How SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Triggers Neurodegenerative Diseases and the Potential of Metformin as a Therapeutic Remedy
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Jun 01, 2024 8 months, 2 weeks, 6 days, 22 hours, 36 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: Neurodegenerative diseases, particularly those characterized by the abnormal aggregation of α-synuclein, are a growing concern in the medical community. These diseases, known as α-synucleinopathies, include Parkinson's disease (PD), Lewy body dementia, and multiple system atrophy (MSA). Recent studies have suggested a potential link between SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, and these neurodegenerative conditions. This
COVID-19 News report explores the mechanisms behind this connection and examines the potential therapeutic role of metformin.
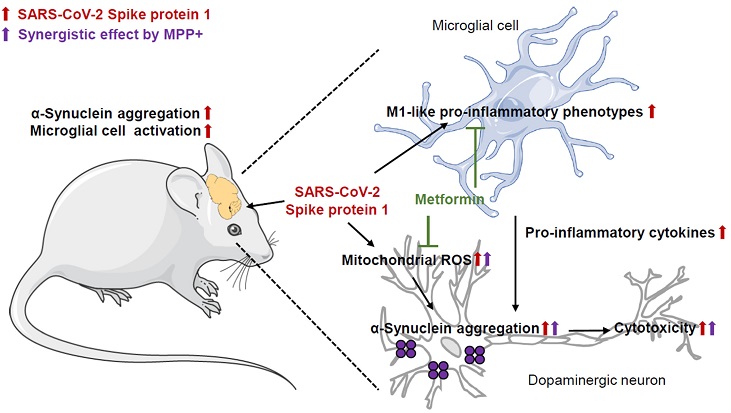 Proposal model of this study. How SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Triggers Neurodegenerative Diseases and the Potential of Metformin as a Therapy
The Role of α-Synuclein in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Proposal model of this study. How SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Triggers Neurodegenerative Diseases and the Potential of Metformin as a Therapy
The Role of α-Synuclein in Neurodegenerative Diseases
α-Synuclein is a protein that, when aggregated abnormally, leads to the formation of toxic structures within nerve cells or fibers. This aggregation is a hallmark of α-synucleinopathies, which can occur sporadically or due to genetic factors. Environmental influences such as neurotoxins, oxidative stress, inflammation, and viral infections also contribute to the onset of these diseases.
SARS-CoV-2 and Neurological Complications
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by SARS-CoV-2, has brought to light numerous long-term health issues, collectively known as long COVID. Among these, neurological complications like brain fog, anxiety, sleep disorders, cognitive problems, and movement disorders have been prominent. These symptoms overlap significantly with those observed in α-synucleinopathies, suggesting a possible link.
Investigating the Mechanisms
Researchers from the Division of Brain Diseases Research at the Korea National Institute of Health conducted a study to uncover the mechanisms by which SARS-CoV-2 might induce α-synucleinopathies. They found that the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein 1 (S1) could induce α-synuclein aggregation in rodent models. The study demonstrated that S1 increases α-synuclein aggregation in dopaminergic neurons through microglia-mediated inflammatory responses and mitochondrial ROS production.
Microglia and Inflammation
Microglia are the primary immune cells in the brain, playing a crucial role in neuroinflammation. The study revealed that S1 treatment led to the activation of microglial cells, which in turn, triggered the aggregation of α-synuclein in the brain. This finding is significant as it highlights the role of neuroinflammation in the development of neurodegenerative diseases.
The Impact of Mitochondrial ROS
In addition to microglia-induced inflammation, the study found that S1 directly affects α-synuclein aggregation through the production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS). Mitochondria, the powerhouses of cells, are crucial for energy production. However,
when they produce excessive ROS, it leads to oxidative stress and cellular damage, contributing to the aggregation of α-synuclein.
Synergistic Effects of S1 and Neurotoxins
The researchers also observed a synergistic effect between S1 and the neurotoxin MPP+, which is known to cause α-synucleinopathies. When combined with a low dose of MPP+, S1 significantly increased α-synuclein aggregation and mitochondrial ROS production. This synergy suggests that environmental factors, alongside viral infections, can exacerbate neurodegenerative processes.
Therapeutic Potential of Metformin
Metformin, a common medication for type 2 diabetes, has shown promise in mitigating the effects of S1-induced neurodegenerative changes. The study found that metformin treatment suppressed S1-induced inflammatory responses and α-synucleinopathy. Metformin's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and confer neuroprotection makes it a potential therapeutic agent for managing α-synucleinopathies and long COVID-related neurological symptoms.
Insights and Implications
This study provides crucial insights into the pathological mechanisms linking SARS-CoV-2 and α-synucleinopathies. By demonstrating that S1 promotes α-synuclein aggregation via microglia-mediated inflammation and mitochondrial ROS production, the research offers a foundation for developing clinical management strategies for neurodegenerative diseases and long COVID.
Future Directions
Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of SARS-CoV-2 on neurodegenerative diseases and to explore the therapeutic potential of metformin and other treatments. The findings of this study open new avenues for investigating the role of viral infections in neurodegenerative processes and developing targeted therapies to combat these debilitating conditions.
Conclusion
The connection between SARS-CoV-2 and neurodegenerative diseases highlights the complex interplay between viral infections and neurological health. As the world continues to grapple with the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing effective treatments. Metformin, with its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, emerges as a promising candidate for managing the neurological complications associated with long COVID and α-synucleinopathies. This study marks a significant step towards unraveling the mysteries of neurodegeneration and improving patient outcomes in the post-COVID-19 era.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Biomedicines.
https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/12/6/1223
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-japanese-doctors-warn-of-cerebrospinal-fluid-leakage-linked-to-covid-19-in-children
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/australian-study-uncovers-roles-of-the-kynurenine-pathway-in-covid-19-neuropathogenesis
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-children-whose-mothers-were-infected-with-covid-19-during-pregnancy-likely-to-suffer-from-neurodevelopmental-delays
