Staff Writer, TMN Jul 21, 2018 7 years, 5 months, 1 week, 21 hours, 18 minutes ago
The use of permanent cosmetics dates back thousands of years in history. Microblading, a technique for creating natural looking eyebrows using pigment, has reemerged in popularity in the 21st century, and has rapidly become one of the most popular cosmetic procedures in the United States .However, it has not completely replaced traditional eyebrow micropigmentation techniques: Many people may not be candidates for microblading because of how the pigment is manually deposited in the skin through tiny “tears” in the skin with this procedure.
The use of microblading has increased exponentially since 2015, as reflected by the millions of searches on popular social media sites. With the increase in the popularity and volume of tattoo artists performing these procedures, there has also been an increase in side effects and complications from microblading provided by poorly trained and unlicensed “artists,” a problem facilitated by the absence of adequate training requirements and/or regulatory oversight in many states.
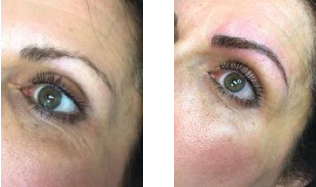
Eyebrows, before and after microblading.
Microblading – also known as eyebrow embroidery, micropigmentation, dermal implantation, microstroking, microfeathering, and 3-D eyebrows – is a permanent make-up technique, and like any tattoo, pigment/ink will fade over time. Compared with traditional tattoos that are done with a machine, microblading is performed manually using a disposable, single-use, sterile, handheld tool to deposit hair-like strokes of pigment into the dermis. Fading occurs faster with microblading than with traditional micropigmentation techniques that are performed with a machine. This is caused by pigment expulsion that occurs because of bleeding during the microblading procedure. Permanent make-up machines are able to rapidly deposit pigment into the dermis, which limits bleeding and pigment expulsion and therefore fades at a slower rate.
Microblading is a revolutionary technique that can transform the lives of patients with hypotrichosis of the eyebrows, trichotillomania, eyebrow loss due to internal disease (such as thyroid disease), chemotherapy-induced eyebrow loss, or alopecia – or simply those seeking it for cosmetic improvement. The art of shaping the eyebrow depends on the natural growth of the brow (if any), facial symmetry, and meticulous measurement and mapping of the brow position based on facial landmarks and bone structure. The color of pigment selection is based on Fitzpatrick skin type and skin color undertones.
As with any tattoo, complications can occur. Although extremely rare, pigment allergy, granulomatous reactions, exacerbation of underlying skin diseases (such as psoriasis or allergic contact dermatitis), and herpes simplex virus infections can occur. Also, if performed by someone with little or no knowledge about blood safety practices, infectious diseases can be contracted.
While dermatologists usually do not perform microblading, we may see patients with these complications. Practitioners treating patients who have had eyebrow microblading should also be aware of how to prevent premature fading of the eyebrow tattoo pigment. Tattooed eyebrows should be covered with petroleum jelly prior to the use of alpha hydroxy acids, vitamin C, chemical peels, hydroquinone, or retinols because these preparations can fade the pigment rapidly even if applied far from the microblading site. Any UV exposure, heat (such as steam from a facial), LED light exposure, or radio frequency
can fade the pigment and exacerbate postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. Patients who have a history of hypertrophic scarring or keloids or are using isotretinoin concurrently should avoid microblading entirely. Resurfacing lasers and intense pulsed-light lasers should be used with caution as these aesthetic procedures will cause fading of the eyebrow pigment even if applied at a considerable distance from the eyebrow. Microbladed eyebrows should be covered with 20% zinc oxide paste prior to the use of any intense pulsed-light or resurfacing lasers.
Fading and removal of microblading tattoos is controversial and remains a challenge. The process of removing a microblading treatment should be done by a highly trained provider. Scarring from the removal process is more likely when microblading has been performed than when removing a traditional tattoo, a result of how microblading tools deposit pigment through dragging motions in the skin.
The pigment used in eyebrow colors also may be composed of a mixture of iron oxide pigments, which should not be removed with traditional Q-switched lasers, with which not only is there potential for the pigment to darken but also postinflammatory hyper- or hypopigmentation to occur as well. Hairs can be singed, and the light absorbed by the pigment chromophore in the hair follicle can permanently damage the follicle, leading to hair loss in the area.
Despite the absolute precision and aggressive safety precautions needed for microblading, there are wide state-to-state variations in training and regulatory oversight. Infectious diseases, poor treatment outcomes, and unsterile conditions are just a few of the horrific consequences of unlicensed and untrained tattoo artists. Regulations should be imposed in every state to protect consumers and prevent serious
medical complications related to microblading.
In addition, dermatologists should be aware of this procedure and be cautious regarding exfoliating skin care regimens and in-office procedures that may
affect the aesthetics or longevity of microblading eyebrows and for any cosmetic tattoo. Our patients inquiring about treatments should be counseled to find a highly trained, licensed micropigmentation artist licensed in their state, who also has proper safety certification (Bloodborne Pathogens training and First Aid Certification), insurance, and is performing the services in a licensed body art facility with sterile, single-use, disposable tools and pigments.
Like other cosmetic treatments, cheaper is never better