Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team Feb 11, 2025 2 months, 5 days, 8 hours, 46 minutes ago
Medical News: Understanding Liver Fibrosis and Its Challenges
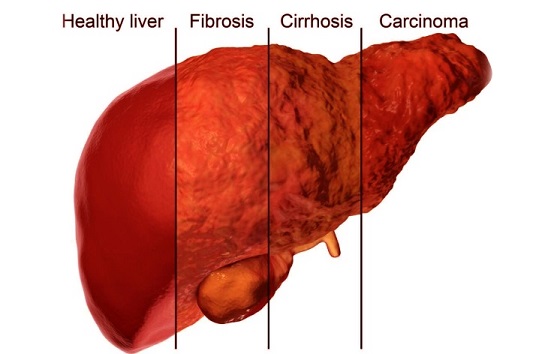
Liver fibrosis is a major health concern worldwide, resulting from long-term liver damage caused by factors such as viral infections, excessive alcohol consumption, and metabolic disorders. The condition occurs when the liver responds to chronic injury by forming excessive scar tissue, which can ultimately lead to cirrhosis and even liver cancer. Despite advances in medical research, there are currently no approved chemical or biological drugs specifically targeting liver fibrosis. The urgent need for effective treatments has driven researchers to explore the role of the interleukin (IL) family, a group of immune system proteins that play a key role in inflammation and immune response.
 Interleukins and Their Role in Liver Fibrosis
Interleukins and Their Role in Liver Fibrosis
This
Medical News report highlights findings from researchers at the Central Laboratory, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and the School of Clinical Medicine, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, who have studied how various interleukins contribute to the development and progression of liver fibrosis. Their work sheds light on the complex mechanisms behind liver fibrosis and presents potential therapeutic targets that could pave the way for new treatment options.
The Role of Interleukins in Liver Fibrosis
The human liver is not only responsible for detoxifying harmful substances but also serves as an essential immune organ that produces and regulates various cytokines, including interleukins. These proteins act as messengers, influencing inflammation, immune responses, and the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the primary drivers of fibrosis.
Interleukins can be categorized based on their function in liver fibrosis. Some interleukins, such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-17, IL-18, IL-33, and IL-36, are pro-inflammatory and contribute to liver damage and fibrosis progression. Others, like IL-10, IL-35, and IL-37, exhibit anti-inflammatory properties and help mitigate fibrosis by suppressing immune responses and reducing scar tissue formation. Certain interleukins, including IL-4 and IL-22, play a dual role, exerting both pro-fibrotic and anti-fibrotic effects depending on the context.
Key Findings on Pro-Inflammatory Interleukins
Among the interleukins that promote liver fibrosis, IL-1 plays a significant role by triggering inflammatory pathways and activating HSCs. Research indicates that IL-1 increases the production of fibrotic proteins and promotes the release of other pro-inflammatory mediators. Similarly, IL-6 is found to be highly expressed in liver fibrosis and correlates with disease severity. IL-6 activates signaling pathways that contribute to liver inflammation, fibrosis, and progression to cirrhosis.
IL-17 is another crucial cytokine in liver fibrosis. It stimulates HSC activation and enhances the production of fibrotic molecules, exacerbating liver damage. IL-18 further promotes fibrosis by accelerating HSC differentiation into fibrotic cells.
Meanwhile, IL-33 interacts with immune cel
ls and plays a role in both inflammation and fibrosis progression. Studies show that high levels of IL-33 are associated with increased fibrotic tissue in the liver. IL-36, though less studied, is emerging as a key player in liver inflammation and fibrosis due to its ability to amplify immune responses and worsen tissue damage.
Protective Effects of Anti-Inflammatory Interleukins
In contrast to the damaging effects of pro-inflammatory interleukins, IL-10 is known to protect against liver fibrosis. It helps suppress inflammation, reduce HSC activation, and limit excessive collagen production. IL-35 and IL-37 exhibit similar protective effects by modulating immune responses and preventing tissue damage.
Interestingly, IL-4 and IL-22 show mixed effects on liver fibrosis. IL-4 has been linked to both pro-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory responses. It influences macrophage activity, which in turn affects HSC activation. IL-22, on the other hand, plays a role in liver regeneration but can also contribute to fibrosis under certain conditions, particularly in chronic liver disease patients.
Potential for Future Therapies
The study suggests that targeting specific interleukins could be a promising approach for treating liver fibrosis. Therapies that block pro-inflammatory interleukins such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-17, and IL-18 might help reduce liver damage and slow fibrosis progression. Meanwhile, treatments that enhance the effects of protective interleukins like IL-10 and IL-37 could support liver repair and regeneration.
Several experimental treatments are currently under investigation, including inhibitors for IL-1 and IL-6, as well as therapeutic agents that enhance IL-10 activity. These approaches could lead to new breakthroughs in managing liver fibrosis, offering hope for millions of people affected by chronic liver disease.
Conclusion
Liver fibrosis remains a significant global health burden, but research into the interleukin family provides valuable insights into the disease’s underlying mechanisms. The findings from Chengdu University researchers highlight the dual roles of interleukins in either promoting or inhibiting fibrosis. Understanding these complex interactions can lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies. By targeting the right interleukins, researchers may be able to halt fibrosis progression and even reverse some of the damage. Further studies and clinical trials are needed to confirm these potential treatments and bring new hope to patients suffering from chronic liver conditions.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal: Frontiers in Immunology.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1497095/full
For the latest on Liver Fibrosis, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/using-selenium-to-treat-multi-organ-fibrosis
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-worsens-existing-liver-disease-and-could-spur-liver-cancer-development
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/thailand-medical-scientists-find-that-phytochemicals-from-leaves-of-kaffir-lime-shows-promise-in-treating-liver-fibrosis
