Herbs And Phytochemicals: Naringin And Naringenin From Various Fruits Can Help With Many Long COVID Manifestations
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Feb 05, 2024 1 year, 2 months, 3 weeks, 18 hours, 5 minutes ago
Herbs And Phytochemicals: The global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has unveiled a complex spectrum of illnesses associated with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Beyond the acute phase of infection, an alarming phenomenon known as long COVID has emerged, wherein patients experience a myriad of post-acute sequelae. These lingering effects can persist for up to six months or more, encompassing cognitive dysfunction, immune dysregulation, microbiota dysbiosis, myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome, myocarditis, pulmonary fibrosis, cough, diabetes, pain, reproductive dysfunction, and thrombus formation. Remarkably, recent studies suggest that natural compounds found in herbs, particularly naringin and naringenin, exhibit palliative effects on various long COVID manifestations. This
Herbs And Phytochemicals news report delves into the molecular mechanisms and clinical impacts of these flavonoids, proposing them as potential therapeutic agents for long COVID and envisioning a future where they may serve as nutraceuticals or clinical supplements.
 Naringin And Naringenin From Various Fruits Can Help With Many Long COVID Manifestations.
Understanding the Pathogenesis of Long COVID
Naringin And Naringenin From Various Fruits Can Help With Many Long COVID Manifestations.
Understanding the Pathogenesis of Long COVID
Long COVID, formally referred to as post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), poses a significant challenge in terms of both diagnosis and treatment. Studies indicate that nearly half of COVID-19 patients globally develop long COVID, with diverse symptoms affecting various organ systems. Dizziness, fatigue, sleep difficulties, memory loss, anxiety and depression, pulmonary fibrosis, and thrombus formation are among the prevalent manifestations. The underlying pathogenic mechanisms include persistent SARS-CoV-2 presence, microthrombosis, immune dysregulation, mitochondrial dysfunction, activation of pathogens like Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and human herpesvirus 6 (HHV6), changes in microbiota, and persistent inflammation.
Current Treatment Landscape and the Potential of Naringin and Naringenin
Presently, the treatment of long COVID is symptom-based, lacking definitive medications. However, promising avenues are being explored in natural compounds derived from medicinal plants. Naringin and naringenin, both belonging to the flavanone class and commonly found in various herbs and citrus fruits including grapefruit, bergamot, sour orange, tart cherries, tomatoes, cocoa, Greek oregano, water mint, as well as in beans, and, have demonstrated a diverse range of therapeutic properties. Their anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antioxidant, cardiovascular-protective, antiviral, and immune-modulation effects position them as potential candidates for mitigating long COVID complications.
Therapeutic Potential Explored
-Cognitive Dysfunction: Cognitive dysfunction, often referred to as "brain fog," is a persistent psychiatric manifestation post-COVID-19. Studies show that nearly one-fifth of patients experience continued cognitive impairment at 9 months after infection. Naringin and naringenin show promise in ameliorating cognitive dysfunctio
n by modulating glial cell activation, protecting against nervous system stresses, and regulating neurotransmitters. Their protective effects on neuronal mitochondrial function, reduction of oxidative stress, and potential to cross the blood-brain barrier highlight their neuroprotective properties.
-Immune Dysregulation: Long-term effects of COVID-19 on the immune system manifest as changes in immune cells, increased autoantibodies, and reactivation of dormant viruses. Naringenin exhibits a palliative effect on T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases, modulating the immune response by influencing T cell growth and cytokine signaling. By inhibiting the growth and specialization of harmful pro-inflammatory T cells, naringenin helps maintain immune balance, potentially addressing the immune dysregulation seen in long COVID patients.
-Microbiota Dysbiosis: Naringin and naringenin play a regulatory role in the composition and metabolism of gut flora. Their intake helps control the intestinal microenvironment, reducing the abundance of disease-related bacteria and enhancing probiotic content. By regulating the growth and gene expression of intestinal commensal microorganisms, these flavonoids contribute to maintaining gut health and preventing microbiota dysbiosis.
-Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS): ME/CFS, characterized by persistent fatigue, myalgia, and exercise intolerance, shares overlapping symptoms with long COVID. Naringin and naringenin exhibit anti-fatigue effects by stabilizing redox balance, elevating blood glucose levels, and protecting mitochondrial function. Their potential to alleviate neuropathic pain and regulate carbohydrate and lipid metabolism further positions them as promising agents for managing ME/CFS-like symptoms in long COVID.
-Myocarditis: Enduring cardiac impairment leading to myocarditis is observed in some long COVID survivors. Naringin and naringenin showcase cardioprotective properties by reducing inflammatory factors associated with cardiovascular injury and protecting heart mitochondria from damage. Additionally, their potential to alter cellular channel currents contributes to antiarrhythmic effects, presenting a multifaceted approach to addressing myocarditis in long COVID patients.
