Mayo Clinic Researchers Discover That SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Protein Is The Key Factor That Is Causing COVID-19 Disease Severity
Source: SARS-CoV-2-ORF8 - Medical- News Feb 04, 2022 3 years, 2 months, 1 week, 2 days, 9 hours, 59 minutes ago
Researchers from Mayo Clinic-Minnesota-USA along with experts from the University of California San Diego-California-USA have in a new study discovered that the
SARS-CoV-2-ORF8 protein is the key factor that is causing COVID-19 disease severity.
Prior to this study, despite extensive research, the specific factor associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection that mediates the life-threatening inflammatory cytokine response in patients with severe Covid-19 remains unidentified.
The study team demonstrated that the virus-encoded Open Reading Frame 8 (ORF8) protein is abundantly secreted as a glycoprotein in vitro and in patients with newly diagnosed COVID-19.
The ORF8 protein specifically binds to the NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) in CD14+/CD16+ monocytes to induce an inflammasomal cytokine response.
It was found that the levels of ORF8 protein in the blood correlate with disease mortality in patients with acute infection, and the disease trajectory in patients with severe COVID-19.
The study also showed that in vitro the ORF8-induced inflammasome response can be readily inhibited by the selected NLRP3 inhibitors.
The study findings identify the SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 protein as the pathogenic cause and mechanism of severe disease and suggest that NLRP3 inhibitors can be used to treat severe COVID-19.
The study findings were published on a preprint serve and are currently being peer reviewed.
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.02.470978v1
Most significantly, the study findings showed that the open reading frame 8 (ORF8) protein is highly expressed in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection. Furthermore, the ORF8 is found to have specific binding activity with a receptor on CD14+/CD16+ monocytes which induce proinflammatory cytokines.
The study findings point to ORF8 as the missing factor that connects the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) to symptoms associated with severe infection. Understanding ORF’s role in severe COVID-19 illness may also be the virus’s Achilles heel as researchers try to manipulate it for future treatment strategies.
The study team constructed a SARS-CoV-2 model by infecting HEK293 cells with one of 22 lentiviruses expressing a SARS-CoV-2 protein. Western blotting looking at protein expression confirmed the expression of most viral proteins except for NSP13, ORF10, MEM and NSP4.
Interestingly, unlike the other viral proteins, ORF8 was the most expressed protein. Further analysis showed that the other expressed proteins had an unconventional protein secretion signal, but it was ORF8 that had a classic protein signal sequence and a N-link glycosylation site.
The study findings indicate that ORF8 likely secretes from the classic endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi protein secretion pathway.
The ORF8 protein also induces inflammatory response seen in SARS-CoV-2 infections. An overabundance of the ORF8 protein appears to stimulate the expression of COVID-19 associated proinflammatory cytokines.
The study team found this result after testing human peripheral mononuclear cells from non-infected donors with NSP
proteins or ORF8.
Upon testing for cytokine RNA expression, the study team observed no cytokine expression after cells interacted with NSP proteins. However, ORF8 with CM elicited a 5-fold increase in mRNA expression of several cytokines, including IL1b, IL6, IL8, and CCL2.
Furthermore, a test between glycosylated ORF8 and glycosylated ORF8 showed that glycosylation is needed for cytokine induction.
Typically, monocytes are ORF8’s intermediary targets for cytokine expression. In order to produce COVID-19 related cytokines, ORF8 targets monocytes to do its bidding. Specifically, CD14, CD16, CD68, and HLA-DR were enriched when there was increased mRNA expression of cytokine IL1b, IL8, and CCL2.
It was found that the ORF’s mechanism of action in targeting CD14+/CD16+ relies on the activation of the NLRP3-mediated inflammasome response.
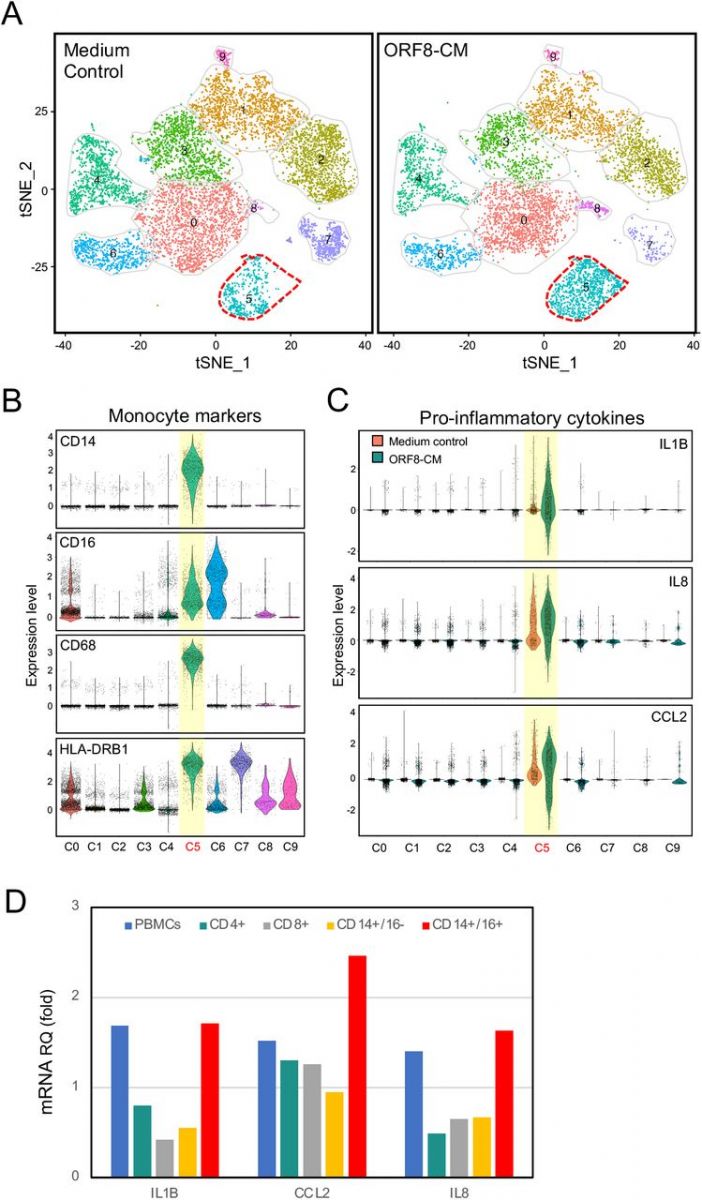 Single cell RNA sequencing of ORF8 treated PBMCs. A. tSNE maps of cell clusters using concatenated scRNA-Seq data from PBMC samples of two responding donors. Cluster 5 shows cells respond to ORF8 treatment. B. Violin plots showing the expression of intermediate monocyte markers CD14, CD16, CD68 and HLA-DRB1. C. Violin plots showing the expression of
