Italian Researchers Uncover That SARS-CoV-2 ORF3C Protein Hijacks Mitochondrial Metabolism and Autophagy
COVID-19 News - SARS-CoV-2 ORF3C - Hijacks Mitochondrial Metabolism and Autophagy Jun 17, 2023 1 year, 8 months, 1 week, 2 days, 14 hours, 50 minutes ago
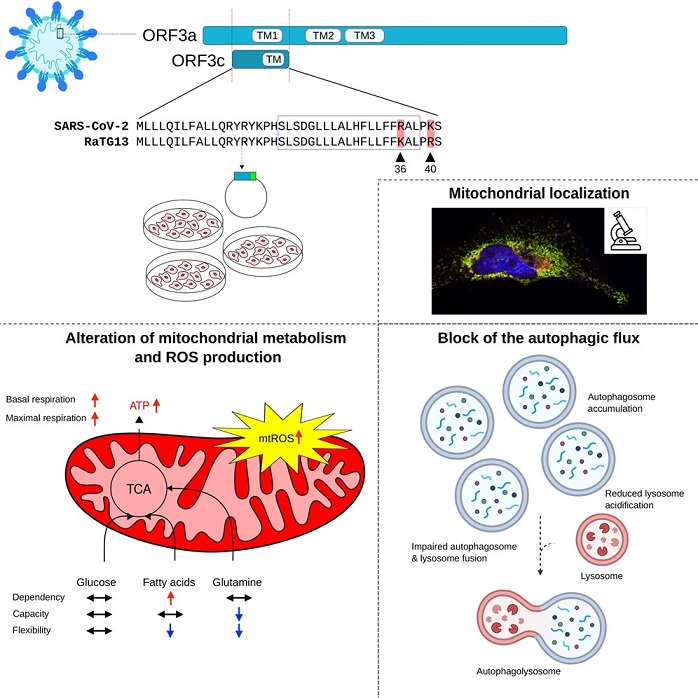
ORF3c localizes to mitochondria, alters mitochondrial metabolism, increases oxidative stress and ROS production, impedes autophagic flux via lysosomal acidification disruption.
COVID-19 News: As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to evolve, scientists around the world are tirelessly studying the SARS-CoV-2 virus to uncover its secrets and develop effective strategies for prevention and treatment. Among the various proteins encoded by SARS-CoV-2, accessory proteins have received less attention despite their potential role in immune evasion and host-virus interactions. One such protein, ORF3c, has remained relatively unexplored until now. In a groundbreaking study, researchers from the Scientific Institute IRCCS E. MEDEA-Italy and the University of Milano-Bicocca in Italy have shed light on the elusive ORF3c protein and its profound effects on mitochondrial respiratory metabolism, oxidative stress, and autophagic flux.
 The Mysterious ORF3c Protein
The Mysterious ORF3c Protein
SARS-CoV-2 belongs to a family of viruses known as coronaviruses, which encode accessory proteins that can influence viral replication and pathogenesis. These proteins have the potential to interact with various cellular components, including mitochondria, and disrupt essential cellular processes. Recent studies have highlighted the involvement of mitochondria in SARS-CoV-2 infection, indicating the significance of exploring accessory proteins with mitochondrial localization.
ORF3c and Mitochondrial Metabolism
The researchers discovered that the ORF3c protein localizes to the mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell responsible for energy production.
A previous
COVID-19 News report also indicated that the ORF3C proteins localizes to the mitochondria.
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-research-study-finds-that-sars-cov-2-orf3c-protein-localizes-to-mitochondria,-inhibiting-innate-immunity-by-restricting-ifn-%CE%92-production
Through a series of experiments, they found that ORF3c alters mitochondrial metabolism, leading to a shift from glucose to fatty acid oxidation and enhanced oxidative phosphorylation. This metabolic reprogramming induces an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, contributing to oxidative stress within the cell.
