Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Feb 14, 2025 2 months, 18 hours, 48 minutes ago
Medical News: New Research Sheds Light on the Link Between Inflammation and Schizophrenia
A new study has revealed that neuroinflammation plays a significant role in altering the brain’s glutamate and dopamine signaling, which may contribute to the development of schizophrenia. Researchers from various institutions, including Usha Nayak from Manipal Academy of Higher Education-India, Jyothsna Manikkath from Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences-India, Devinder Arora from the Griffith University-Australia, and Jayesh Mudgal from Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences-India, have provided an updated understanding of how inflammation affects brain function in schizophrenia patients.
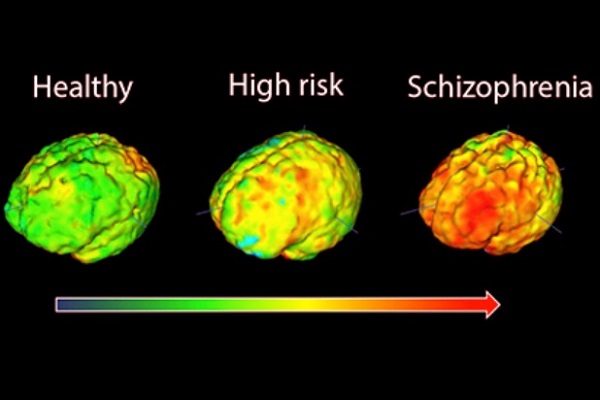 How Brain Inflammation Affects Glutamate and Dopamine in Schizophrenia
How Brain Inflammation Affects Glutamate and Dopamine in Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder affecting about 1% of the global population. It is marked by disruptions in perception, cognition, and social interactions. While previous research has focused on neurotransmitter imbalances, this
Medical News report highlights the emerging evidence on how inflammation might be a crucial factor in driving these changes.
How Inflammation Disrupts Brain Chemistry
The study explores how inflammation in the brain, particularly through the activation of immune cells called microglia, leads to disruptions in glutamate and dopamine signaling. Microglia are responsible for maintaining brain health, but when overactivated due to chronic inflammation, they release inflammatory markers that interfere with normal brain function.
One of the key findings is that inflammatory markers can trigger the production of an enzyme called indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), which alters the kynurenic acid pathway. This pathway is essential in regulating glutamate and dopamine levels. Inflammation leads to excessive kynurenic acid production, which blocks NMDA receptors - key components in glutamate signaling. This blockage contributes to cognitive and behavioral deficits seen in schizophrenia patients.
Additionally, inflammation increases the production of quinolinic acid, a neurotoxic compound that exacerbates brain damage.
Dopamine levels are also significantly impacted by inflammation. The study indicates that inflammatory markers like interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) can suppress dopamine production in some brain regions while increasing it in others. This imbalance is linked to both the positive symptoms (hallucinations, delusions) and negative symptoms (apathy, social withdrawal) of schizophrenia. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies on schizophrenia patients show increased uptake of fluorodopa (18F-DOPA), indicating abnormal dopamine synthesis, which may be driven by inflammatory processes.
Role of the Gut Brain Axis in Schizophrenia
The study also explores the connection between gut health and brain inflammation. Researchers found that disruptions in gut microbiota, known as gut dysbiosis, can lead to systemic inflammation, which in turn affects brain function. Patients with schizophre
nia often show reduced gut microbiome diversity, which may contribute to neurotransmitter imbalances.
By altering the gut microbiota, inflammation can influence the production of serotonin and glutamate, further exacerbating schizophrenia symptoms. The study suggests that probiotics and prebiotics may help restore gut health, potentially improving symptoms in schizophrenia patients.
Can Anti Inflammatory Drugs Help Treat Schizophrenia
Given the strong link between inflammation and neurotransmitter imbalances, the study discusses the potential benefits of anti-inflammatory drugs in managing schizophrenia. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), particularly COX-2 inhibitors like celecoxib, have shown promise in clinical trials. These drugs work by reducing inflammation in the brain, thereby improving glutamate and dopamine balance.
A recent randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial on schizophrenia patients demonstrated that adding aspirin (an NSAID) to standard antipsychotic treatment resulted in significant symptom improvement. This suggests that targeting inflammation may enhance the effectiveness of existing treatments.
Conclusion
The findings of this study emphasize the critical role of neuroinflammation in schizophrenia. By influencing glutamate and dopamine pathways, inflammation may be a major contributor to the disorder’s symptoms. The research highlights the potential of anti-inflammatory treatments as a complementary approach to existing therapies. Future studies should focus on developing targeted anti-inflammatory strategies, including gut microbiome modulation and immunotherapy, to provide more effective treatments for schizophrenia.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Metabolic Brain Disease.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11011-025-01548-3
For the latest on Neuroinflammation and Schizophrenia, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/intermittent-high-fat-diet-triggers-brain-inflammation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/phytochemicals-nobiletin-and-eriodictyol-can-help-suppress-neuroinflammation-caused-by-sars-cov-2-spike-protein
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/neuroinflammation-in-the-brainstem-and-its-link-to-pots-and-long-covid
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/lactoferrin-and-its-promising-role-in-combating-neuroinflammation-and-promoting-neuronal-health
Follow us on:
https://x.com/ThailandMedicaX
https://www.facebook.com/ThailandMedicalNews
https://bsky.app/profile/thailandmedical.bsky.social
https://gettr.com/user/thailandmedicalnews
https://www.tribel.com/thailandmedical/wall
and 33 other social media platforms
