Herbs And Phytochemicals: Harringtonine From Cephalotaxus Fortunei Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 And Exhibits Excellent Lung Pharmacokinetic Properties
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Apr 17, 2024 1 year, 1 week, 2 days, 12 hours, 22 minutes ago
Herbs And Phytochemicals: Harringtonine (HT), a natural alkaloid derived from Cephalotaxus fortunei Hook. f., has emerged as a potential therapeutic agent in the battle against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus responsible for the global COVID-19 pandemic. Initially studied for its efficacy against leukemia, HT and related compounds have demonstrated promising inhibitory effects on the growth of various cancer cells. The onset of COVID-19 prompted researchers to explore the repurposing of existing natural compounds, leading to investigations highlighting HT's ability to target critical proteins involved in the SARS-CoV-2 replication cycle.
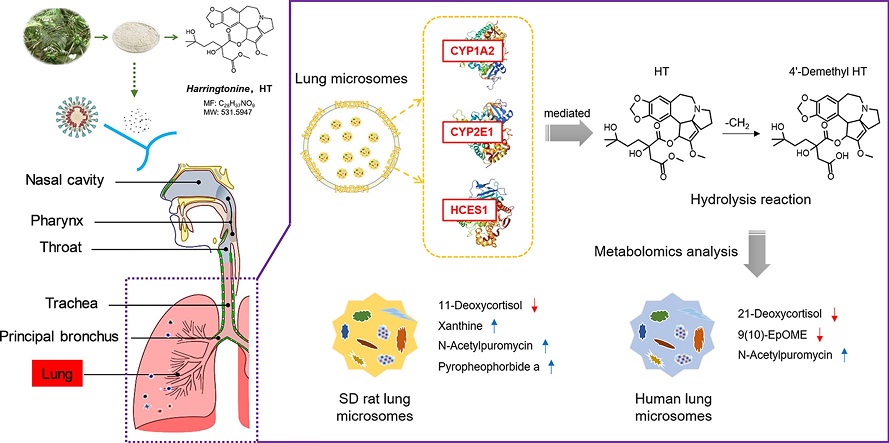 Graphical Abstract - Harringtonine From Cephalotaxus Fortunei Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 And Exhibits Excellent Lung Pharmacokinetic Properties.
Exploring HT's Antagonistic Mechanisms Against SARS-CoV-2
Graphical Abstract - Harringtonine From Cephalotaxus Fortunei Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 And Exhibits Excellent Lung Pharmacokinetic Properties.
Exploring HT's Antagonistic Mechanisms Against SARS-CoV-2
In recent years,
Herbs And Phytochemicals research has shed light on HT's potential as an antagonist against SARS-CoV-2. Specifically, HT has been found to bind selectively to the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein and host cell transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2). This binding interaction disrupts the process of membrane fusion, a pivotal step in the virus's entry into host cells. By impeding this crucial mechanism, HT demonstrates promise as an effective antiviral agent against SARS-CoV-2, potentially inhibiting viral replication and spread.
Pharmacokinetic Insights into HT's Behavior in the Lung
A recent comprehensive study conducted at Xi'an Jiaotong University in China delved into the in vitro pharmacokinetic characteristics of HT, with a specific focus on its behavior within the lung - a primary target organ for SARS-CoV-2 infection. The study employed a rapid and sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-fluorescence detection method to quantify Harringtonine (HT) accurately. Through meticulously designed incubation systems that simulated lung microsomes and metabolic enzymes, the researchers elucidated the metabolites and metabolic pathways of HT, providing valuable insights into its pharmacological activity.
Key Findings from the Study
The study's findings revealed the robustness of the HPLC-fluorescence method in quantifying HT, showcasing its specificity, high accuracy, and stability.
Importantly, it was elucidated that Harringtonine (HT) primarily undergoes phase I metabolism, with its main metabolite identified as 4′-demethyl HT, produced through hydrolysis reactions. Enzymes such as cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2), cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1), and the esterase HCES1 in the lung were implicated in HT metabolism.
Moreover, metabolomics analysis unveiled significant pathways impacted by HT treatment, including cortisol synthesis, steroid hormone biosynthesis, and linoleic acid metabolism. Notably, the downregulation of key biomarkers associated with immunosuppression and viral infection further underscored HT's potential in combating SARS-CoV-2.
r />
Implications for COVID-19 Treatment
Understanding HT's pharmacokinetics and metabolic pathways in the lung holds immense significance for developing targeted therapies against COVID-19. The study's insights into HT's mechanisms of action and its impact on crucial metabolic pathways provide a solid foundation for further clinical applications. Harnessing HT's antiviral properties through inhalation therapy could offer a promising avenue in the fight against COVID-19, particularly in addressing lung-related complications and reducing viral load.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comprehensive exploration of HT's pharmacokinetics and metabolic behavior in the lung presents a compelling case for its therapeutic potential against SARS-CoV-2. The study's methodologies and findings pave the way for future research aimed at optimizing HT-based treatments for COVID-19. As the global healthcare community continues to seek effective strategies against the pandemic, natural compounds like HT offer valuable insights and possibilities in the realm of antiviral therapy. Further investigations and clinical trials are warranted to fully harness HT's therapeutic benefits and contribute to the ongoing efforts to combat COVID-19 and its associated challenges.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Phytomedicine.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0944711324002472
For the latest on Herbs And Phytochemicals, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
