an in vivo model of LPS(Lipopolysaccharide)-induced ALI in mice. The impact of erianin on neutrophil chemotaxis was evaluated using the Transwell and Zigmond chamber assays. Advanced techniques such as drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS) assay, cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA), and molecular docking analyses were employed to identify the therapeutic target of erianin and elucidate its binding capability.
Study Findings
Erianin demonstrated significant protective effects against LPS-induced acute lung injury. Key findings include: -
-Reduction in Lung Injury: Erianin treatment resulted in reduced total cell and neutrophil counts and diminished total protein contents in BALF, indicating a decrease in lung injury severity.
-Suppression of Inflammatory Cytokines: Erianin effectively reduced the production of proinflammatory cytokines in lung tissues and BALF.
-Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling: Erianin suppressed the activation of NF-κB signaling in the lung tissues of LPS-challenged mice, highlighting its anti-inflammatory potential.
-Neutrophil Adhesion and Rolling: Erianin blocked the adhesion and rolling of neutrophils on activated endothelial cells. Notably, it did not influence the endothelial expression or translocation of P-selectin but significantly reduced the ligand affinity between P-selectin and P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1).
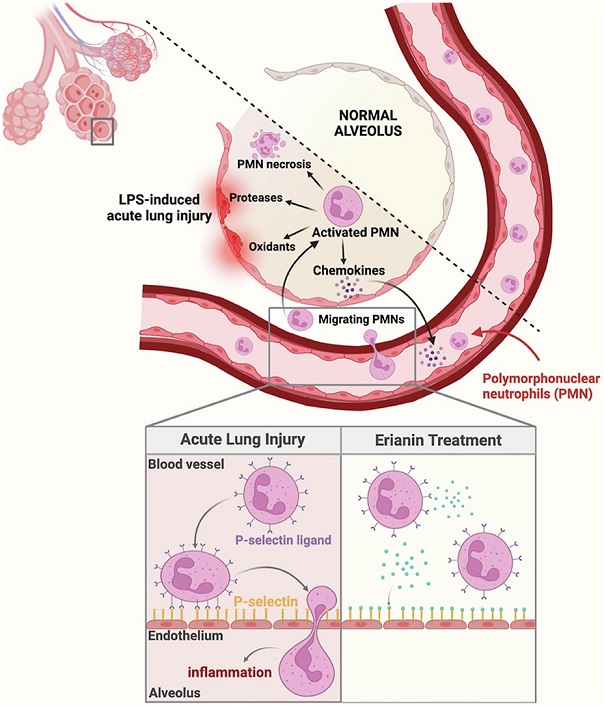 Graphical Abstract - Erianin From Dendrobium Officinale Alleviates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury
Mechanistic Insights - Role of P-Selectin in Neutrophil Recruitment
Graphical Abstract - Erianin From Dendrobium Officinale Alleviates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury
Mechanistic Insights - Role of P-Selectin in Neutrophil Recruitment
P-selectin, a cell adhesion molecule expressed on activated vascular endothelium, plays a crucial role in the early stages of neutrophil recruitment during acute inflammation. The interaction between P-selectin and its ligand, PSGL-1, facilitates the tethering and rolling of neutrophils along the endothelial surface, enabling their subsequent extravasation into inflamed tissues.
Erianin's ability to alleviate ALI is attributed to its interference with P-selectin-mediated neutrophil adhesion. By reducing the ligand affinity between P-selectin and PSGL-1, erianin disrupts the adhesion and rolling of neutrophils on endothelial cells, thereby mitigating excessive neutrophil infiltration into the lung tissues.
Furthermore, erianin's suppression of NF-κB signaling contributes to its anti-inflammatory effects. NF-κB is a key transcription factor involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, erianin reduces the production of proinflammatory cytokines, thereby alleviating lung inflammation.
Therapeutic Implications
Potential for ALI Treatment
The findings of this study highlight the potential of erianin as a promising therapeutic agent for ALI. Its ability to reduce neutrophil adhesion and infiltration, along with its anti-inflammatory effects, positions erianin as a viable candidate for ALI treatment. Given the critical role of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of ALI, targeting their recruitment and activation offers a novel approach to mitigating lung injury.
Broader Implications for Inflammatory Diseases
Beyond ALI, erianin's anti-inflammatory properties may have broader implications for the treatment of other inflammatory diseases. Conditions characterized by excessive neutrophil infiltration and activation, such as sepsis and autoimmune diseases, could potentially benefit from erianin-based therapies. Further research is warranted to explore the full therapeutic potential of erianin in various inflammatory conditions.
Conclusion
Erianin, derived from the traditional Chinese medicinal herb Dendrobium officinale, has demonstrated significant potential in alleviating LPS-induced acute lung injury. Through its antagonistic effects on P-selectin-mediated neutrophil adhesion and its suppression of NF-κB signaling, erianin effectively reduces lung inflammation and injury. These findings underscore the promise of erianin as a lead compound for ALI treatment and highlight the potential of medicinal herbs in discovering novel bioactive compounds for therapeutic applications.
The emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic has amplified the urgency for effective treatments for acute lung injury. As research continues to explore the therapeutic potential of natural compounds, erianin represents a beacon of hope in the quest for innovative and effective treatments for ALI and other inflammatory diseases. The integration of traditional herbal medicine with modern pharmacological research holds immense promise for advancing human health and combating complex diseases.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed Journal of Ethnopharmacology.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378874124006354
For the latest on
Herbs And Phytochemicals, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.