Single cell RNA sequencing of ORF8 treated PBMCs. A. tSNE maps of cell clusters using concatenated scRNA-Seq data from PBMC samples of two responding donors. Cluster 5 shows cells respond to ORF8 treatment. B. Violin plots showing the expression of intermediate monocyte markers CD14, CD16, CD68 and HLA-DRB1. C. Violin plots showing the expression of
pro-inflammatory cytokines IL1B, IL8, and CCL2 mRNAs in cells of cluster 5. D. Validation study showing cytokine mRNA expression in total PBMCs, pure CD4+, CD8+, CD14+/CD16- and CD14+/CD16+ subsets stimulated with ORF8 containing conditioned medium.
A detailed pathway enrichment analysis confirmed the finding as the SAR-CoV-2 infection pathway was the most enriched pathway in cells. Additionally, parts of the NOD-like receptor signaling sub-pathway were also enriched.
In order to learn how the ORF8 glycoprotein initiates NLRP3-mediated inflammasome activation, the research team studied cells exposed to the ORF8 glycoprotein for two hours to maximize the chances of all ORF8 proteins binding to cell receptors. After washing out any ORF8 proteins that did not bind, the team found robust IL1b mRNA expression in all cells that were continuously exposed to ORF8, not just those that were preincubated with ORF8.
The study findings suggest the ORF8 protein most likely enters monocytes through a non-receptor mediated process such as phagocytosis.
Importantly, of the potential surface receptors, only the intracellular NLRP3 receptor was physically bound to the ORF8 binding protein.
The first part of the experiments in the study confirmed the SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 protein is involved in triggering the production of proinflammatory cytokines in vitro.
However, the next step was to see if the following played out in real-life scenarios as well.
The study team collected glycosylated blood from patients diagnosed with COVID-19 infection. Western blotting was used to measure protein samples in the serum.
The study findings showed that 92% of newly diagnosed patients had detectable ORF8 protein levels. When comparing the sizes of ORF8 proteins, results confirmed patients had glycosylated ORF8 proteins.
Although the study team could not determine the exact quantity of ORF8 in the blood, about 4 µl of serum samples had significant levels of the ORF8 protein during COVID-19 infection.
Interestingly, a correlation was observed between ORF8 protein levels and disease severity. Of the 25 hospitalized patients, the seven who died from infection had significantly high ORF8 protein levels.
It was also found that all patients with low ORF8 protein had only mild symptoms, recovered quickly from infection, and no one died.
The study also found that administration of certain NLRP3 inhibitors succeeded in inhibiting IL1b production.
The study team concluded that targeting the ORF8/NLRP3 axis is a promising strategy for treating patients with symptomatic COVID-19.
Thailand
Medical News would like to add that examples of existing drugs that can be used as a NLRP3 inhibitor includes: β-Hydroxybutyrate (BHB), Parthenolide, Glyburide, 3,4-Methylenedioxy-β-nitrostyrene (MNS) and Tranilast.
The phytochemical Oridonin which is a bioactive ent-kaurane diterpenoid is also an excellent but safe NLRP3 inhibitor while the supplement melatonin is also an effective NLRP3 inhibitor.
For more about
SARS-CoV-2-ORF8 Proteins And COVID-19 Disease Severity, keep on logging to Thailand Medical News.
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-study-discovers-that-sars-cov-2-orf8-encoded-protein-contains-a-histone-mimic-that-disrupts-human-host-cell-epigenetic-regulation  Single cell RNA sequencing of ORF8 treated PBMCs. A. tSNE maps of cell clusters using concatenated scRNA-Seq data from PBMC samples of two responding donors. Cluster 5 shows cells respond to ORF8 treatment. B. Violin plots showing the expression of intermediate monocyte markers CD14, CD16, CD68 and HLA-DRB1. C. Violin plots showing the expression of
Single cell RNA sequencing of ORF8 treated PBMCs. A. tSNE maps of cell clusters using concatenated scRNA-Seq data from PBMC samples of two responding donors. Cluster 5 shows cells respond to ORF8 treatment. B. Violin plots showing the expression of intermediate monocyte markers CD14, CD16, CD68 and HLA-DRB1. C. Violin plots showing the expression of