Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jun 18, 2024 10 months, 1 week, 2 days, 23 hours, 59 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: The COVID-19 pandemic has introduced the world to many medical challenges, and one of the more severe but lesser-known complications is pulmonary cavitation. This condition, though rare, has been observed in some COVID-19 patients and can lead to significant health issues. This
COVID-19 News report covers cases studies of COVID-19 induced lung cavities reported by medical researchers from Zanjan University of Medical Sciences-Iran, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences-Iran and the National Taipei University of Nursing and Health Sciences-Taiwan.
 Hidden Dangers of COVID-19: Understanding Lung Cavities
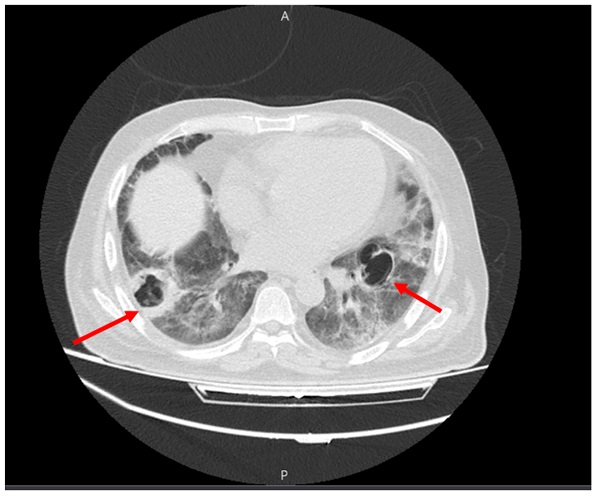
Multiple cavities with thick, septoid walls in the lower lobes on both sides (red arrows).
What Are Lung Cavities?
Hidden Dangers of COVID-19: Understanding Lung Cavities
Multiple cavities with thick, septoid walls in the lower lobes on both sides (red arrows).
What Are Lung Cavities?
A lung cavity is essentially a hollow space within the lung, often filled with air, fluid, or both. These cavities can be caused by infections, malignancies, or autoimmune diseases. In the context of COVID-19, lung cavitation has been reported, albeit infrequently, in patients experiencing severe respiratory symptoms.
Case Studies Highlighting Pulmonary Cavitation in COVID-19 Patients
Several cases from a recent report shed light on this complication:
-Case 1: Bacterial and Fungal Infections
A 52-year-old woman with no prior health issues developed severe respiratory symptoms and tested positive for COVID-19. Despite initial treatment, her condition worsened, and she was admitted to the ICU. A few weeks later, she developed large lung cavities due to bacterial and fungal infections. She received extensive antibiotic and antifungal treatments and was eventually discharged in improved condition.
-Case 2: Severe Respiratory Failure and Co-infections
A 60-year-old man with no significant medical history experienced severe COVID-19 symptoms. He was treated with a combination of steroids, antiviral drugs, and supportive oxygen therapy. After initial recovery, he developed multiple lung cavities due to co-infections, including fungal and bacterial pathogens. He was treated with a broad spectrum of antibiotics and antifungal medications, showing significant improvement before discharge.
-Case 3: Complications Post-COVID-19 Treatment
A 72-year-old woman with a history of hypothyroidism developed severe COVID-19 symptoms and was treated with high doses of steroids and antiviral medications. Post-recovery, she experienced gastrointestinal bleeding and was found to have a large lung cavity. She received antibiotics for a suspected pulmonary abscess and was discharged with instructions for follow-up care.
-Case 4: Persistent Lung Cavities and Bacterial Infections
A 73-year-old man with hypertension developed severe COVID-19 symptoms. Despite intensive care and treatment, he developed persiste
nt lung cavities due to multi-drug-resistant bacterial infections. He underwent various antibiotic treatments and procedures to manage his condition and was eventually transferred to a specialized center for further care.
Understanding the Causes and Mechanisms
The formation of lung cavities in COVID-19 patients can occur due to several reasons:
-Direct Viral Damage: The severe inflammation caused by SARS-CoV-2 can lead to lung tissue damage and cavity formation.
-Bacterial Superinfections: Secondary bacterial infections, particularly with resistant strains like Staphylococcus epidermidis and Klebsiella pneumoniae, can lead to the development of cavities.
-Fungal Infections: Fungi such as Aspergillus species can colonize lung cavities, forming structures known as aspergillomas.
Diagnosing and Managing Pulmonary Cavitation
Diagnosis typically involves imaging techniques like CT scans, which can reveal the presence and extent of lung cavities. Treatment strategies vary based on the underlying cause:
-Antibiotics: Broad-spectrum antibiotics are often used to treat bacterial infections.
-Antifungals: In cases of fungal infection, antifungal medications are administered.
-Supportive Care: Oxygen therapy and mechanical ventilation may be necessary for patients with severe respiratory distress.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early recognition of pulmonary cavitation in COVID-19 patients is crucial. Physicians should be vigilant, especially in patients receiving high doses of steroids, as these individuals are more susceptible to secondary infections. Regular monitoring and prompt intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of severe complications.
Conclusion
While pulmonary cavitation is a rare complication of COVID-19, it presents significant challenges in patient management. Understanding the potential causes and ensuring early diagnosis and treatment are vital steps in improving patient care. As the pandemic evolves, continued research and clinical vigilance are necessary to manage and mitigate such complications effectively.
Key Takeaways
-Pulmonary cavitation is a rare but severe complication in COVID-19 patients.
-Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
-Secondary bacterial and fungal infections are common causes of lung cavities.
-Regular monitoring and a multidisciplinary approach to treatment can help manage this condition effectively.
By staying informed and proactive, healthcare providers can better navigate the complexities of COVID-19 and its associated complications, ensuring the best possible care for their patients.
The case series was published in the peer reviewed journal: Acta Microbiologica Hellenica.
https://www.mdpi.com/2813-9054/69/2/8
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/altered-serum-concentrations-of-il-8-il-10-and-il-32-in-individuals-with-lung-impairment-6-months-after-covid-19
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/neutrophil-activity-and-lung-tissue-destruction-in-fatal-covid-19-cases-and-long-covid
