Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Nov 12, 2024 5 months, 1 day, 8 hours, 29 minutes ago
Medical News: Recent studies dive into the intricate role of the extracellular matrix (ECM) within our blood vessels and its contribution to the development and stability of atherosclerotic plaques. Researchers from Centro Cardiologico Monzino IRCCS in Milan, Italy, aim to unravel the ECM's influence on atherosclerosis and explore potential treatments that target ECM remodeling to stabilize blood vessel walls and potentially prevent cardiovascular diseases.
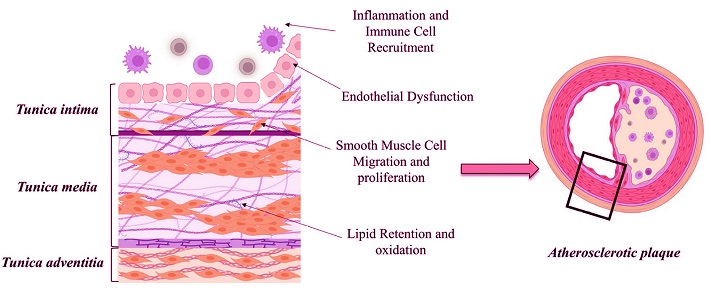 Schematic representation of Extracellular Matrix (ECM) highlighting key processes influenced by atherosclerosis
What is the Extracellular Matrix?
Schematic representation of Extracellular Matrix (ECM) highlighting key processes influenced by atherosclerosis
What is the Extracellular Matrix?
The ECM is a complex structure surrounding cells, especially critical in cardiovascular tissues, providing both support and flexibility to withstand blood flow pressures. It consists of collagens, elastin, fibronectin, laminin, and proteoglycans, each playing a role in maintaining vascular strength and integrity. Collagen provides tensile strength, elastin gives elasticity, and proteoglycans help with hydration and cushioning, all essential for blood vessel health.
The Role of ECM in Atherosclerosis
In the early stages of atherosclerosis, changes in the ECM contribute to endothelial cell dysfunction. This Medical News report explains that endothelial cells - lining the inner walls of blood vessels - can become more permeable, allowing lipid particles to accumulate and eventually form plaque. When ECM proteins are modified by enzymes, inflammatory cells enter the vessel wall, exacerbating the buildup of atherosclerotic plaque.
How ECM Changes Contribute to Plaque Growth
The ECM undergoes constant remodeling, with enzymes like matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) breaking down ECM components to allow new formation. However, in atherosclerosis, MMP activity becomes excessive, degrading ECM proteins like collagen and elastin, weakening the vessel walls, and making plaques more prone to rupture. Additionally, the ECM traps lipoproteins that oxidize and trigger inflammation, which accelerates plaque growth. Smooth muscle cells (SMCs) migrate to the plaque, producing ECM components like collagen that stabilize the plaque, but SMCs may lose their contractile function, contributing further to vascular stiffness.
Key Findings on ECM Components in Atherosclerosis
-Collagen
Collagen provides structural support but may accumulate excessively in advanced plaques, leading to vessel stiffness. A thinner collagen layer can make plaques vulnerable to rupture, posing a risk of heart attacks or strokes.
-Elastin
Elastin allows blood vessels to stretch and contract, crucial for normal blood flow. In atherosclerosis, elastin fibers degrade due to enzymes like elastases, causing vessel stiffness and increasing the risk of calcification in plaques.
-Proteoglycans
Proteoglycans in the ECM bind with LDL cholesterol, encouraging its retention in the artery wall. Over time, LDL gets trapped and oxidized, triggering an inflammatory response that attracts immune cells to the site, fueling plaque d
evelopment.
-Fibronectin
This glycoprotein aids in cellular adhesion and migration, essential during wound healing. However, in plaques, fibronectin encourages SMC migration, which helps stabilize plaques but can lead to disorganized growth and vulnerability.
Therapeutic Implications
Scientists are exploring ways to control ECM remodeling by targeting MMPs, cathepsins, and serine proteases, key enzymes in ECM breakdown. MMP inhibitors could potentially reduce collagen degradation, thus preserving plaque stability. However, early MMP inhibitors had side effects due to their broad activity across multiple tissues, underscoring the need for more targeted approaches.
Researchers are also looking at synthetic molecules mimicking tissue inhibitors of MMPs, gene therapy to regulate ECM remodeling, and drugs that enhance elastin synthesis, offering potential pathways to prevent artery stiffness.
Another potential strategy involves reducing the ECM’s capacity to retain LDL cholesterol by altering proteoglycan structures or preventing LDL binding. This would reduce the initial trigger for plaque formation, helping to prevent disease progression.
Anti-Inflammatory Therapies and ECM
Inflammation is a major driver of ECM breakdown in atherosclerosis. Targeting inflammatory pathways, like IL-1β, could indirectly protect the ECM from excessive degradation. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as canakinumab, which inhibit IL-1β, have shown promise in reducing cardiovascular events by stabilizing ECM within plaques.
ECM Stability as a Target
Some therapies focus on restoring ECM stability to reduce plaque rupture risk. For example, drugs that promote collagen synthesis can strengthen the fibrous cap, while elastin-promoting therapies may improve vessel elasticity. Inhibitors of neutrophil elastase, a protein-degrading enzyme, might help maintain elastin levels, reducing vessel stiffness and making plaques less prone to rupture.
Conclusion
Research into the ECM’s role in atherosclerosis provides exciting potential for new therapies that target the underlying causes of plaque formation and instability. By regulating ECM remodeling, researchers hope to reduce inflammation, improve vessel elasticity, and prevent plaque rupture, all of which could significantly lower the risk of cardiovascular events. This approach, alongside traditional treatments, offers a comprehensive strategy against atherosclerosis, providing a foundation for future breakthroughs in cardiovascular health.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/22/12017
For the latest on Atherosclerosis, keep on logging on to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/t-cells-play-a-role-in-atherosclerosis
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/american-study-warns-that-covid-19-is-triggering-the-onset-and-progression-of-atherosclerosis-in-many
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/is-platelet-activating-factor-the-key-link-between-covid-19-and-atherosclerosis-risk
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/geniposide-a-promising-treatment-for-covid-19-and-atherosclerosis-patients
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/malaysian-study-finds-that-timps-can-be-used-as-biomarkers-in-predicting-atherosclerosis-and-coronary-artery-disease
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/discovery-of-slc-genes-paves-the-path-for-new-targets-for-inflammatory-diseases-and-atherosclerosis-treatments.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breakthrough-:-minocycline-identified-for-treating-atherosclerosis-after-mechanism-causing-artery-hardening-discovered
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/atherosclerosis:-scripps-research-identifies-cyclic-peptides-that-alters-gut-microbiome-leading-to-lower-cholesterol-and-atherosclerosis-inhibition
