Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jun 11, 2024 1 year, 8 months, 1 week, 3 days, 22 hours, 22 minutes ago
Herbs And Phytochemicals: Revolutionizing Cancer Treatment with Natural Compounds. Recent advancements in cancer research have unveiled an exciting new approach to combat hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a common type of liver cancer. Scientists from Hainan Women and Children’s Medical Center, along with collaborators from Hainan General Hospital and Hainan Medical University in China, have developed a promising new treatment leveraging the power of natural herbal extracts. This
Herbs And Phytochemicals breakthrough involves the use of galangin-loaded nanozymes, a novel approach that combines traditional herbal medicine with cutting-edge nanotechnology to effectively target and destroy cancer cells.
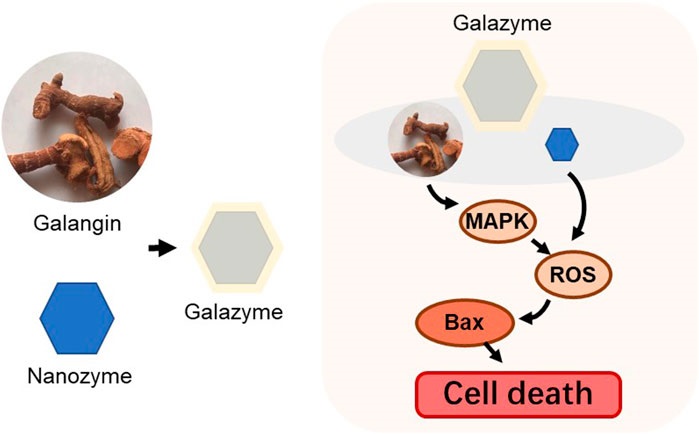 Galangin Nanozymes Targets Liver Cancer Cells.
Schematic illustration of the fabrication of the Galazyme.
The Power of Galangin
Galangin Nanozymes Targets Liver Cancer Cells.
Schematic illustration of the fabrication of the Galazyme.
The Power of Galangin
Galangin, a bioactive compound found in the roots of the Alpinia galanga plant, is known for its impressive anti-cancer properties. However, the effectiveness of galangin has been historically limited due to its poor solubility and low bioavailability. These challenges have significantly hindered its use in medical applications. The new study addresses these limitations by encapsulating galangin in a nanozyme, which enhances its solubility, stability, and ability to penetrate cell membranes.
Introducing Galazyme
The newly developed nanozyme, named Galazyme, combines galangin with copper nanoparticles, which are further coated with DSPE-PEG. This sophisticated design amplifies the oxidative stress within cancer cells, inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death) through the regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. This innovative approach not only improves the bioavailability of galangin but also enhances its anti-cancer efficacy.
Mechanism of Action
Upon entering liver cancer cells, Galazyme demonstrates significant peroxidase-like activity, which enables it to convert excess hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) within the cells into highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (OH ions). This conversion process generates substantial oxidative stress, which is crucial for triggering apoptosis. The MAPK pathway is subsequently activated, leading to the upregulation of pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Caspase 3. These proteins play vital roles in the apoptosis process, ensuring the effective and irreversible death of cancer cells.
In Vitro and In Vivo Success
Both in vitro (lab-based) and in vivo (animal-based) experiments have shown promising results. In vitro studies using HepG-2 liver cancer cells demonstrated that Galazyme significantly inhibits tumor cell growth and induces apoptosis more effectively than galangin alone. The in vivo experiments further confirmed these findings, showing that Galazyme not only suppresses tumor growth in mice but also
promotes extensive cancer cell death without causing significant side effects.
Detailed Analysis and Observations
The study involved various detailed analyses to understand the effectiveness of Galazyme. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images revealed the structural integrity and size distribution of the nanoparticles. The stability and catalytic activity of Galazyme were assessed through dynamic light scattering (DLS) and UV-visible spectroscopy, confirming its robustness and efficiency in biological environments.
Additionally, the fluorescence imaging of cells treated with Galazyme indicated a higher ROS level compared to those treated with free galangin. This observation was corroborated by the elevated expression levels of Bax and Caspase 3, which were measured using quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and immunofluorescence staining.
Animal Studies Confirm Efficacy
In the animal studies, mice bearing HepG-2 tumors were divided into different treatment groups, including a control group and groups treated with either galangin, nanozyme, or Galazyme. The results were striking: Galazyme-treated mice exhibited the most significant reduction in tumor size and the highest levels of apoptosis. Importantly, there were no significant changes in the body weight of the mice, indicating the treatment's safety.
Future Prospects and Potential
The success of Galazyme in preclinical trials marks a significant milestone in the fight against liver cancer. This study provides compelling evidence that nanozymes can enhance the therapeutic potential of natural compounds like galangin, opening new avenues for cancer treatment. The researchers are optimistic about the future applications of Galazyme and plan to conduct further studies to explore its efficacy in other types of cancer and its potential for clinical use.
Conclusion
The development of Galazyme represents a groundbreaking advancement in cancer therapy, merging the benefits of natural herbal extracts with the precision of nanotechnology. This innovative approach not only overcomes the limitations of traditional treatments but also offers a more effective and targeted solution for combating liver cancer. As research progresses, Galazyme holds the promise of becoming a powerful tool in the arsenal against cancer, bringing hope to patients and healthcare providers alike.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Frontiers in Chemistry.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2024.1426634/full
For the latest on
Herbs and Phytochemicals, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/cancer-news-tim-3-and-cd38-proteins-identified-as-potential-tumor-markers-for-hepatocellular-carcinoma
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/ai-in-medicine-singaporean-and-thai-researchers-explore-using-ai-to-diagnose-hepatocellular-carcinoma-earlier-and-more-accurately
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/cancer-news-swiss-study-finds-that-arginine-promotes-tumor-growth-in-liver-cancer-via-metabolic-reprogramming
