Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist (IL1RN) rs419598 Gene Variant Protects Males Under 75 From COVID-19 Disease Severity
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Mar 14, 2024 1 year, 1 month, 1 week, 5 days, 2 hours, 46 minutes ago
COVID-19 News: In the relentless battle against COVID-19, researchers are delving deep into the genetic landscape to uncover hidden allies in the fight against severe illness and mortality. Among the myriad genetic factors under scrutiny, one particular variant has emerged as a potential guardian against the ravages of the virus: the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL1RN) rs419598 gene variant.
 IL1RN rs419598 Gene Variant Protects Males Under 75 From COVID-19 Severity
IL1RN rs419598 Gene Variant Protects Males Under 75 From COVID-19 Severity
This
COVID-19 News report explores the study by researchers from NYU Grossman School of Medicine-USA that sheds light on how this genetic variant confers protection, particularly among men under the age of 75, and its implications for understanding and combating the COVID-19 pandemic.
Understanding the Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist (IL1RN) Gene Variant
The IL1RN gene encodes for the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra), a critical player in the body's immune response. IL-1Ra acts as a brake on inflammation, dampening the excessive immune response that can lead to tissue damage and organ failure in severe cases of infection. Within the IL1RN gene, the rs419598 variant has garnered attention for its potential role in modulating the inflammatory cascade unleashed by SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19.
Unraveling the Protective Mechanism
The study, co- led by investigator and molecular biologist Dr Mukundan Attur, Ph.D., an associate professor in the Department of Medicine at NYU Langone Health, has provided compelling evidence of the protective effects of the IL1RN rs419598 variant against severe COVID-19 outcomes. By analyzing blood samples from over 2,500 individuals hospitalized for COVID-19, the researchers unearthed a striking association between the presence of the IL1RN variant and reduced disease severity and mortality.
Guardians Among Men: Selective Protection
The study's findings unveiled a fascinating gender-specific dimension to the protective effects of the IL1RN rs419598 variant. While men have historically borne the brunt of severe COVID-19 outcomes, particularly mortality, the presence of the IL1RN variant conferred significant protection, but only among men under the age of 75. This selective effect underscores the intricate interplay between genetic factors and age-related vulnerabilities in shaping COVID-19 outcomes.
Insights from Genetic Analysis
Utilizing advanced sequencing technologies, the research team meticulously analyzed the genetic makeup of hospitalized COVID-19 patients, shedding light on the molecular mechanisms underlying disease severity. Elevated levels of IL-1Ra, the anti-inflammatory protein encoded by IL1RN, were observed in individuals carrying the rs419598 variant, suggesting a potent dampening effect on inflammation that mitigates the cytokine storm associated with severe COVID-19.
Dr Attur told Thailand
al.news/">Medical News, "Our study findings show that among hospitalized patients, while women are still overall less likely than men to die from COVID-19, those men age 74 and younger who possess the IL1RN gene variant rs419598 are much less likely to suffer the severe inflammation tied to SARS-CoV-2 infection and less likely to die from the disease."
Translating Insights into Therapeutic Strategies
The identification of the IL1RN rs419598 variant as a genetic guardian against severe COVID-19 opens new avenues for therapeutic intervention. By targeting the interleukin-1 pathway, researchers envision a novel approach to mitigating COVID-19-related inflammation and reducing the risk of adverse outcomes. Promising candidates such as IL-1 receptor antagonists, including anakinra, canakinumab, and rilonacept, hold potential as targeted therapies to modulate the inflammatory response and improve patient outcomes.
Other Findings
Interestingly, among the study's other findings was that average blood levels of the anti-inflammatory protein IL-1Ra, coded by IL1RN, were 14 times higher in 181 hospitalized men than in healthy male study controls from the general population and 10 times as high in 178 hospitalized women than in healthy females. However, researchers say the increased levels of IL-1Ra in women did not result in any statistically significant reductions in death.
Study senior investigator Dr Steven Abramson, MD, the Frederick H. King Professor of Internal Medicine at NYU Langone added, "Our analysis offers substantial evidence of the biological link between the severe inflammation seen in SARS-CoV-2 and that which occurs in rheumatoid arthritis.”
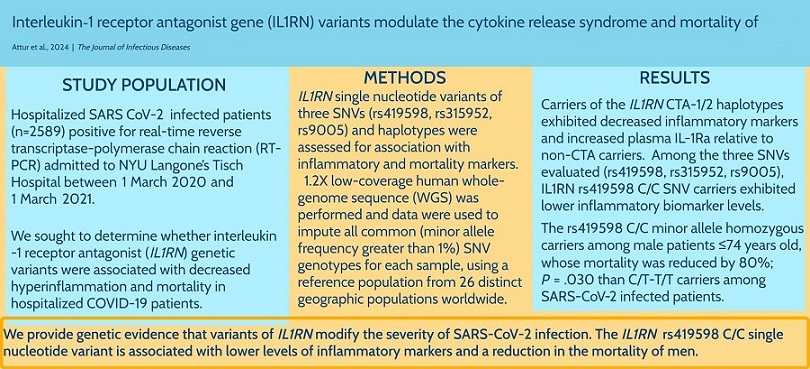 Study Abstract
Beyond COVID-19: Implications for Long-Term Health
Study Abstract
Beyond COVID-19: Implications for Long-Term Health
The implications of the IL1RN variant extend beyond the immediate threat of COVID-19, offering insights into broader health outcomes and disease susceptibility. By elucidating the role of genetic factors in shaping immune responses, researchers are poised to unravel the mysteries of complex diseases and develop personalized approaches to treatment and prevention. Moreover, ongoing investigations into the IL-1 pathway's involvement in long COVID may provide crucial insights into the lingering symptoms and sequelae of the disease.
Charting a Path Forward: Precision Medicine in the COVID-19 Era
As we navigate the complexities of the COVID-19 pandemic, the quest for effective therapies and preventive strategies has never been more urgent. The discovery of genetic guardians such as the IL1RN variant underscores the transformative potential of precision medicine in combatting infectious diseases. By harnessing the power of genetics, immunology, and cutting-edge technologies, we can tailor interventions to individual genetic profiles, optimize treatment efficacy, and ultimately curb the devastating impact of COVID-19 on global health.
C
onclusion
The IL1RN rs419598 gene variant stands as a beacon of hope in the fight against COVID-19, offering a glimpse into the intricate interplay between genetics, inflammation, and disease outcomes. As researchers continue to unravel the genetic mysteries of COVID-19, the promise of precision medicine looms large on the horizon, paving the way for targeted therapies, personalized interventions, and a brighter future in the ongoing battle against the pandemic.
The study findings will be published in the peer reviewed journal: The Journal of Infectious Diseases (Oxford Journals.)
https://apps.crossref.org/pendingpub/pendingpub.html?doi=10.1093%2Finfdis%2Fjiae031
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.