-Cough: Chronic cough is a prevalent symptom in long COVID patients. Naringin and naringenin demonstrate positive antitussive effects by reducing inflammation and suppressing the growth of airway-inflammatory factors. Their ability to attenuate neurogenic inflammation and induce the relaxation of airway smooth muscle cells positions them as potential remedies for persistent cough in long COVID.
-Diabetes: Both new-onset diabetes and underlying diabetic activation are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Naringin and naringenin exhibit antidiabetic potential by protecting pancreatic β-cells, enhancing insulin sensitivity, and regulating carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Their impact on glucose metabolism, insulin secretion, and glycogen synthesis suggests a potential role in managing diabetes-like complications in long COVID.
-Pain: Long COVID patients often experience persistent pain, including headaches and musculoskeletal pain. Naringin and naringenin showcase effective analgesic effects by inhibiting inflammatory responses, reducing pain perception pathways, and modulating pain-related receptors. Their ability to attenuate neuropathic pain and inflammatory pain positions them as potential analgesic agents for long COVID patients.
-Thrombus Formation: Endothelial damage induced by SARS-CoV-2 can lead to coagulation dysfunction and thrombus formation. Naringin and naringenin exhibit antithrombotic effects by protecting endothelial cells, inhibiting platelet activation, and impeding thrombin activity. Their ability to mitigate endothelial dysfunction, reduce inflammation, and influence coagulation-associated proteins suggests a potential role in preventing thrombus formation in long COVID patients.
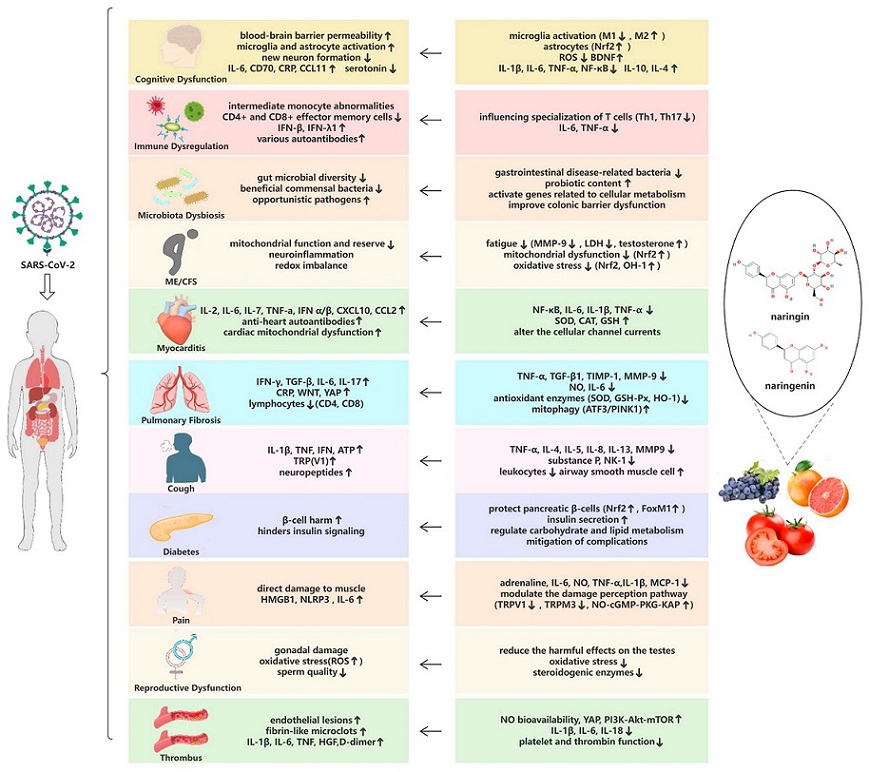 Summary of long COVID symptom pathogenesis (left) and potential therapeutic mechanisms (right). Upward arrows (↑) in the colored panels of the table indicate increases and downward arrows (↓) indicate decreases. Leftward arrows (←) between the panels indicate the palliative and therapeutic effects of naringin on long COVID symptoms.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Summary of long COVID symptom pathogenesis (left) and potential therapeutic mechanisms (right). Upward arrows (↑) in the colored panels of the table indicate increases and downward arrows (↓) indicate decreases. Leftward arrows (←) between the panels indicate the palliative and therapeutic effects of naringin on long COVID symptoms.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
This comprehensive exploration highlights the diverse therapeutic potential of naringin and naringenin in addressing multiple complications associated with long COVID. Their multifaceted benefits, including anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antiviral, and cardiovascular-protective effects, position them as promising candidates for further investigation and potential integration into long COVID treatment strategies. However, further research is essential to establish their true efficacy, optimal dosage, and safety profile in long COVID patients through rigorous studies and clinical trials.
The study review by researchers from Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou-China and Guangdong Laboratory for Lingnan Modern Agriculture-China, was published in the peer reviewed journal: Microorganisms.
https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/12/2/332
For the latest on
Herbs And Phytochemicals, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.