Impaired Autophagy and Lysosomal Dysfunction
Autophagy is a cellular process involved in the degradation and recycling of cellular components, including damaged organelles and proteins. The researchers observed that ORF3c disrupts the normal autophagic flux, resulting in the accumulation of autophagosomes and autolysosomes. They identified that ORF3c affects lysosomal acidification, impairing the degradation process within these cellular compartments. This blockage of autophagy can have significant implications for ce
llular health and virus replication.
Comparing SARS-CoV-2 and BatCoV RaTG13 ORF3c Proteins
Interestingly, the researchers also examined the effects of ORF3c from the closely related bat coronavirus RaTG13. While both SARS-CoV-2 and RaTG13 ORF3c proteins demonstrated similar trends, the effects were more pronounced with SARS-CoV-2 ORF3c. Further analysis revealed that two amino acid differences at positions 36 and 40 were crucial in determining the differential effects on autophagy. These findings suggest that substitutions in ORF3c may contribute to the emergence of viral variants and potentially impact disease severity.
Implications and Future Directions
Understanding the role of accessory proteins, such as ORF3c, is vital for unraveling the pathogenic mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 and developing targeted therapeutic strategies. The researchers' findings shed light on how the ORF3c protein hijacks mitochondrial metabolism, induces oxidative stress, and disrupts autophagic flux. Further studies are needed to uncover the precise molecular mechanisms underlying these effects and explore potential therapeutic interventions.
 Graphical Abstract
Conclusion
Graphical Abstract
Conclusion
The study provides crucial insights into the mysterious ORF3c protein of SARS-CoV-2 and its impact on mitochondrial metabolism, oxidative stress, and autophagy. By unraveling these hidden effects, scientists are gaining a deeper understanding of the virus's pathogenic mechanisms and paving the way for potential therapeutic interventions.
With the knowledge gained from this study, researchers can now explore targeted approaches to counteract the detrimental effects of the ORF3c protein. By developing drugs or therapies that specifically target mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, or autophagy dysregulation induced by ORF3c, it may be possible to mitigate the pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2.
Furthermore, the identification of ORF3c as a mitochondrial protein opens up new avenues for studying the interactions between the virus and host cell organelles. This knowledge could be applied not only to SARS-CoV-2 but also to other related coronaviruses or even other viral infections that exploit similar mechanisms.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: iScience.
https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(23)01195-1
For the latest
COVID-19 News, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-genomics-scientist-uncover-hidden-novel-overlapping-gene-orf3d-in-sars-cov-2-genome-that-might-not-be-detectable-by-t-cells-
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/-greek-study-shows-that-inhibition-of-perk-kinase-shown-to-dramatically-reduce-lung-cell-damage-caused-by-sars-cov-2-orf3a-protein
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/study-find-that-sars-cov-2-proteins-orf3a-and-nsp5-regulate-autophagy-receptor-p62-levels,-decreasing-it-and-leading-to-hyperinflammation-states
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/study-finds-that-sars-cov-2-orf3a-interacts-with-the-clic-like-chloride-channel-1-clcc1-and-triggers-an-unfolded-protein-response
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-research-study-finds-that-mutations-on-orf3a-determines-sars-cov-2-viral-fitness-through-modulation-of-lipid-droplets
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-research-u-s-nih-funded-study-discovers-that-sars-cov-2-orf3a-is-not-an-ion-channel-but-does-interact-with-trafficking-proteins
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-sars-cov-2-orf3a-protein-damages-renal-tubules-via-trim59-induced-stat3-activation-causing-acute-kidney-injury
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/yale-study-discovers-that-sars-cov-2-proteins-orf7a-and-orf3a-downregulates-mhc-i-expression-aiding-in-immune-evasion-and-immune-dysfunction
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/covid-19-immunology-study-shows-that-sars-cov-2-viral-protein-orf3a-activates-nlrp3-inflammasome-causing-severe-inflammatory-responses
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-coronavirus-news-orf3b-identified-as-viral-factor-that-impairs-immune-responses-in-covid-19-patients-alarmingly-new-variant-also-found

