miR-149-5p's Regulatory Role in Airway Epithelial Responses to Respiratory Viruses
Nikhil Prasad Fact checked by:Thailand Medical News Team May 29, 2024 1 year, 7 months, 2 days, 21 hours, 49 minutes ago
Medical News: Respiratory viruses are notorious for causing airway inflammation, leading to epithelial injury and repair processes. Among the many molecules involved in these pathways, microRNAs (miRNAs) play a pivotal role. miR-149-5p, in particular, has garnered attention for its regulatory functions in various pathological conditions. This
Medical News report delves into the distinct effects of respiratory viral infection models on miR-149-5p, IL-6, and p63 expression in bronchial (BEAS-2B) and alveolar (A549) epithelial cells.
 miR-149-5p's Regulatory Role in Airway Epithelial Responses to Respiratory Viruses
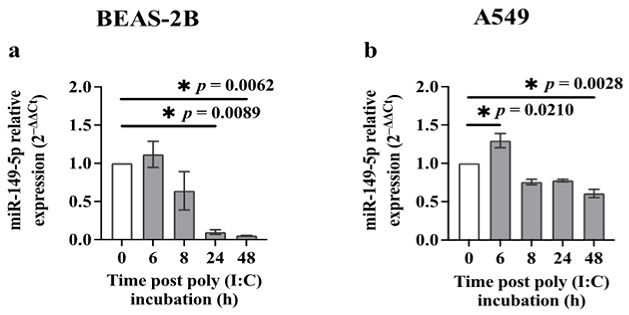
Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid or poly (I:C) suppresses miR-149-5p expression in airway epithelial cells. BEAS-2B or A549 cells were cultured in a 24-well plate at 1 × 105 cells per well in a BEGM or F-12K medium (FBS, 10%), respectively, for 24 h. Cells were then incubated in a BEBM or F-12K medium containing ITS+1 (1%) with poly (I:C) (0.5 μg/mL). miR-149-5p levels were assessed at 0, 6, 8, 24 and 48 h using RT-qPCR. (a) miR-149-5p expression in BEAS-2B cells after incubation with poly (I:C). (b) miR-149-5p expression in A549 cells after incubation with poly (I:C). The cycle threshold (Ct) value of miR-149-5p was normalised to that of RNU44 (ΔCt). Data are presented relative to the control at baseline (ΔΔCt) as mean ± SEM. * p ≤ 0.05, compared with the control group, using one-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni post-test, n = 3.
The Role of Respiratory Viruses
miR-149-5p's Regulatory Role in Airway Epithelial Responses to Respiratory Viruses
Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid or poly (I:C) suppresses miR-149-5p expression in airway epithelial cells. BEAS-2B or A549 cells were cultured in a 24-well plate at 1 × 105 cells per well in a BEGM or F-12K medium (FBS, 10%), respectively, for 24 h. Cells were then incubated in a BEBM or F-12K medium containing ITS+1 (1%) with poly (I:C) (0.5 μg/mL). miR-149-5p levels were assessed at 0, 6, 8, 24 and 48 h using RT-qPCR. (a) miR-149-5p expression in BEAS-2B cells after incubation with poly (I:C). (b) miR-149-5p expression in A549 cells after incubation with poly (I:C). The cycle threshold (Ct) value of miR-149-5p was normalised to that of RNU44 (ΔCt). Data are presented relative to the control at baseline (ΔΔCt) as mean ± SEM. * p ≤ 0.05, compared with the control group, using one-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni post-test, n = 3.
The Role of Respiratory Viruses
Respiratory viruses such as influenza A and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pose significant public health threats. These viruses incite robust inflammatory responses in the airway epithelium, the first line of defense against inhaled pathogens. Bronchial epithelial cells, which line the large airways, are particularly responsive to viral infections due to their higher density of viral receptors and stronger inflammatory responses compared to alveolar epithelial cells.
Investigating Epithelial Responses: BEAS-2B and A549 Cell Lines
Immortalized cell lines like BEAS-2B (bronchial epithelial cells) and A549 (alveolar epithelial cells) are extensively used to study respiratory viral responses. These cells express pattern-recognition receptors, including the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family, which recognize virus-generated pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and initiate inflammatory host responses. Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid, a synthetic analog of viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), and the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunits (S1 and S2) are commonly used to mimic viral infections in these cells.
miR-149-5p: A Key Regulator
miRNAs are non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally. miR-149-5p is involved in various cellular processes, including cell cycle regulation, proliferation, apopt
osis, and inflammation. It targets IL-6 in gastric stromal fibroblasts and modulates the interaction between tumor cells and the tumor stroma. Prediction databases have suggested that the 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs) of IL-6 and p63 mRNAs contain potential miR-149-5p response elements.
Experimental Setup
To understand miR-149-5p's role in airway epithelial cells, BEAS-2B and A549 cells were incubated with Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid or transfected with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunits (S1 or S2). miR-149-5p expression, along with IL-6 and p63 levels, was then analyzed using various molecular techniques.
Results
-miR-149-5p Expression
In BEAS-2B cells, miR-149-5p expression was significantly downregulated following Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid incubation for 24 and 48 hours. This suppression correlated with increased IL-6 and p63 expression. A549 cells also exhibited decreased miR-149-5p levels after Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid exposure, but p63 protein was undetectable. Interestingly, miR-149-5p expression remained unchanged in both cell lines upon S1 or S2 transfection.
-IL-6 and p63 Regulation
IL-6, a major pro-inflammatory cytokine, showed elevated expression in BEAS-2B cells following Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid treatment. This upregulation was much more pronounced in BEAS-2B cells compared to A549 cells. Additionally, S1 transfection significantly increased IL-6 levels in BEAS-2B cells, but not in A549 cells. Ectopic overexpression of miR-149-5p in BEAS-2B cells suppressed both IL-6 and p63 mRNA levels, inhibiting the Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid-induced increase in these markers. A luciferase reporter assay confirmed that miR-149-5p directly targets IL-6 mRNA but not p63.
-Differential Responses in BEAS-2B and A549 Cells
The distinct responses of BEAS-2B and A549 cells to Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid and SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins underscore the specificity of miR-149-5p regulation. BEAS-2B cells demonstrated higher sensitivity to Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid, exhibiting significant cell death, elevated IL-6 secretion, and increased p63 expression. Conversely, A549 cells showed limited IL-6 response and no detectable p63 expression.
Implications for Inflammatory and Repair Pathways
The study findings highlight the cell type-specific role of miR-149-5p in regulating inflammatory and repair pathways in airway epithelial cells. The differential expression of TLRs (TLR3 in BEAS-2B and TLR2 in response to SARS-CoV-2) may explain the varied responses to viral PAMPs. These results suggest that miR-149-5p could be a potential therapeutic target for modulating inflammatory responses in bronchial epithelial cells.
Limitations and Future Directions
While this study provides valuable insights, it has some limitations. The use of immortalized cell lines may not fully capture the complexities of primary epithelial cells. Future studies should explore miR-149-5p functions in primary cells and in more physiologically relevant models, such as air-liquid interface cultures. Investigating miR-149-5p's regulatory effects on other inflammatory cytokines and co-culturing epithelial cells with macrophages could also enhance our understanding of its role in viral infections.
Conclusion
The study elucidates the distinct responses of BEAS-2B and A549 cells to different respiratory viral PAMPs, emphasizing the role of miR-149-5p in regulating IL-6 and p63 expression. These findings pave the way for further research into miR-149-5p's therapeutic potential in managing airway inflammation and repair processes during respiratory viral infections. By understanding these intricate cellular mechanisms, we can develop more targeted and effective treatments for respiratory viral infections, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing the global burden of these diseases.
The study findings were published in the peer reviewed journal: Cells.
https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/13/11/919
For more about miR-149-5p, keep on logging to Thailand
Medical News
Read Also:
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/mir-452-5p-a-promising-new-target-in-the-fight-against-cardiac-fibrosis
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/indonesian-study-finds-soy-based-tempeh-s-isoflavones-can-inhibit-breast-cancer-via-mir-7-5p-upregulation
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/sars-cov-2-suppresses-ifn-beta-induction-via-n-protein-dependent-linc01002-mir-4324-frmd8-axis
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/study-finds-that-sars-cov-2-orf3a-modulates-pi3k-akt-signaling-in-lung-epithelial-cells-via-hsa-mir-155-5p
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-study-finds-that-gdnf-and-mirna-29a-can-be-used-as-biomarkers-for-cognitive-status-in-individuals-with-psychosis
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/breaking-covid-19-news-australian-scientists-discover-a-microrna-called-cov2-mir-o8-that-is-encoded-by-sars-cov-2-and-is-possibly-pathogenetic
https://www.thailandmedical.news/news/mycoplasma-pneumoniae-kukoamine-a-from-cortex-lycii-radices-improves-infections-by-regulating-mir-222-3p-superoxide-dismutase-2
